A) the rotation period of the Moon about its axis
B) the rotation period of Earth about its axis
C) the period of Earth's motion around the Sun
D) the period of the Moon's motion around Earth
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In 1 hour, the motion of the Moon across our sky as seen against the background of stars is: (Hint: Through what angle around the sky does the Moon move in 1 month?)
A) its own diameter or 1/2°
B) 4°
C) 1/10°
D) 13°
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the Moon is located at the vernal equinox on September 20, what is the phase of the Moon?
A) new
B) third quarter
C) first quarter
D) full
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
At the ancient Egyptian city of Syene, the Sun was directly overhead only at summer solstice. Thus, Syene must have been very close to:
A) the equator.
B) the Tropic of Cancer.
C) the Tropic of Capricorn.
D) the prime meridian.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
You are standing at the equator of the Moon and a particular star is overhead at that time. How long will it be before that star is approximately overhead again?
A) The star will always remain overhead since the Moon does not rotate on its axis.
B) 29 1/2 days
C) 365 1/4 days
D) 27 1/3 days
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Greek astronomer who first measured the radius of Earth reasonably accurately was:
A) Archimedes.
B) Eratosthenes.
C) Aristotle.
D) Ptolemy.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
During a month we see only approximately half of the moon's surface. Which one of the following changes would allow us to see all of the Moon's surface during 1 month?
A) reversing the direction of the Moon's rotation about its axis
B) changing the period of Earth's motion around the Sun
C) reversing the direction of Earth's motion around the Sun
D) reversing the direction of Earth's rotation about its axis
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose the Moon rotated on its axis with the same period it has now but in the opposite direction. Which of the following would change?
A) the length of a synodic month
B) the length of a sidereal month
C) the frequency of lunar eclipses
D) None of these would change.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If on a particular day the Sun is at one of the solstices and the Moon is at one of the equinoxes, then the lunar phase on that day is:
A) not predictable from this information alone.
B) full.
C) new.
D) either first or last quarter.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The waxing gibbous phase of the Moon occurs when the Moon passes:
A) from third quarter to new moon.
B) between the two positions when the Moon and the Sun are at right angles to each other during which new moon occurs.
C) from new moon to first quarter.
D) from first quarter to full moon.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In about 280 B.C., Aristarchus devised a method of estimating the relative distance of the Sun and the Moon from Earth by:
A) measuring the angle between the Sun and Moon when the Moon is at first or third quarter.
B) calculating their orbital radii from their orbital periods around Earth, using Kepler's law.
C) noting the size of Earth's shadow on the Moon during a lunar eclipse.
D) estimating the positions of the Moon and Sun in the sky from different positions on Earth as they passed through the due south direction on the same day.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The gravitational pull of the Sun on the Moon causes each one of the changes listed below EXCEPT ONE. Which one is the EXCEPTION?
A) The length of a sidereal month varies slightly from one orbit to the next.
B) The length of a synodic month varies slightly from one orbit to the next.
C) The Moon's orbit changes slightly from one month to the next.
D) The appearance of the Moon seen from Earth varies significantly from one month to the next.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When will the first quarter moon rise, approximately? (You may want to examine Figure 3-2 of Universe, 11th ed., and think about where you would need to stand on Earth to see the first quarter moon rising.)
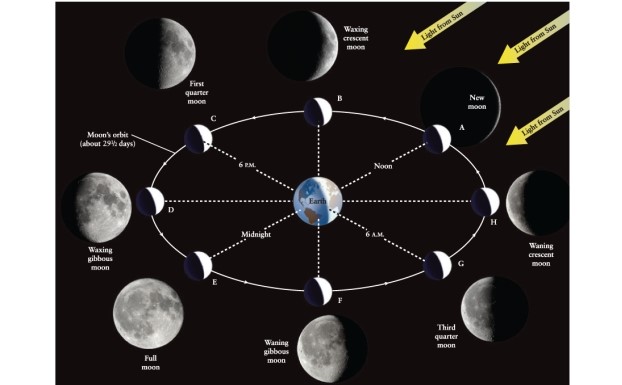
A) 6 A.M.
B) noon
C) 3 A.M.
D) 6 P.M.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which significant observation led the Greeks to accept the idea that Earth was a sphere?
A) The shape of the darkening across the Sun's disk during a solar eclipse always appeared circular.
B) The shape of Earth's shadow on the Moon during a lunar eclipse was always circular.
C) The Sun disappears below one horizon each day and reappears above the opposite horizon.
D) The shape of the eclipse shadow on Earth during a solar eclipse was always circular.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Total solar eclipses seen at approximately the same latitude occur in a sequence with a time interval, the saros, of 223 lunar sidereal months. How many eclipse years is this?
A) 19
B) 16.7
C) 18
D) 17.6
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Moon is now in its waxing crescent phase. If you could view the far side of the Moon it would be:
A) full.
B) waxing crescent.
C) waning gibbous.
D) dark, as always.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The ancient Greek astronomer Aristarchus is famous for devising a method for measuring the:
A) length of an eclipse cycle.
B) diameter of Earth.
C) relative distances of the Sun and the Moon.
D) precise distance between Alexandria and Syene in ancient Egypt.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the Moon is now in its waxing crescent phase, 2 weeks from now it will be:
A) waxing gibbous.
B) full.
C) waning gibbous.
D) waning crescent.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Aristarchus measured the Sun-Earth-Moon angle at quarter moon to be 87° and calculated that the Sun is 20 times as far away as the Moon. Actually, the Sun is almost 400 times as far away as the Moon. Thus the actual Sun-Earth-Moon angle at quarter moon must be:
A) less than 45°.
B) 45°.
C) 86.5°.
D) 89.5°.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Eratosthenes, an ancient Greek astronomer, is famous for:
A) measuring the diameter of Earth by comparing the direction to the Sun at noon at two different points on Earth.
B) measuring the diameter of Earth by timing how long it took the Moon to traverse Earth's shadow during a lunar eclipse.
C) measuring the relative distances to the Sun and the Moon by timing the exact moments when the Moon was at first and third quarter.
D) measuring the distance to each of the known planets by timing how long it took the planet to orbit the Sun.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 67
Related Exams