A) the quantity produced by the monopolistically competitive firm is higher than that of the perfectly competitive firm.
B) the profit earned by the monopolistically competitive firm is higher than that of the perfectly competitive firm.
C) the marginal revenue of the monopolistically competitive firm is lower than that of the perfectly competitive firm at the profit-maximizing quantity.
D) the long run average cost of the monopolistically competitive firm is higher than that of the perfectly competitive firm at the profit-maximizing quantity.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following most closely approximates the conditions of a monopolistically competitive market?
A) The market for Grade A eggs, which is characterized by a large number of firms producing a homogeneous product.
B) The restaurant industry, which is characterized by firms producing a differentiated product in a market with low entry barriers.
C) Local cable television service, where a licensed supplier competes with firms offering satellite service.
D) The market for jumbo aircraft, where one major domestic firm competes with one major foreign firm.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is a distinction between perfectly competitive and monopolistic competition?
A) Perfectly competitive firms must compete with rival sellers; monopolistically competitive firms do not confront rival sellers.
B) Monopolistically competitive firms can raise their price without losing sales; perfectly competitive firms must lower their price in order to sell more of their product.
C) Perfectly competitive firms confront a perfectly elastic demand curve; monopolistically competitive firms face a downward-sloping demand curve.
D) Perfectly competitive firms may make either economic profits or losses in the short run, but monopolistically competitive firms always earn an economic profit.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Exhibit 10-2 A monopolistic competitive firm
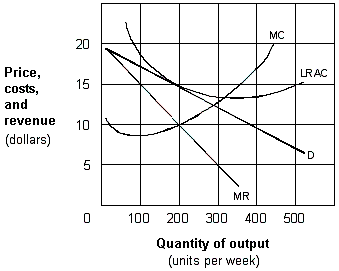 To maximize long-run profits, the monopolistically competitive firm shown in Exhibit 10-2 will charge a price per unit of:
To maximize long-run profits, the monopolistically competitive firm shown in Exhibit 10-2 will charge a price per unit of:
A) zero.
B) $5.
C) $10.
D) $15.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Exhibit 10-2 A monopolistic competitive firm
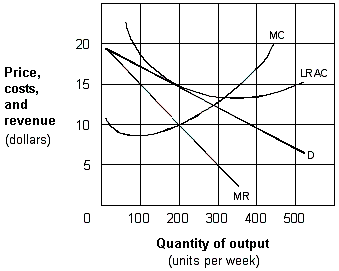 If all firms in a monopolistic competitive industry have demand and cost curves like those shown in Exhibit 10-2, we would expect that in the long run:
If all firms in a monopolistic competitive industry have demand and cost curves like those shown in Exhibit 10-2, we would expect that in the long run:
A) all firms will leave the industry.
B) some firms will leave the industry.
C) firms in the industry earn zero economic profits.
D) a number of new firms will enter the industry.
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In monopolistic competition if there is profit, there is:
A) a signal for new firms to enter.
B) a motive for existing firms to increase prices.
C) proof that advertising works.
D) a motive for existing firms to decrease prices.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When the price and output decisions of one firm include the possible price and output reactions of the firm's rivals, the market is
A) a monopoly characterized by differentiated products.
B) an oligopoly characterized by mutual interdependence.
C) perfectly competitive characterized by collusion.
D) monopolistically competitive characterized by nonprice competition.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Exhibit 10-1 A monopolistic competitive firm
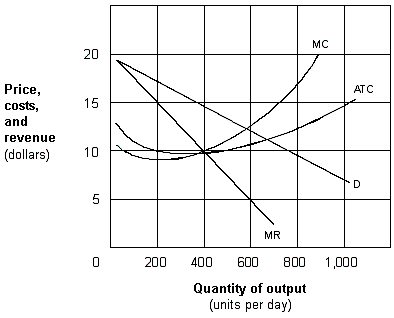 As represented in Exhibit 10-1, the maximum long-run economic profit earned by this monopolistic competitive firm is:
As represented in Exhibit 10-1, the maximum long-run economic profit earned by this monopolistic competitive firm is:
A) zero.
B) $200 per day.
C) $1,000 per day.
D) $20,000 per day.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The kinked demand theory attempts to explain why an oligopolistic firm:
A) has relatively large advertising expenditures.
B) fails to invest in research and development.
C) infrequently changes its price.
D) engages in excessive brand proliferation.
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The industry that most closely approximates the conditions of the oligopoly model is:
A) restaurants.
B) retail clothing.
C) home construction.
D) tires.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
As a result of a kinked demand curve, the price:
A) fluctuates.
B) falls below the kink.
C) settles at the kink.
D) rises above the kink.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The market for Product A has many sellers, selling identical products, each earning an economic profit of zero in the long run. The market for Product B has many sellers, selling differentiated products, each earning an economics profit of zero in the long run. Given this information, one can conclude that
A) The markets for Product A and Product B are perfectly competitive.
B) The markets for Product A and Product B are monopolistically competitive.
C) The market for Product A is monopolistically competitive and the market for Product B is perfectly competitive.
D) The market for Product A is perfectly competitive and the market for Product B is monopolistically competitive.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Monopolistic competition is inefficient because:
A) firms earn positive economic profits.
B) the firms' marginal costs and marginal revenues are not equal.
C) firms have excess capacity in the long run.
D) entry is difficult.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is always associated with monopolistic competition?
A) identical products
B) economic profits in the short run
C) product differentiation
D) Demand curves become more inelastic as new entry occurs.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The theory of monopolistic competition predicts that in long-run equilibrium a monopolistically competitive firm will:
A) produce the output level at which price equals long-run marginal cost.
B) operate at minimum long-run average cost.
C) overutilize its insufficient capacity.
D) produce the output level at which price equals long-run average cost.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose Ford, GM, and Dodge make the majority of pick-up trucks sold in the United States If they all sell for approximately the same price, and Ford offers a $2,000 rebate on new truck sales, what can Ford expect to see?
A) an unprecedented increase in truck sales
B) an immediate response by GM and Dodge
C) a visit from the antitrust authorities of the government
D) a revolution from Ford stockholders
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Compared to monopoly, the market results with monopolistic competition are usually expected to be:
A) worse because consumers get fewer choices.
B) worse because consumers pay a higher price.
C) better because consumers pay a lower price.
D) better because consumers get less output.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The automobile, steel, and oil markets are all examples of:
A) perfectly competitive markets.
B) monopolies.
C) monopolistically competitive markets.
D) oligopolies.
Correct Answer

verified
D
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is true for perfect competition, monopolistic competition, and monopoly?
A) The product of all firms is homogeneous.
B) Firms will earn zero economic profits in the long run.
C) Short-run profits are maximized when marginal cost equals marginal revenue.
D) Price is greater than marginal cost at the profit-maximizing quantity.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In long-run equilibrium, output is expanded to the minimum long-run average total cost by:
A) perfectly competitive firms but not by monopolistically competitive firms.
B) monopolistically competitive firms but not by perfectly competitive firms.
C) both monopolistically competitive firms and perfectly competitive firms.
D) neither perfectly competitive firms nor monopolistically competitive firms.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 97
Related Exams