A) 1, 2, and 11
B) 3, 7, and 8
C) 5, 9, and 10
D) 11, 12, and 13
E) 12, 14, and 15
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The bonding of two amino acid molecules to form a larger molecule requires which of the following?
A) removal of a water molecule
B) addition of a water molecule
C) formation of a glycosidic bond
D) formation of a hydrogen bond
E) both removal of a water molecule and formation of a hydrogen bond
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Changing a single amino acid in a protein consisting of 325 amino acids would
A) alter the primary structure of the protein, but not its tertiary structure or function.
B) cause the tertiary structure of the protein to unfold.
C) always alter the biological activity or function of the protein.
D) always alter the primary structure of the protein and disrupt its biological activity.
E) always alter the primary structure of the protein, sometimes alter the tertiary structure of the protein, and affect its biological activity.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The following questions are based on the 15 molecules illustrated in the figure below.Each molecule may be used once,more than once,or not at all.
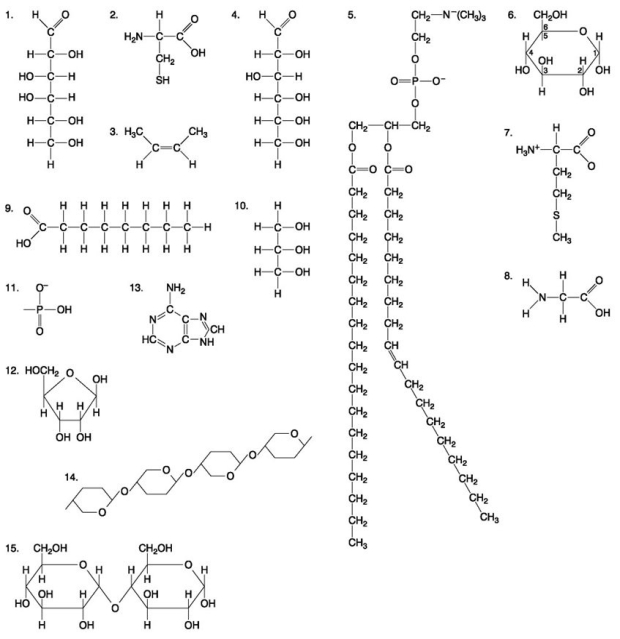 -Which of the following molecules contains a glycosidic linkage type of covalent bond?
-Which of the following molecules contains a glycosidic linkage type of covalent bond?
A) 4
B) 6
C) 12
D) 13
E) 15
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A glycosidic linkage is analogous to which of the following in proteins?
A) an amino group
B) a peptide bond
C) a disulfide bond
D) a β pleated sheet
E) an α helix
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements best summarizes the differences between DNA and RNA?
A) DNA encodes hereditary information, whereas RNA does not.
B) The bases in DNA form base-paired duplexes, whereas the bases in RNA do not.
C) DNA nucleotides contain a different sugar than RNA nucleotides.
D) DNA contains the base uracil, whereas RNA contains the base thymine.
E) DNA encodes hereditary information, whereas RNA does not; the bases in DNA form base-paired duplexes, whereas the bases in RNA do not; and DNA nucleotides contain a different sugar than RNA nucleotides.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is an example of hydrolysis?
A) the reaction of two monosaccharides, forming a disaccharide with the release of water
B) the synthesis of two amino acids, forming a peptide with the release of water
C) the reaction of a fat, forming glycerol and fatty acids with the release of water
D) the reaction of a fat, forming glycerol and fatty acids with the consumption of water
E) the synthesis of a nucleotide from a phosphate, a pentose sugar, and a nitrogenous base with the production of a molecule of water
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Refer to the following figure to answer the questions below.
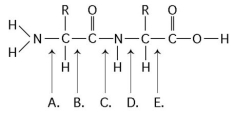 -Which bond is closest to the amino terminus of the molecule?
-Which bond is closest to the amino terminus of the molecule?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What maintains the secondary structure of a protein?
A) peptide bonds
B) hydrogen bonds between the amino group of one peptide bond and the carboxyl group of another peptide bond
C) disulphide bonds
D) hydrophobic interactions
E) hydrogen bonds between the R groups
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The following questions are based on the 15 molecules illustrated in the figure below.Each molecule may be used once,more than once,or not at all.
 -Which of the following molecules is a purine type of nitrogenous base?
-Which of the following molecules is a purine type of nitrogenous base?
A) 2
B) 3
C) 5
D) 12
E) 13
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The genome of humans and chimpanzees are ________ identical.
A) less than 50%
B) 70-75%
C) 85-90%
D) 95-98%
E) 100%
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What type of covalent bond between amino acid side chains (R groups) functions in maintaining a polypeptide's specific three-dimensional shape?
A) ionic bond
B) hydrophobic interaction
C) van der Waals interaction
D) disulphide bond
E) hydrogen bond
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the term used for a protein molecule that assists in the proper folding of other proteins?
A) tertiary protein
B) chaperonin
C) enzyme protein
D) renaturing protein
E) denaturing protein
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is not a polymer?
A) glucose
B) starch
C) cellulose
D) chitin
E) DNA
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the difference between an aldose sugar and a ketose sugar?
A) the number of carbons
B) the position of the hydroxyl groups
C) the position of the carbonyl group
D) One is a ring form, and the other is a linear chain.
E) One has a nitrogen.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Humans and mice differ because of which of the following?
A) Their cells have different small organic molecules.
B) Their cells make different types of large biological molecules.
C) Their cells make different types of lipids.
D) Their cells have some differences in the sequence of nucleotides in their nucleic acids.
E) Their cells make different types of proteins.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The tertiary structure of a protein is the
A) bonding together of several polypeptide chains by weak bonds.
B) order in which amino acids are joined in a polypeptide chain.
C) unique three-dimensional shape of the fully folded polypeptide.
D) organization of a polypeptide chain into an α helix or β pleated sheet.
E) overall protein structure resulting from the aggregation of two or more polypeptide subunits.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The bonding of two amino acid molecules to form a larger molecule requires
A) the release of a water molecule.
B) the release of a carbon dioxide molecule.
C) the addition of a nitrogen atom.
D) the addition of a water molecule.
E) the release of a nitrous oxide molecule.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following information to answer the questions below. You have just had a breakfast of toast (high-fibre bread) with butter and jam (no added sugar) along with a glass of milk. -Which of the following categories includes all others in the list?
A) monosaccharide
B) disaccharide
C) starch
D) carbohydrate
E) polysaccharide
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The basis for diversity,both within a species and among species,is a result of the
A) arrangement of a few base molecules into many different macromolecular combinations.
B) shared structures of polymers and lipids.
C) infinite number of base molecules to build from.
D) ratio of lipid to protein.
E) fact that some individuals have mutations.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 131
Related Exams