A) increase output.
B) decrease output.
C) maintain its current output.
D) shut down.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The profit maximizing or loss minimizing quantity of output for any firm to produce exists at that output level in which:
A) total revenue is maximized.
B) total cost is minimized.
C) marginal cost is minimized.
D) marginal revenue equals marginal cost.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the expansion of output in an industry leads to unchanged resource prices, the industry is most likely to be a(n) :
A) decreasing cost industry.
B) increasing cost industry.
C) constant cost industry.
D) industry characterized by economies of scale.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The demand for the product of a competitive price-taker firm is:
A) perfectly inelastic.
B) perfectly elastic.
C) greater than zero but less than one.
D) dependent on the availability of substitutes for the firm's product.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a firm equates MR and MC, then:
A) TR is at a maximum, and TC is at a minimum.
B) output is at a maximum.
C) both TR and TC are at a maximum.
D) profits are at a maximum or losses are at a minimum.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Exhibit 8-19 Long-run perfectly competitive industry
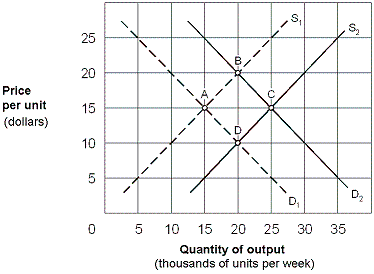 As shown in Exhibit 8-19, assume that a perfectly competitive industry is in long-run equilibrium at point A and the demand curve shifts from D1 to D2. The result is a long-run supply curve drawn from point:
As shown in Exhibit 8-19, assume that a perfectly competitive industry is in long-run equilibrium at point A and the demand curve shifts from D1 to D2. The result is a long-run supply curve drawn from point:
A) A to point B.
B) B to point A.
C) A to point D.
D) A to point C.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In a perfectly competitive industry, assume the short-run average total cost increases as the output of the industry expands. In the long run, the industry supply curve will:
A) have a positive slope.
B) have a negative slope.
C) be perfectly horizontal.
D) be perfectly vertical.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following best describes why a perfectly competitive firm will sometimes continue producing in the short run even if it incurs a loss?
A) As long as price exceeds average variable cost, the loss from producing will be smaller than the loss from shutting down, which is equal to the amount of total fixed costs.
B) Short-run losses turn into long-run profits when there is entry into the market.
C) A perfectly competitive firm should never produce if it incurs a loss because it is unable to influence the market price.
D) If price exceeds average total cost, the loss from covering the fixed costs will be smaller than the loss from covering the variable costs.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Exhibit 8-12 Marginal revenue and cost per unit curves
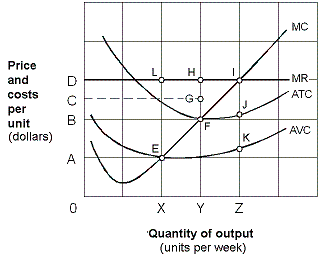 As shown in Exhibit 8-12, the firm will shut down in the short-run at a price below:
As shown in Exhibit 8-12, the firm will shut down in the short-run at a price below:
A) OA.
B) OB.
C) OC.
D) OD.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the short run, a firm will stay in business as long as:
A) price equals average revenue.
B) marginal revenue is greater than or equal to marginal cost.
C) price exceeds average variable cost.
D) price is less than average variable cost.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The price-taker firm should discontinue production immediately if:
A) the market price exceeds the firm's average total costs.
B) the market price is less than the firm's average variable costs.
C) the market price is less than the firm's average total costs, but greater than its average variable cost.
D) its accounting statement indicates that it is suffering losses.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Exhibit 8-4 Marginal cost and revenue for a firm
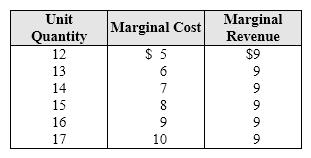 In Exhibit 8-4, what is this firm's profit-maximizing rate of output?
In Exhibit 8-4, what is this firm's profit-maximizing rate of output?
A) 13.
B) 14.
C) 15.
D) 16.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A firm operating in a perfectly competitive market is a price taker because:
A) each firm has a significant market share.
B) each firm's product is perceived as different.
C) setting a price higher than the market price results in zero sales.
D) the market demand curve is perfectly elastic.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Exhibit 8-12 Marginal revenue and cost per unit curves
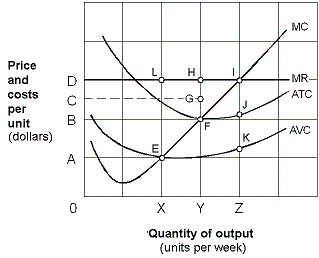 As shown in Exhibit 8-12, the firm will not produce in the short-run if the price is below:
As shown in Exhibit 8-12, the firm will not produce in the short-run if the price is below:
A) OA.
B) OB.
C) OC.
D) OD.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a firm shuts down in the short run, it will:
A) incur losses equal to its fixed costs.
B) have total revenue greater than total fixed costs.
C) reduce its losses to zero.
D) do this because P > AVC.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider a firm operating with the following: price = 10; MR = 10; MC = 10; ATC = 10. This firm is:
A) making an economic profit of 10.
B) an example of monopolistic competition.
C) perfectly competitive in long-run equilibrium.
D) a monopolist for a product with a relatively inelastic demand.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Exhibit 8-3 Cost per unit curves
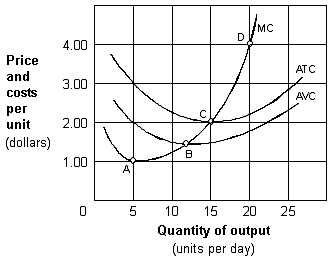 As shown in Exhibit 8-3, the price at which the firm earns zero economic profit in the short-run is:
As shown in Exhibit 8-3, the price at which the firm earns zero economic profit in the short-run is:
A) $1.00 per unit.
B) $1.50 per unit.
C) $2.00 per unit.
D) $4.00 per unit.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The neighborhood ice cream shop finds that when it charges $3 per ice cream cone, its total revenues are $90,000. It has total variable costs of $30,000 and total fixed costs of $40,000. From this we can infer the:
A) shop sells 10,000 ice cream cones.
B) price is less than average total cost.
C) economic profits are $20,000.
D) shop will be closed in the long run.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Exhibit 8-3 Cost per unit curves
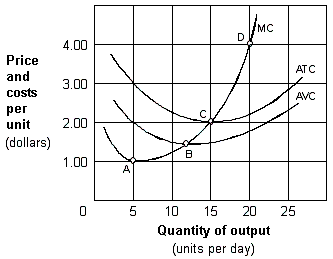 As shown in Exhibit 8-3, the firm will produce in the short run if the price is at least equal to:
As shown in Exhibit 8-3, the firm will produce in the short run if the price is at least equal to:
A) $1.00 per unit (point A) .
B) $1.50 per unit (point B) .
C) $2.00 per unit (point C) .
D) $4.00 per unit (point D) .
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The market price for wallets is $20. Your technology is such that at your most efficient production point, the average total cost of producing a wallet is $2.50. Your manager runs into your office and shouts, "Boss!!! Average costs are rising!! Average costs are rising!!" To make a profit-maximizing decision, you should:
A) ask the manager about the average total cost.
B) immediately stop production.
C) completely ignore your manager.
D) ask the manager about the marginal cost.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 101 - 120 of 126
Related Exams