A) beneath its production possibilities curve.
B) at a corner of its production possibilities curve.
C) anywhere along its production possibilities curve.
D) outside of its production possibilities curve.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
On a production possibilities curve diagram, greater entrepreneurship:
A) causes the curve to shift outward.
B) keeps the economy on the curve.
C) prevents movement along the curve.
D) keeps the economy at the corners of the curve.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is true ?
A) The production possibilities curve indicates that it will be impossible to expand total output with the passage of time.
B) As long as resources are scarce, output cannot be increased.
C) The size of the economic pie is fixed, and therefore, if one individual has more income, others must have less.
D) Over time, the output of goods and services can be increased through human ingenuity and discovery of better ways of doing things.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The law of increasing costs holds that the opportunity cost:
A) of a good decreases as the quantity of the good produced increases.
B) of a good is proportional to the resources used in its production.
C) of a good increases as more of the good is produced.
D) of a good does not change with the resources used its production.
E) changes as more of the good is produced.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
A nation can accelerate economic growth by increasing its production of consumer goods.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Exhibit 2-1 Production possibilities curve data 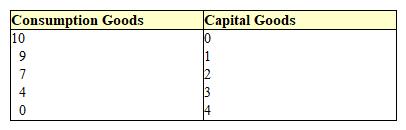 In Exhibit 2-1, the opportunity cost of producing the fourth unit of capital is:
In Exhibit 2-1, the opportunity cost of producing the fourth unit of capital is:
A) 0.
B) 1 unit of consumption goods.
C) 2 units of consumption goods.
D) 4 units of consumption goods.
E) there is not enough information to estimate the opportunity cost.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Compare two economies A and B that start out with identical production possibilities curves. Economy A chooses an efficient point with 6 consumption goods and 3 capital goods, while economy B also chooses an efficient point, but with 4 consumption goods and 5 capital goods. In the future we can predict:
A) economy A will operate inefficiently.
B) economy B will operate inefficiently.
C) economy A and economy B will grow equally fast.
D) economy A will grow faster than economy B.
E) economy B will grow faster than economy A.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The amount of a good that must be given up to produce another good is the concept of:
A) scarcity.
B) specialization.
C) trade.
D) efficiency.
E) opportunity cost.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which fundamental economic question requires society to choose the technological and resource mix used to produce goods?
A) The What to Produce question.
B) The Why to Produce question.
C) The How to Produce question.
D) The For Whom to Produce question.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A major technological advance would be represented on a production possibilities curve by a(n) :
A) movement off the production possibilities curve toward a point outside the curve.
B) movement toward the curve from a point inside the curve.
C) outward shift of the entire curve.
D) movement to the left along the curve to a higher point.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
If some resources went to waste rather to use in production, the economy would operate outside its production possibility curve.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The production possibilities curve shows that:
A) some of one good must be given up to get more of another good in an economy that is operating efficiently.
B) no output combination is impossible.
C) an economy that is operating efficiently can have more of one good without giving up some of another good.
D) scarcity can be eliminated.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The law of increasing opportunity costs causes the production possibilities curve to:
A) be a straight line.
B) slope upwards.
C) have a bowed-out shape.
D) shift inward.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
While waiting in line to buy two tacos at 80 cents each and a medium drink for 90 cents, Jordan notices that the restaurant has a value meal containing three tacos and a medium drink all for $3. For Jordan, the marginal cost of the third taco would be:
A) zero.
B) 50 cents.
C) 80 cents.
D) $1.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Any point inside the production possibility curve is:
A) efficient.
B) nonfeasible.
C) inefficient.
D) optimal.
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
On the production possibilities curve, a movement between points that yields a loss of one good in order to raise the output of another good will maintain efficient production.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Economic growth may be represented by a(n) :
A) leftward shift of a production possibilities curve.
B) outward shift of a production possibilities curve.
C) movement along a production possibilities curve.
D) production possibilities curve that remains fixed.
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Exhibit 2-16 Production possibilities curve 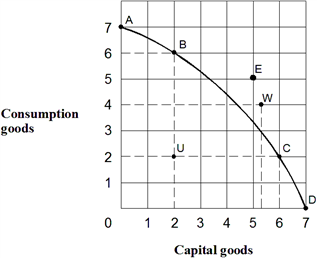 From the information in Exhibit 2-16, which of the following points on the production possibilities curve are attainable with the resources and technology currently available?
From the information in Exhibit 2-16, which of the following points on the production possibilities curve are attainable with the resources and technology currently available?
A) A, B, C, E, U
B) A, B, C, D, W
C) E, U, W
D) B, C, D, U
E) A, B, C, E
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Given a production possibilities curve, a point:
A) inside the curve represents unemployment.
B) on the curve represents full employment.
C) outside the curve is currently unattainable.
D) all of the above.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Exhibit 2-17 Production possibilities curve 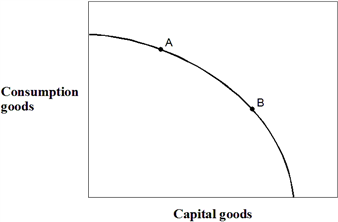 In Exhibit 2-17, if countries A and B currently have the same production possibilities curve (PPC) as given in the figure, but this year country A locates at point A on its PPC and country B locates at point B on its PPC, then country A:
In Exhibit 2-17, if countries A and B currently have the same production possibilities curve (PPC) as given in the figure, but this year country A locates at point A on its PPC and country B locates at point B on its PPC, then country A:
A) is better off than country B.
B) will grow at a faster rate than country B.
C) will grow at a slower rate than country B.
D) is producing more capital goods than country B.
E) is more efficient than country B.
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 209
Related Exams