A) Enable subsecond timers
B) Increase the hold time value
C) Increase the dead timer value
D) Enable stub routing on the spokes
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The implementations group has been using the test bed to do a 'proof-of-concept' that requires both Client 1 and Client 2 to access the WEB Server at 209.65.200.241. After several changes to the network addressing, routing scheme, DHCP services, NTP services, layer 2 connectivity, FHRP services, and device security, a trouble ticket has been opened indicating that Client 1 cannot ping the 209.65.200.241 address. Use the supported commands to isolated the cause of this fault and answer the following questions. What is the solution to the fault condition?
A) Enable OSPF authentication on the s0/0/0 interface using the ip ospf authentication message-digest command
B) Enable OSPF routing on the s0/0/0 interface using the network 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 area 12 command.
C) Enable OSPF routing on the s0/0/0 interface using the network 209.65.200.0 0.0.0.255 area 12 command.
D) Redistribute the BGP route into OSPF using the redistribute BGP 65001 subnet command.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An engineer is working with NETCONF and Cisco NX-OS based devices. The engineer needs a YANG model that supports a specific feature relevant only to Cisco NX-OS. Which model must the engineer choose?
A) Native
B) IEEE
C) OpenConfig
D) IETF
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Refer to the exhibit.  Which statement about the INTERNET ACL is true?
Which statement about the INTERNET ACL is true?
A) The denied entries will be logged because of the explicit deny ipv6 any any log line.
B) A packet with a source address of 2001:DB8:AD59:ACC0:2020:882:DB8:1125 will be denied.
C) HTTPS traffic from the 2001:DB8:AD59:BA21::/64 subnet will automatically be permitted along with HTTP traffic.
D) A packet with a source address of 2001:DB80:AD59:BA21:101:CAB:64:38 destined to port 80 will be permitted.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
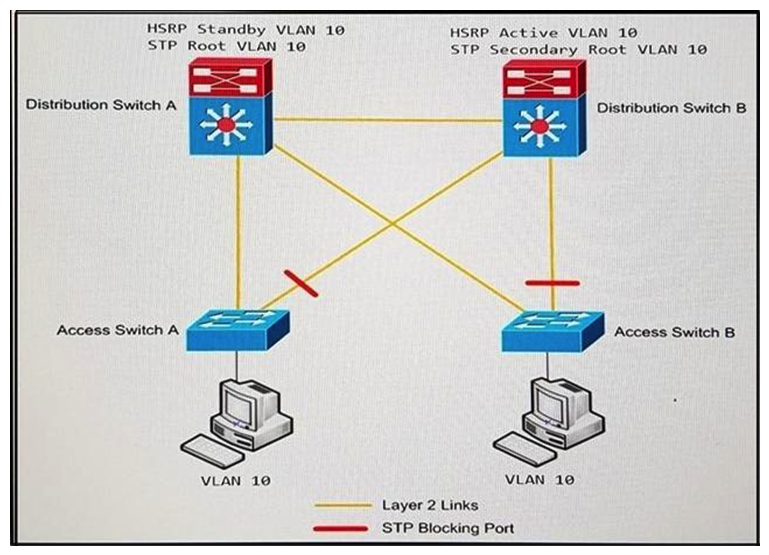 Refer to the exhibit. An engineer must optimize the traffic flow of the network. Which change provides a more efficient design between the access and the distribution layer?
Refer to the exhibit. An engineer must optimize the traffic flow of the network. Which change provides a more efficient design between the access and the distribution layer?
A) Add a link between access switch A and access switch B
B) Reconfigure the distribution switch A to become the HSRP Active
C) Change the link between distribution switch A and distribution switch B to be a routed link
D) Create an EtherChannel link between distribution switch A and distribution switch B
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which two functions are provided by the Cisco SD-WAN orchestration plane? (Choose two.)
A) centralized provisioning
B) primary authentication point
C) NAT traversal facilitation
D) Zero Touch Provisioning
E) troubleshooting and monitoring
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An engineer must design a solution to connect a customer to the Internet. The solution will include a Layer 3 circuit with a CIR of 50 Mbps from the service provider. The hand-off from the provider's switch to the customer's router is 1Gbps. Which solution should the engineer include to prevent potential issues with choppy voice traffic?
A) Reduce the bandwidth of the connection to the router.
B) Implement hierarchical QoS with a parent policing policy.
C) Implement hierarchical QoS with a parent shaping policy.
D) Add a bandwidth statement to the router interface.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is a benefit of using VRRPv3 as compared to VRRPv2?
A) VRRPv3 supports IPv4 and IPv6
B) VRRPv3 supports authentication
C) VRRPv3 supports preemption
D) VRRPv3 supports stateful switchover
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which nonproprietary mechanism can be used to automate rendezvous point distribution in a large PIM domain?
A) Embedded RP
B) BSR
C) Auto-RP
D) Static RP
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An engineer is designing a Layer 3 campus network running EIGRP between the core, aggregation, and access layers. The access layer switches will be connected to the aggregation layer using Layer 3 copper connections. The engineer wants to improve convergence time for access layer switch failures. Which technique must the design include?
A) enabling BFD for EIGRP on the access layer uplinks
B) reducing the EIGRP Hello / Hold timer values
C) EIGRP summarization from core to aggregation layer
D) EIGRP summarization from access to aggregation layer
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which design element should an engineer consider when multicast is included in a Cisco SD-Access architecture?
A) PIM SSM must run in the underlay.
B) Multicast clients reside in the underlay, and the multicast source is outside the fabric or in the overlay.
C) Rendezvous points must be used in a PIM SSM deployment.
D) Multicast traffic is transported in the overlay and the EID space for wired and wireless clients.
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A large chain of stores currently uses MPLS-based T1 lines to connect their stores to their data center. An architect must design a new solution to improve availability and reduce costs while keeping these considerations in mind: The company uses multicast to deliver training to the stores. The company uses dynamic routing protocols and has implemented QoS. To simplify deployments, tunnels should be created dynamically on the hub when additional stores open. Which solution should be included in this design?
A) VPLS
B) GET VPN
C) DMVPN
D) IPsec
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An engineer is designing an EIGRP network for a small branch site where there is only one Layer 3 router. The engineer wants the router to advertise the local LAN network to remote EIGRP neighbors without sending any unnecessary multicast messages on the local LAN. Which action should the engineer take?
A) Use a static default route for this site instead of EIGRP
B) Advertise the local LAN using the network command and the passive-interface feature Advertise the local LAN using the network command and the passive-interface feature
C) Redistribute the local LAN network using the redistribute connected command Redistribute the local LAN network using the redistribute connected command
D) Advertise the local LAN subnet as a stub network
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is one function of the vSmart controller in an SD-WAN deployment?
A) orchestrates vEdge and cEdge connectivity
B) responsible for the centralized control plane of the SD-WAN network
C) provides centralized network management and a GUI to monitor and operate the SD-WAN overlay
D) provides a data-plane at branch offices to pass traffic through the SD-WAN network
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Instructions The main screen consists of two parts; the Main scenario and the Topology tabs. The main scenario describes TSHOOT.com test bed. The Topology tabs allow you to display the appropriate and select the trouble ticket. To complete the item, you will first need to familiarize yourself with the TSHOOT.com test bed by clicking on the master scenario first and then the topologies tabs. Once you are familiar with the test bed and the topologies, you should start evaluating the trouble ticket. You will be presented with a Trouble Ticket scenario that will describe the fault condition. You will need to determine on which device the fault condition is located, to which technology the fault condition is related, and the solution to each trouble ticket. This will be done by answering three questions. Ticket Selection To begin, click on the Ticket on the Topology tabs. Please note. Some of the questions will require you to use the scroll bar to see all options. Fault Isolation Read the ticket scenario to understand the fault condition. Open the appropriate topology, based upon the ticket scenario. Open the console of the desired device by clicking on that device in the topology, based upon your troubleshooting methodology. Use the supported show, ping and trace commands to begin your fault isolation process. Move to other devices as need by clicking on those devices within the topology. Fault Identification The trouble ticket will include three questions that you will need to answer, 1. Which device contains the fault 2. Which technology the fault condition is related to 3. What is the solution to the issue To advance to the next question within the ticket click on " Next Question ". When you click " DONE ", the trouble ticket will turn RED and will no longer be accessible. You may also use the " Previous Question " button to review questions within that specific ticket. To complete a trouble ticket, answer all three questions and click " ". This will store your response to the questions. Do not click on " " unless you have answered all questions within the ticket. Item Completion Click the NEXT button on the bottom of the screen once a ticket is . This action moves you to the next item. Scenario The company has created the test bed network shown in the layer 2 and layer 3 topology exhibits. This network consists of four routers, two layer 3 switches and two layer 2 switches. In the IPv4 layer 3 topology, R1, R2, R3, and R4 are running OSPF with an OSPF process number 1. DSW1, DSW2 and R4 are running EIGRP with an AS of 10. Redistribution is enabled where necessary. R1 is running a BGP AS with a number of 65001. This AS has an eBGP connection to AS 65002 in the ISP's network. Because the company's address space is in the private range, R1 is also providing NAT translations between the inside (10.1.0.0/16 & 10.2.0.0/16) networks and the outside (209.65.200.0/24) network. ASW1 and ASW2 are layer 2 switches. NTP is enabled on all devices with 209.65.200.226 serving as the master clock source. The client workstations receive their IP address and default gateway via R4's DHCP server. The default gateway address of 10.2.1.254 is the IP address of HSRP group 10 which is running on DSW1 and DSW2. In the IPv6 layer 3 topology R1, R2, and R3 are running OSPFv3 with an OSPF process number 6. DSW1, DSW2 and R4 are running RIPng process name RIP_ZONE. The two IPv6 routing domains, OSPF 6 and RIPng are connected via GRE tunnel running over the underlying IPv4 OSPF domain. Redistribution is enabled where necessary. Recently the implementation group has been using the test bed to do a 'proof-of-concept' on several implementations. This involved changing the configuration on one or more of the devices. You will be presented with a series of trouble tickets related to issues introduced during these configurations. 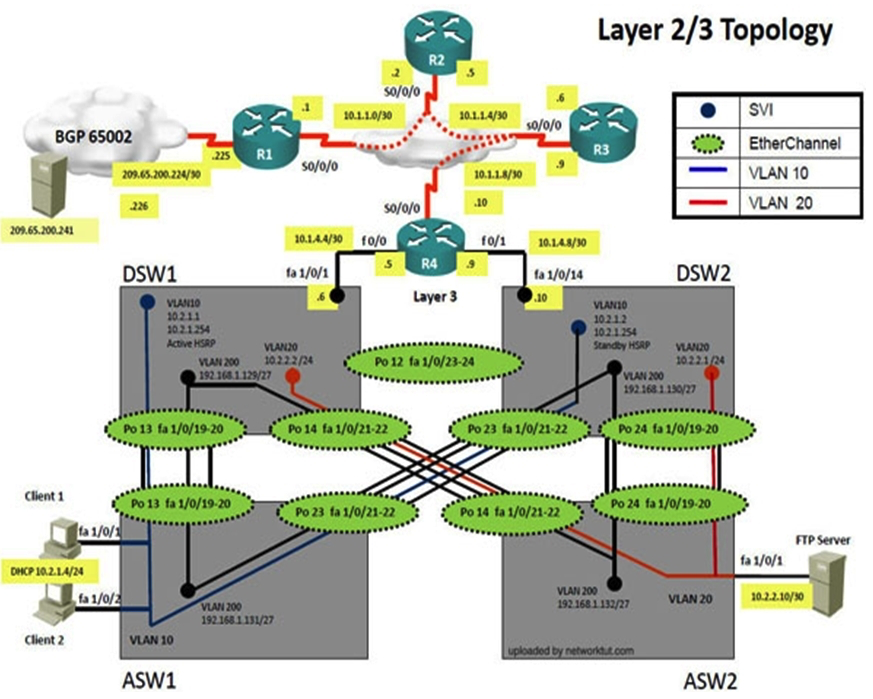 The implementation group has been using the test bed to do a 'proof-of-concept' that requires both Client 1 and Client 2 to access the WEB Server at 209.65.200.241. After several changes to the network addressing, routing schemes, DHCP services, NTP services, and FHRP services, a trouble ticket has been opened indicating that Client 1 cannot ping the 209.65.200.241 address. Use the supported commands to isolate the cause of this fault and answer the following questions. On which device is the fault condition located?
The implementation group has been using the test bed to do a 'proof-of-concept' that requires both Client 1 and Client 2 to access the WEB Server at 209.65.200.241. After several changes to the network addressing, routing schemes, DHCP services, NTP services, and FHRP services, a trouble ticket has been opened indicating that Client 1 cannot ping the 209.65.200.241 address. Use the supported commands to isolate the cause of this fault and answer the following questions. On which device is the fault condition located?
A) R1
B) R2
C) R3
D) R4
E) DSW1
F) DSW2
G) ASW1
H) ASW2
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An architect is creating a migration strategy for a large organization in which the choice made by the application between IPv6 and IPv4 is based on the DNS request. Which migration strategy does the architect choose?
A) AFT for public web presence
B) host-initiated tunnels
C) dual stack
D) site-to-site IPv6 over IPv4 tunnels
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A branch office has a primary L3VPN MPLS connection back to the main office and an IPSEC VPN tunnel that serves as backup. Which design ensures that data is sent over the backup connection only if the primary MPLS circuit is down?
A) Use EIGRP to establish a neighbor relationship with the main office via L3VPN MPLS and the IPSEC VPN tunnel.
B) Use BGP with the multipath feature enabled to force traffic via the primary path when available.
C) Use static routes tied to an IP SLA to prefer the primary path while a floating static route points to the backup connection.
D) Use OSPF with a passive-interface command on the backup connection. Use OSPF with a passive-interface command on the backup connection.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which two techniques improve the application experience in a Cisco SD-WAN design? (Choose two.)
A) utilizing forward error correction
B) implementing a stateful application firewall
C) implementing AMP
D) utilizing quality of service
E) implementing Cisco Umbrella
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An infrastructure team is concerned about the shared memory utilization of a device, and for this reason, they need to monitor the device state. Which solution limits impact on the device and provides the required data?
A) IPFIX
B) static telemetry
C) on-change subscription
D) periodic subscription
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What are two valid scaling techniques when an EIGRP network is designed that consists of more than 1000 routers? (Choose two.)
A) Use structured hierarchical topology with route summarization
B) Used sub-second timers
C) Use the distribute-list command to filter routes Use the distribute-list command to filter routes
D) Modify delay parameters on the links
E) Implement multiple EIGRP autonomous systems
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 109
Related Exams