A) full
B) new
C) third quarter
D) Earth does not appear to go through phases when observed from the Moon.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If you were standing on the Moon in darkness on the opposite side from Earth at a particular time, which of the following conditions would be true?
A) You would never see the Sun from that position.
B) You would see Earth in about 7 days.
C) It would take about 1/4 year (3 months) before you would see Earth from that position.
D) You would never see Earth from that position.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If astronauts landed on the Moon near the center of the visible surface at full moon, how many Earth days would pass before the astronauts would experience darkness on the Moon?
A) 1 week
B) 2 weeks
C) 1 month
D) They would never experience darkness.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The time interval between one total solar eclipse and the next total solar eclipse, visible from the same location on Earth, must be all of the following EXCEPT ONE. Which is the EXCEPTION?
A) a whole number of lunar months
B) a whole number of sidereal months
C) a whole number of eclipse years
D) a whole number of saros intervals
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
One day from sunrise to sunrise for a space explorer at her lunar base will be how many Earth days long? (A diagram might help.)
A) 365 1/4 days
B) 29 1/2 days
C) 1 day
D) 27 1/3 days
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
During a total solar eclipse the Moon just covers the Sun as viewed from Earth. If you know both the diameter and distance of the Moon, what else can you determine from this information?
A) the diameter of the Sun but not its distance
B) the distance to the Sun but not its diameter
C) both the diameter and distance to the Sun
D) only the ratio of the Sun's diameter to its distance
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
One eclipse year is the time needed for:
A) three saros intervals.
B) the line of nodes of the Moon's orbit to go from alignment with respect to the Sun-Earth line to the next identical alignment.
C) 365 successive eclipses.
D) two consecutive identical alignments of the Sun, the Moon, and the line of nodes.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The attempt by Aristarchus to measure the relative distances to the Sun and to the Moon from Earth produced a result now known to be incorrect. The source of this error was that:
A) Aristarchus did not know the distance to the Moon to any great precision.
B) Aristarchus' hypothesis was fundamentally incorrect.
C) Aristarchus was unable to measure accurately the angle between the Moon and Sun at first or third quarter.
D) the Moon-Sun-Earth angle is not really a right angle at first and third quarters.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose the Moon orbited Earth with the same period it has now but in the opposite direction. Which one of the following would NOT change?
A) the length of a synodic month
B) the length of a sidereal month
C) the frequency of solar eclipses
D) the frequency of lunar eclipses
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the right ascension of the Moon?
A) 0 hours
B) 20 minutes
C) 23 hours 40 minutes
D) a number that changes significantly over 1 month
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In a period of 1 month, the Moon moves across the sky:
A) parallel to the horizon.
B) precisely along the ecliptic plane.
C) precisely along the celestial equator.
D) along a plane that is neither the ecliptic plane nor the celestial equator, nor is it parallel to the horizon.
Correct Answer

verified
D
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose Eratosthenes had measured the length of a shadow at Syene and then compared it with the shadow measured not at Alexandria, but at a location half way between Syene and Alexandria-both measurements being made at the summer solstice. What would he have found?
A) The difference in the lengths of these shadows would have been greater than that found by comparing Syene and Alexandria, suggesting a larger value for the circumference of Earth than what he actually found.
B) The difference in the lengths of these shadows would have been larger than that found by comparing Syene and Alexandria, suggesting a smaller value for the circumference of Earth than what he actually found.
C) The difference in the lengths of these shadows would have been smaller than that found by comparing Syene and Alexandria.
D) The difference in the lengths of these shadows would have been the same as that found by comparing Syene with Alexandria.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If an observer on Earth sees the Moon to be at first quarter, then at the same time, an observer on the Moon would observe Earth to be at what phase?
A) first quarter
B) third quarter
C) full
D) Earth does not appear to go through phases when observed from the Moon.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The approximate rotation period of the Moon is:
A) 1 day.
B) 1 week.
C) 1 month.
D) infinite, since the Moon does not rotate, but keeps one face toward Earth at all times.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the declination of the Moon?
A) 0°
B) +5°
C) -5°
D) a number that changes significantly over 1 month
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Eratosthenes, an astronomer in ancient Greece, measured the radius of Earth by making observations of:
A) the Sun's direction at midday at two positions on Earth, on the same day of the year.
B) the tidal ebb and flow of ocean waters.
C) the deviation of magnetic north, as seen from a compass, from true north.
D) relative times of arrival of the Sun due south of an observer at two positions on Earth.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the Moon is now in its waxing crescent phase, 1 week ago it was:
A) new.
B) waning crescent.
C) waxing gibbous.
D) full.
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements about the Moon's position and motion is NOT correct?
A) The Moon does not rotate at all, since it keeps one face toward Earth at all times.
B) The Moon's rotation period is equal to its orbital period.
C) The time from full moon to full moon is longer than the Moon's orbital period.
D) The time from full moon to full moon is longer than the Moon's rotation period on its axis.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which way will the "horns," or sharp ends of the crescent, of the Moon point in the sky when the Moon is above the western horizon at sunset, at a phase 3 days after new moon? (Hint: Think about what causes the crescent phase of the Moon; Figure 3-2 of Universe, 11th ed., may help.)
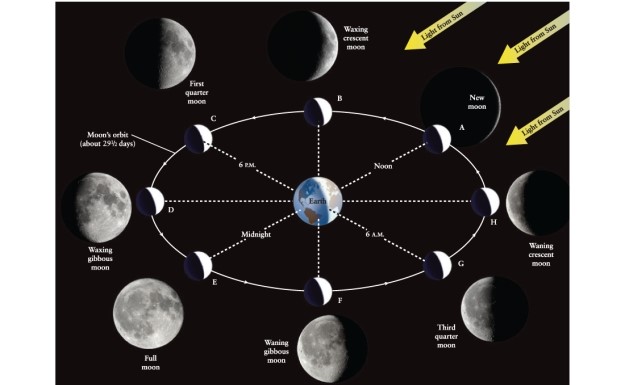
A) The horn points toward the Sun, westward.
B) The Moon is not crescent shaped at this phase.
C) The horn points at a right angle to direction of the Sun, northward.
D) The horn points away from the Sun, eastward.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How does the Moon rotate to keep one face pointed toward Earth at all times, as can be seen in Figure 3-4 of Universe, 11th ed.?
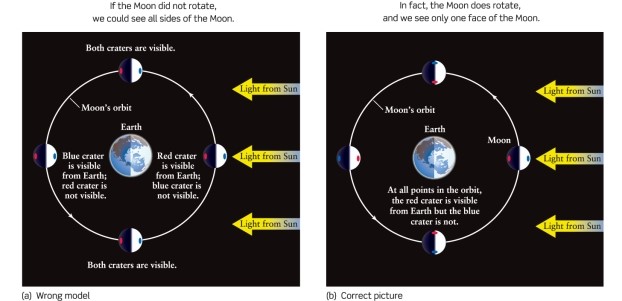
A) It rotates once per month.
B) It rotates once per year.
C) It rotates once per day.
D) It does not rotate at all.
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 67
Related Exams