A) president of the United States.
B) secretary of the Treasury.
C) chairperson of the Council of Economic Advisers.
D) chairperson of the Joint Economic Committee of Congress.
E) chairperson of the Federal Reserve Board.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An increase in the money supply
A) shifts the aggregate demand curve to the left.
B) shifts the aggregate demand curve to the right.
C) shifts the aggregate supply curve to the left.
D) shifts the aggregate supply curve to the right
E) affects neither the aggregate demand nor the aggregate supply curve, only interest rates.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Federal Reserve System was established by Congress in
A) 1887.
B) 1907.
C) 1913.
D) 1929.
E) 1934.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Changes in the discount rate principally affect
A) expectations.
B) the ratio of reserves to deposits.
C) foreign exchange rates.
D) policy lags.
E) government spending levels.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The next question is based on this table.
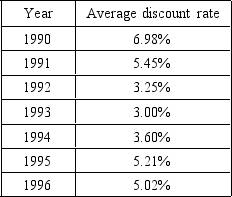 -In December 1991,the Fed cut the discount rate by a full percentage point to 3.5 percent,the lowest discount rate in 27 years.This move clearly reflects the Fed's
-In December 1991,the Fed cut the discount rate by a full percentage point to 3.5 percent,the lowest discount rate in 27 years.This move clearly reflects the Fed's
A) concern that inflation was getting out of control.
B) desire to reduce bank reserves.
C) effort to eliminate the large government budget deficit.
D) need to borrow more money from abroad.
E) attempt to send a clear signal to the banking system that it was time to expand credit.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Virtually all economists agree that the key to the Fed's power lies in its ability to
A) control the reserves of the banking system.
B) change the discount rate whenever it wants to.
C) issue Federal Reserve notes.
D) persuade Congress to change fiscal policy.
E) raise or lower taxes.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Under normal conditions the president may appoint a member to the Federal Reserve Board every
A) year.
B) two years.
C) four years.
D) seven years.
E) 14 years.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Responsibilities of the Federal Reserve System do NOT include which of the following?
A) collecting federal taxes
B) supplying the public with currency
C) acting as fiscal agents for the federal government
D) providing facilities for check collection
E) supervising the operation of the member commercial banks
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Over the 2001-03 period,the Fed steadily reduced the discount rate to 2 percent.These moves suggest that monetary policy was
A) selective.
B) redundant.
C) tight.
D) autonomous.
E) easy.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Federal Open Market Committee is made up of
A) five of the seven Federal Reserve Board governors.
B) the Board of Governors plus five of the presidents of the 12 Federal Reserve banks.
C) 12 members of the Federal Advisory Council plus the chairperson of the Federal Reserve Board.
D) the president of the United States, the secretary of the Treasury, and the members of the Federal Reserve Board.
E) 12 commercial bank presidents chosen by the president of the United States.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The table above shows the net effect of an open market operation undertaken by the Fed. Use it to answer the following question.
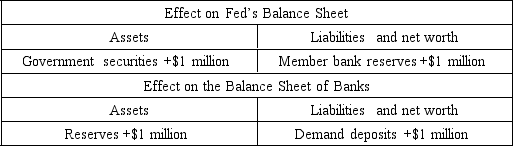 -The Fed has
-The Fed has
A) increased bank reserves, thereby decreasing the supply of money.
B) sold government securities, thereby decreasing the supply of money.
C) sold government securities, thereby increasing the supply of money.
D) increased the national debt.
E) purchased government securities, thereby increasing the supply of money.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Economic stabilization activity,which is the responsibility of the executive and legislative branches of the U.S.government,is called ________,while that presided over by the U.S.central bank is called ________.
A) deficit financing; functional finance
B) supply-side economics; liquidity preference
C) incomes policy; commercial policy
D) fiscal policy; monetary policy
E) positive economics; normative economics
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Federal Reserve Bank's exercising control over the quantity of money and interest rates is called
A) fiscal policy.
B) commercial banking.
C) monetary policy.
D) functional finance.
E) incomes policy.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In addition to controlling the money supply,the Federal Reserve System also
A) holds deposits for the public.
B) acts as fiscal agents for the federal government.
C) regulates the market for corporate securities.
D) governs the International Monetary Fund.
E) insures most commercial bank accounts through the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The table below shows the net effect of an open market operation undertaken by the Fed. Use it to answer the following question.
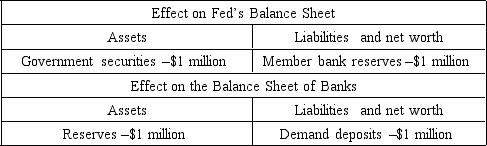 -The Fed has
-The Fed has
A) increased bank reserves, thereby decreasing the supply of money.
B) sold government securities, thereby decreasing the supply of money.
C) sold government securities, thereby increasing the supply of money.
D) increased the national debt.
E) purchased government securities, thereby increasing the supply of money.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The major liability of the Federal Reserve System is
A) gold certificates.
B) government securities.
C) loans to commercial banks.
D) Federal Reserve notes.
E) treasury deposits.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Banking Act of 1935 has been called the "single most important piece of banking legislation since the original Federal Reserve Act" because the act
A) guaranteed the solvency of member banks.
B) gave the Fed authority to take a leadership role in setting monetary policy.
C) made the Fed subservient to the Treasury, thus ensuring control of its power.
D) made the Fed a "reactive" agency, thus encouraging more sensitivity to political pressures of the times.
E) committed the U.S. government to continue backing its currency with gold.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If one pictures the Federal Reserve System as a pyramid,the apex (top peak) of the pyramid represents
A) the president.
B) Congress.
C) the Federal Reserve Board.
D) the Federal Open Market Committee.
E) the presidents of large commercial banks.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the long run,increases or decreases in the money supply
A) cause real potential output to rise and fall.
B) must ultimately be approved by Congress.
C) may increase or decrease aggregate supply but not aggregate demand.
D) are tied to increases and decreases in the U.S. government holdings of gold.
E) raise and lower the price level but have no effect on real GDP.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Our nation's currency is
A) created by the commercial banks in the Federal Reserve System.
B) created by both the commercial banking system and the Federal Reserve System.
C) issued by the Federal Reserve System.
D) a fractional-reserve currency.
E) issued by the Treasury.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 71
Related Exams