A) instead of near money.
B) to transact purchases they expect to make.
C) as insurance against unexpected needs.
D) to speculate in the stock market.
E) to take advantage of changes in interest rates.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The transmission mechanism is the effect of changes in monetary policy on prices, real GDP, and employment.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Exhibit 16-4 Aggregate demand and supply model 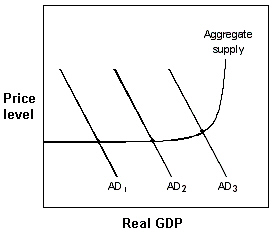 In Exhibit 16-4, which one of the following actions could the Fed use to shift the AD curve from AD1 to AD2?
In Exhibit 16-4, which one of the following actions could the Fed use to shift the AD curve from AD1 to AD2?
A) Raise the legal reserve requirement.
B) Raise the discount rate.
C) Lower the federal funds rate.
D) Buy government securities.
E) Print currency.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A decrease in the interest rate, other things being equal, causes a(n) :
A) upward movement along the demand curve for money.
B) downward movement along the demand curve for money.
C) rightward shift of the demand curve for money.
D) leftward shift of the demand curve for money.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The Keynesian viewpoint is that the investment curve is highly responsive to the changes in the rate of interest.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to monetarists, which of the following would be most important for the control of inflation?
A) a steady increase in federal expenditures
B) the imposition of price controls
C) keeping the growth rate of the money supply low and steady
D) a steady increase in the size of the budget deficit
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If people attempt to sell bonds because of excess money demand, then the interest rate will:
A) rise.
B) fall.
C) remain unchanged
D) react unpredictably.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Classical economists traditionally believed that:
A) there are three motives for demanding money.
B) a change in the money supply can affect real GDP.
C) the transactions demand for money influences the velocity of money.
D) the velocity of money is constant.
E) the economy does not always operate at full employment.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The monetarists totally reject the importance of changes in the money stock as determinants of changes in real GDP, the price level, and employment.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The precautionary demand for money is the demand for money:
A) for normal transactions purposes.
B) for normal investment purposes.
C) for special stock purchases.
D) to protect against inflation.
E) to cover unexpected events.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the Fed wants to raise interest rates, then it can use its open market operations to:
A) increase the money supply.
B) decrease the money supply.
C) increase money demand.
D) decrease money demand.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Other things being equal, the quantity of money that people wish to hold in currency and their checking accounts can be expected to:
A) increase as the interest rate increases.
B) decrease as the interest rate increases.
C) decrease as real GDP increases.
D) none of these.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The transmission mechanism is the effect of changes in monetary policy on the stock market.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The average number of times per year each dollar is used to transact an exchange is known as the:
A) liquidity of money.
B) velocity of money.
C) quantity theory of money.
D) equation of exchange
E) rapidity index
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Since classical economists believe that both V and Q are constants for an economy in short-run equilibrium, the equation of exchange becomes a theory in which:
A) the quantity of money explains prices.
B) the quantity of money explains velocity.
C) the quantity of money explains real GDP.
D) changes in M cause changes in V.
E) prices are never flexible
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The quantity theory of money of the Classical economists says that a change in the money supply will produce a:
A) proportional change in the price level.
B) greater than proportional change in the price level.
C) less than proportional change in the price level.
D) wide variation in the velocity of money.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The velocity of money is:
A) money supply divided by prices.
B) spending divided by output.
C) required monetary reserves divided by income.
D) GDP divided by the money supply.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose that the current money market equilibrium features an interest rate of 5 percent and a quantity of $2 trillion. If the Fed raises the discount rate, which of the following is most likely to be the new money market equilibrium?
A) An interest rate of 6 percent and a quantity of $1.5 trillion.
B) An interest rate of 5 percent and a quantity of $2 trillion.
C) An interest rate of 4 percent and a quantity of $2.5 trillion.
D) None of the above.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The downward slope of the demand for money curve is created by the:
A) transactions demand for money.
B) precautionary demand for money.
C) speculative demand for money.
D) all of these.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In a two-asset economy with money and T-bills, the quantity of money that people will want to hold, other things being equal, can be expected to:
A) increase as the real GDP interest rate increases.
B) decrease as the real GDP interest rate increases.
C) decrease as real GDP increases.
D) none of these.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 213
Related Exams