Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
At all points along the production possibilities frontier, _____
A) the greatest achievable output levels are produced.
B) resources are not fully employed.
C) more of one good can be obtained without giving up more of the other.
D) more efficient output levels are possible.
E) society is equally well off.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 2.2 -Refer to 2.2. You have $100 to spend and five options to choose from. What is the opportunity cost of choosing option C when you really wanted option B?
A) $100
B) $25 in terms of C.
C) $50 in terms in terms of B
D) the total value of all the options taken together
E) the value of none of options if B were chosen
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Exhibit 2.2
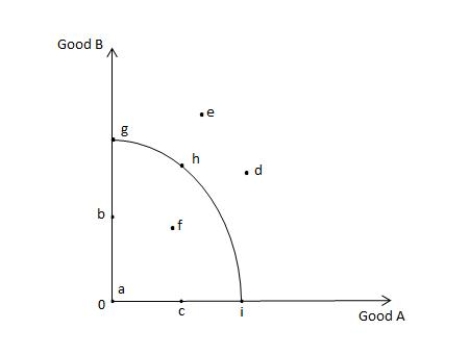 -Refer to Exhibit 2.2, which shows the production possibilities frontier for Good A and Good B. When moving from point f to point g, the production of _____
-Refer to Exhibit 2.2, which shows the production possibilities frontier for Good A and Good B. When moving from point f to point g, the production of _____
A) Good B increases without a change in the production of Good A.
B) Good A increases without a change in the production of Good B.
C) both Good A and Good B increases.
D) both Good A and Good B decreases.
E) Good B increases and the production of Good A decreases.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A downward-sloping straight-line production possibilities frontier indicates _____
A) that society cannot decide which good it prefers.
B) an absence of scarcity.
C) a constant opportunity cost.
D) that labor is inefficient.
E) that labor is specialized.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Opportunity costs exist because _____
A) technology is fixed.
B) of comparative advantage.
C) resources are scarce but wants are unlimited.
D) the value of lost opportunities varies.
E) of costs.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 2.3 -Refer to Table 2.3, which shows the production possibilities frontier between the production of capital goods and consumer goods in an economy. What is the opportunity cost of producing 3 units of capital goods at point D?
A) 35 units of capital goods.
B) 13 units of consumer goods.
C) 7 units of consumer goods.
D) 15 units of consumer goods.
E) 5 units of consumer goods.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The Sultan of Brunei, one of the world's richest people, does not face the problem of scarcity.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A command economy that is now allowing for a role for markets is known as a _____
A) traditional system.
B) transitional system.
C) pure command system.
D) mixed system.
E) pure capitalism system.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Barter is _____
A) illegal in the United States.
B) an efficient system of exchange.
C) most useful when there is much specialization and international trade.
D) only possible if money is used as a medium of exchange.
E) the direct exchange of goods without the use of money.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A major distinguishing feature between capitalist and socialist (or command) economies is that _____
A) the average citizen is wealthy in capitalist economies, whereas the average citizen is poor in socialist economies.
B) decision making is decentralized in socialist economies, while decision making is centralized in capitalist economies.
C) resources are privately owned in capitalist economies, whereas private property rights are enforced in command economies.
D) resources are publicly owned in capitalist economies, whereas resources are privately owned in command economies.
E) decision making is decentralized under capitalism, while decision making is centralized in command economies.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When drawing a production possibilities frontier for two goods, all of the following are usually assumed, except for one. Which of the following is the exception?
A) The quantity of resources is rapidly growing.
B) Technology is fixed.
C) Resources can be shifted from the production of one good to the other.
D) The production possibilities frontier is drawn for a particular time period.
E) Resources are fully and efficiently employed.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An improvement in the technology used to produce goods would _____
A) enable an economy to produce outside its original production possibilities frontier.
B) enable an economy to move along its original production possibilities frontier.
C) eliminate scarcity, and the production possibilities frontier would no longer exist.
D) have no effect on the production possibilities frontier.
E) change the production possibilities frontier to a line with a positive slope.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
On a given production possibilities frontier, which of the following is not assumed to be fixed?
A) the amount of labor available
B) the amount of capital available
C) the level of technology
D) the amount of land and natural resources available
E) the amount of goods produced
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 2.3 -Refer to Table 2.3, which shows the production possibilities frontier between the production of capital goods and consumer goods in an economy. Moving from D to B means _____
A) 1 unit of capital goods is given up for 7 units of consumer goods.
B) 2 units of capital goods are given up for 13 units of consumer goods.
C) 1 unit of capital goods is given up for 13 units of consumer goods.
D) 2 units of capital goods are given up for 28 units of consumer goods.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Exhibit 2.5
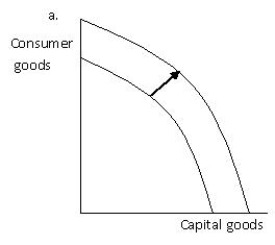
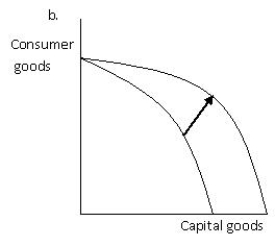
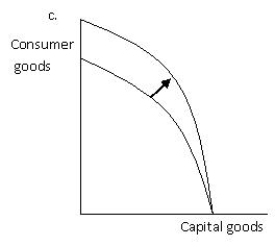
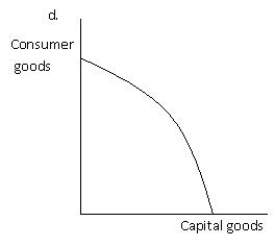 -Refer to Exhibit 2.5, which shows the production possibilities frontier for capital goods and consumer goods. Which of the graphs given best illustrates the impact on the production possibilities frontier of a technological improvement that will make the use of the resources used to produce consumer goods more efficient?
-Refer to Exhibit 2.5, which shows the production possibilities frontier for capital goods and consumer goods. Which of the graphs given best illustrates the impact on the production possibilities frontier of a technological improvement that will make the use of the resources used to produce consumer goods more efficient?
A) a
B) b
C) c
D) d
E) b and d
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
_____ is the value of the best alternative forgone when an item or activity is chosen.
A) The choice cost
B) The opportunity cost
C) The direct cost
D) The implicit cost
E) The explicit cost
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A production possibilities frontier can shift outward for all of the following reasons except _____
A) a decrease in the size of the labor force.
B) an increase in population.
C) an improvement in technology.
D) a larger work force.
E) a larger capital stock.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 2.2 -Refer to Table 2.2. You have $100 to spend and five options to choose from. What is the opportunity cost if you spent all the $100?
A) $100
B) $50 in terms of D
C) $15 in terms in terms of B
D) the total value of all the options
E) the value of the option given up if A were not chosen
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following provides the best evidence of the specialization of labor?
A) a firm that produces a line of related products, such as eight kinds of breakfast cereal
B) an architect who is willing to practice in only one geographic area
C) a physician who practices cardiology and orthopedic surgery
D) a family that eats at Wendy's every Thursday night
E) a retailer who sells goods but does not provide services
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 181 - 200 of 209
Related Exams