A) monetarists.
B) Keynesians.
C) supply siders.
D) rational expectations theorists.
E) new classical macroeconomists.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A favorable supply shock
A) pushes the aggregate demand curve to the right.
B) shifts aggregate supply to the right.
Shifts aggregate supply to the left
C) shifts aggregate demand to the left.
D) shifts aggregate demand to the right.
E) has no effect on either the aggregate supply or aggregate demand, only on the quantities supplied and demanded.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A(n) ________ policy rule allows the behavior of the variable governed by the policy rule to change based on future circumstances.
A) effective
B) domestic
C) feedback
D) managerial
E) golden
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If menu costs associated with a price increase are $15,000,under which of the following situations will it pay the firm to raise prices?
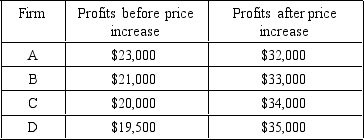
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) It should raise prices in all of these situations.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The view that the cause of economic stabilization is best served by adherence to a rigid monetary rule is associated with
A) Milton Friedman.
B) new Keynesians.
C) Franco Modigliani.
D) policy activists.
E) eclectic subversives.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Real business cycle theorists maintain that business fluctuations are due to
A) changes in the real money supply.
B) inflexible wages and prices.
C) increases and decreases in government spending.
D) shifts in the aggregate supply curve.
E) variability in household spending decisions on durable goods.
Correct Answer

verified
D
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The next question is based on the following table:
Wage Increases in First, Second, and Third Years of Union Contracts, United States, 1997-2003
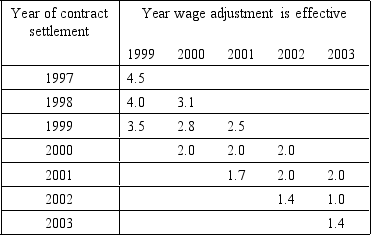 -What can be said on the basis of the union contract settlement data shown?
-What can be said on the basis of the union contract settlement data shown?
A) Unions are becoming much more powerful in their ability to negotiate wage increases.
B) Price levels in the country are rising rapidly.
C) The most recently negotiated wage increase for a given year is below the average increase prevailing under continuing contracts for that year.
D) Wage rates adjust immediately throughout the economy in response to changing labor market conditions.
E) Labor markets are tight, so firms are increasing employment.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
New classical macroeconomists believe that the predominant factor causing fluctuations in aggregate demand is
A) increases in taxes.
B) instability in the investment function.
C) the weak self-regulating mechanisms of a free enterprise economy.
D) the unstable marginal propensity to consume.
E) erratic and unpredictable government policy.
Correct Answer

verified
E
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Opponents of policy activism argue that even if intended private spending is NOT stable,economic stability nonetheless occurs because of
A) large government budget deficit spending.
B) the willingness of banks to hold excess reserves.
C) offsetting fluctuations in the velocity of circulation.
D) flexible wages and prices.
E) the acceleration effect.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Supply-siders advocate influencing aggregate supply through the use of reductions in
A) spending.
B) income.
C) money.
D) tax rates.
E) foreign imports.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Critics of the new classical macroeconomics argue that
A) the necessary information for firms to formulate rational expectations is not generally available.
B) deviations from the natural rate of unemployment are too small and transitory to have resulted from purely unexpected events.
C) the theory neglects the slow and adaptive manner in which wages and prices adjust, thus extending the duration of a business cycle.
D) markets clear too rapidly and continuously for individuals and firms to plan effectively.
E) the natural rate of unemployment stated in the assumptions of the new classical macroeconomic theory is too high to be of much use to policy makers.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Philosophically,the monetarists are most closely aligned with the views of
A) Karl Marx.
B) Keynes.
C) classical economists.
D) the Federal Reserve System.
E) Walter Heller.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The monetarist views of economic stabilization policy gained significant support during the late
A) 1930s.
B) 1940s.
C) 1950s.
D) 1960s.
E) 1970s.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Monetary policy seems to be of little use during a depression because
A) even though money is made available, there is no way to ensure it will be spent.
B) increases in the money supply raise interest rates and choke off investment.
C) people do not save when incomes are low.
D) if more money is created, it goes to pay taxes.
E) increases in money lead to inflation.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In real business cycle models,a favorable supply shock
A) pushes the aggregate demand curve to the right.
B) causes real GDP to rise.
C) lowers the income of firms and individuals.
D) increases the price level.
E) pushes the aggregate supply curve to the left.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
One strategy consistent with the new classical macroeconomists' theories would have
A) fiscal policy focus on maintaining full employment regardless of the size of the resulting budget deficit.
B) monetary policy stick to an announced policy to keep the rate of inflation to some specified low figure.
C) the government emphasize policies of wage and price controls to achieve a targeted full-employment rate with stable prices.
D) monetary authorities impose a structure of variable tax rates that automatically adjusts to changes in the unemployment rate.
E) both fiscal and monetary policy coordinated in a way that ensures that both the Phillips curve and long-run aggregate supply curves are vertical.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The phrase "You can't push on a string" is
A) a line from a 1930s song.
B) used to suggest that monetary policy can make money available but cannot ensure it will be spent.
C) an analogy used by monetarists to describe the ineffectiveness of fiscal policy.
D) used by rational expectations theorists in their criticisms of supply-side economics.
E) a reference to the fact that Congress is in control of the government's purse strings and determines spending without regard to economic impact.
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the listed policy rules tends to be supported by the new classical macroeconomists?
A) feedback
B) golden
C) marginal
D) discretionary
E) rigid
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
One explanation for why product prices adjust slowly is that
A) most markets are perfectly competitive.
B) businesses incur menu costs when they change prices.
C) markets clear continuously, making price adjustments difficult.
D) if wages adjust rapidly, prices take a while to catch up.
E) most markets are subject to government price control laws.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In which of the following countries has the central bank NOT adopted the policy framework known as inflation targeting?
A) Australia
B) Canada
C) Sweden
D) the United Kingdom
E) the United States
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 70
Related Exams