Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following best describes the journey of an oxygen molecule in a lung?
A) It travels from an alveolus to a bronchiole to a capillary to a red blood cell to hemoglobin.
B) It travels from a bronchiole to an alveolus to a capillary to hemoglobin to a red blood cell.
C) It travels from a bronchiole to an alveolus to a capillary to a red blood cell to hemoglobin.
D) It travels from a bronchiole to an alveolus to a red blood cell to a capillary to hemoglobin.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Another name for the "pacemaker" is the
A) atrioventricular (AV) node.
B) sino atrial (SA) node.
C) atrium.
D) ventrical.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the figure below, the arrow is pointing to the 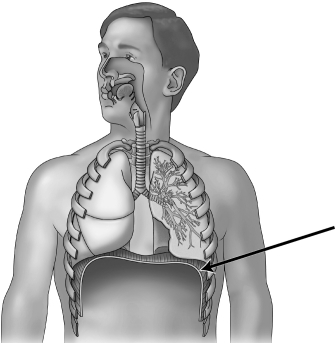
A) bronchus.
B) trachea.
C) diaphragm.
D) larynx.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A mitochondrion in a cell undergoing cellular respiration would
A) have a higher concentration of oxygen than the surrounding cytosol.
B) lose oxygen by diffusion.
C) lose carbon dioxide by diffusion.
D) gain oxygen by being in direct contact with hemoglobin.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The process of inhalation requires more energy than the process of exhalation.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Air entering the lungs has a
A) higher concentration of carbon dioxide than air in an alveolus.
B) higher concentration of both carbon dioxide and oxygen than in an alveolus.
C) higher concentration of oxygen and a lower concentration of carbon dioxide than in an alveolus.
D) lower concentration of oxygen and a concentration of carbon dioxide equal to that in an alveolus.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Blood arriving at a cell that is performing cellular respiration would
A) contain red blood cells with oxygen bound to most of its hemoglobin and a lower concentration of carbon dioxide than the cell.
B) contain little remaining hemoglobin and a higher concentration of carbon dioxide than the cell.
C) deposit its hemoglobin onto the plasma membrane of the cell to release oxygen and pick up carbon dioxide.
D) contain hemoglobin largely depleted of oxygen and a lower concentration of carbon dioxide than the cell.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
The figure below illustrates the inhalation step of gas exchange in humans.
![The figure below illustrates the inhalation step of gas exchange in humans. In this figure, the diaphragm and the muscles of the rib cage are ____________________ [relaxed or contracted].](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1040/11ea435e_2a89_ebbb_a5da_a38b776fc912_TB1040_00.jpg) In this figure, the diaphragm and the muscles of the rib cage are ____________________ [relaxed or contracted].
In this figure, the diaphragm and the muscles of the rib cage are ____________________ [relaxed or contracted].
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In human lungs, gases are exchanged in tiny sacs called
A) gills.
B) tracheoles.
C) alveoli.
D) spongy parenchyma.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements about oxygen-binding pigments is false?
A) They float freely in the liquid portion of human blood.
B) They increase the blood's ability to carry oxygen.
C) They are made of a complex protein bound to iron atoms.
D) They bind reversibly to oxygen.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What tube connects the pharynx to the bronchi?
A) the trachea
B) the alveoli
C) the bronchioles
D) the tracheoles
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Ectothermic animals have a larger surface area available for gas exchange than endothermic animals.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The smaller the distance over which a gas must diffuse, the more slowly it will diffuse.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The tiniest bronchiole extensions open into the
A) trachea.
B) bronchi.
C) alveoli.
D) pharynx.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The concentration of oxygen in blood plasma near an alveolus is lowered when
A) nearby red blood cells release carbon dioxide.
B) oxygen diffuses into red blood cells and binds to hemoglobin.
C) carbon dioxide diffuses into an alveolus.
D) oxygen diffuses out into the alveolus.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Too much salt in the diet can increase blood pressure because
A) greater solute levels cause interstitial fluid and blood plasma volume to increase with water.
B) the blood volume loses water and becomes too thick.
C) salt forces the blood vessels to constrict.
D) interstitial fluid and blood plasma are more concentrated with salt and make the heart beat quicker.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Blood in a capillary leaving a nearby cell would contain
A) a lower concentration of carbon dioxide than when it arrived.
B) a higher concentration of carbon dioxide than when it arrived.
C) a higher concentration of oxygen than when it arrived.
D) less hemoglobin than when it arrived.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
Hemoglobin, like many other oxygen-binding pigments, contains the metallic element ____________________.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Examine the table below. 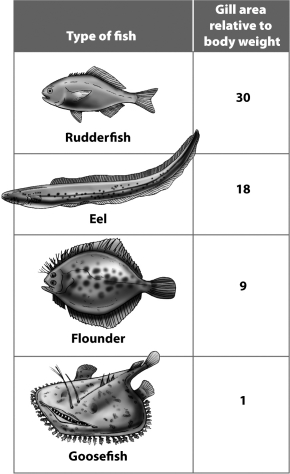 Based on the data in this table, which of these fish is probably the fastest swimmer?
Based on the data in this table, which of these fish is probably the fastest swimmer?
A) rudderfish
B) eel
C) flounder
D) goosefish
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 77
Related Exams