A) seek to maximize profits and output.
B) normally can purchase inputs at fixed prices.
C) employ technology, which is always fixed.
D) purchase inputs whose prices rise as output rises.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Many economists describe the 2007-2009 period in the United States as being a condition of a(n)
A) deflationary gap.
B) recessionary gap.
C) inflationary gap.
D) reflationary gap.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How are aggregate supply and stagflation related?
A) Stagflation usually causes an adverse shift in aggregate supply.
B) An adverse supply shift usually causes stagflation.
C) Stagflation only follows inflation, with no relation to aggregate supply.
D) There is no relationship between the two.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The reason why inflation reduces the value of the multiplier is that part of the change in demand is
A) absorbed by price changes.
B) saved rather than spent.
C) matched by changes in supply.
D) matched by changes in income.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the price level decreases, what will happen to the level of real GDP supplied?
A) It will usually decrease.
B) It will usually increase.
C) Nothing.
D) It will decrease at first and then increase.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An inflationary gap will exist when
A) aggregate demand grows more slowly than aggregate supply.
B) there is downward pressure on prices.
C) expenditures are not equal to aggregate demand.
D) equilibrium GDP is greater than full employment GDP.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An equilibrium point beyond a potential GDP is termed as
A) deflationary gap.
B) recessionary gap.
C) inflationary gap.
D) acceleration gap.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
One complication in the process of reducing inflation by creating recessions is that the price level
A) adjusts more quickly to recessionary gaps than to inflationary gaps.
B) does not apply as it does in inflationary gaps.
C) always rises.
D) rarely falls.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the usual response of firm to an increase in the price of what they sell?
A) An increase in output
B) An increase in hiring factors of production
C) An increase in the profit level of the firm
D) An increase in employment at the firm
E) All of these responses are correct.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The typical result of an adverse supply shock is
A) falling output accompanied by accelerating inflation.
B) falling output accompanied by decelerating inflation.
C) rising output accompanied by accelerating inflation.
D) rising output accompanied by decelerating inflation.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The only factor that can cause movement along the aggregate supply curve is the
A) labor force.
B) capital stock.
C) availability of resources.
D) price level.
E) All of these responses are correct.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to an old saying, when too much money is chasing too few goods, we have a(n)
A) recessionary gap.
B) inflationary gap.
C) full employment.
D) paradox of thrift.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The concept of aggregate supply refers to a
A) fixed number of output.
B) list of products demanded.
C) schedule of output.
D) schedule of production costs.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If aggregate quantity supplied exceeds aggregate quantity demanded, we can expect an unplanned
A) depletion of inventories, causing firms to raise prices.
B) depletion of inventories, causing firms to lower prices.
C) accumulation of inventories, causing firms to raise prices.
D) accumulation of inventories, causing firms to lower prices.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A period of stagflation is the normal aftermath of a period of
A) excess aggregate supply.
B) deficient aggregate demand.
C) excess aggregate demand.
D) high unemployment rates.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 10-5
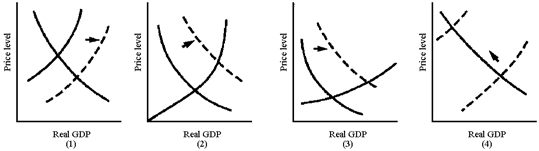 In Figure 10-5, which graph best illustrates the situation of an economy near full employment that experiences an increase in autonomous consumer spending?
In Figure 10-5, which graph best illustrates the situation of an economy near full employment that experiences an increase in autonomous consumer spending?
A) (1)
B) (2)
C) (3)
D) (4)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
As the slope of the aggregate supply curve increases, this indicates that
A) the economy is getting close to potential GDP.
B) the economy is reducing employment.
C) inflation will be less of a problem.
D) output is falling.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The existence of an inflationary gap should cause
A) wages to fall.
B) prices to fall.
C) unemployment to rise.
D) net exports to rise.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When money wages rise, the most significant effect on the aggregate supply curve is that it
A) shifts outward.
B) shifts inward.
C) becomes flatter.
D) becomes steeper.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
College graduates looking for jobs were less fortunate in 2010 than graduates in 2018.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 101 - 120 of 228
Related Exams