A) are always positive because the monopolist is a price-maker.
B) are usually negative because of government price regulation.
C) are always zero because consumers prefer to buy from competitive sellers.
D) may be positive or negative depending on market demand and cost conditions.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the long run, a pure monopolist will maximize profits by producing that output at which marginal cost is equal to
A) average total cost.
B) marginal revenue.
C) average variable cost.
D) average cost.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
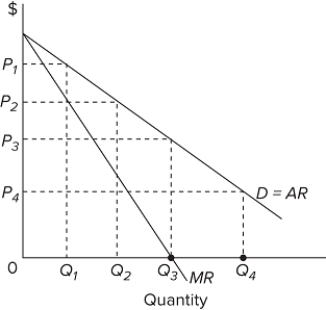 Refer to the graph, which shows the revenue curves for a monopolist. What price should be charged in order to maximize total revenue?
Refer to the graph, which shows the revenue curves for a monopolist. What price should be charged in order to maximize total revenue?
A) P₁
B) P₂
C) P₃
D) P₄
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A pure monopolist is selling six units at a price of $12. If the marginal revenue of the seventh unit is $5, then the
A) price of the seventh unit is $10.
B) price of the seventh unit is $11.
C) price of the seventh unit is greater than $12.
D) firm's demand curve is perfectly elastic.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Assume a pure monopolist is currently operating at a price-quantity combination on the inelastic segment of its demand curve. If the monopolist is seeking maximum profits, it should
A) retain its current price-quantity combination.
B) increase both price and quantity sold.
C) charge a lower price.
D) charge a higher price.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
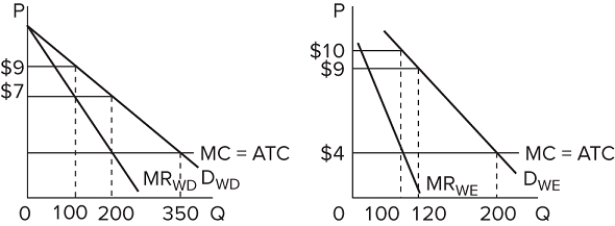 The graphs represent the demand for use of a local golf course for which there is no significant competition. (It has a local monopoly.) P denotes the price of a round of golf, and Q is the quantity of rounds "sold" each day. If the left graph represents the demand during weekdays and the right graph the weekend demand, this profit-maximizing golf course will earn how much economic profit over the course of a full seven-day week?
The graphs represent the demand for use of a local golf course for which there is no significant competition. (It has a local monopoly.) P denotes the price of a round of golf, and Q is the quantity of rounds "sold" each day. If the left graph represents the demand during weekdays and the right graph the weekend demand, this profit-maximizing golf course will earn how much economic profit over the course of a full seven-day week?
A) $4,200
B) $3,700
C) $3,400
D) $2,700
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When a firm is on the inelastic segment of its demand curve, it can
A) increase total revenue by reducing price.
B) decrease total costs by decreasing price.
C) increase profits by increasing price.
D) increase total revenue by more than the increase in total cost by increasing price.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
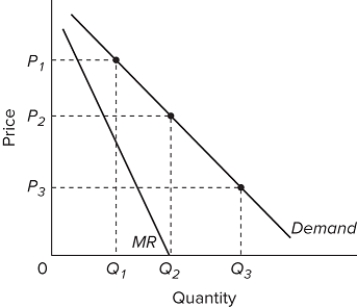 Refer to the graphs of D and MR for a monopolist. Which of the following statements is true?
Refer to the graphs of D and MR for a monopolist. Which of the following statements is true?
A) A price cut from P₁ to P₂ would lead to a decrease in the amount of dollars consumers spend on the product.
B) A price cut from P₁ to P₂ would lead to an increase in the amount of dollars consumers spend on the product.
C) A price cut from P₂ to P₃ would lead to no change in the amount of dollars consumers spend on the product.
D) A price cut from P₂ to P₃ would lead to an increase in the amount of dollars consumers spend on the product.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose that a monopolist calculates that at its present output level, marginal cost is $2.00 and marginal revenue is $3.00. The firm could increase profits by
A) increasing price and decreasing output.
B) decreasing price and increasing output.
C) decreasing price and leaving output unchanged.
D) decreasing output and leaving price unchanged.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Answer the question on the basis of the accompanying demand schedule. 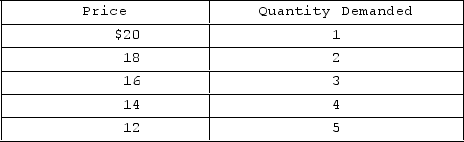 The marginal revenue obtained from selling the fourth unit of output is
The marginal revenue obtained from selling the fourth unit of output is
A) $2.
B) $16.
C) $8.
D) $14.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
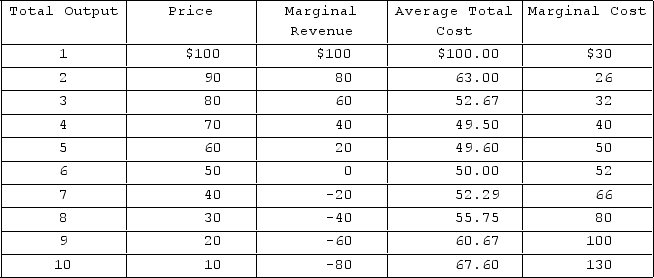 Refer to the data for a nondiscriminating monopolist. At its profit-maximizing output, this firm's total costs will be
Refer to the data for a nondiscriminating monopolist. At its profit-maximizing output, this firm's total costs will be
A) $300.
B) $248.
C) $198.
D) $126.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In many large U.S. cities, taxicab companies operate as near monopolies because of
A) patents.
B) licenses.
C) economies of scale.
D) strategic pricing.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
A patent for a new product or a new business process is typically granted for a hundred years.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
In a monopoly at equilibrium, price is greater than marginal cost.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Answer the question on the basis of the provided demand and cost data for a pure monopolist. 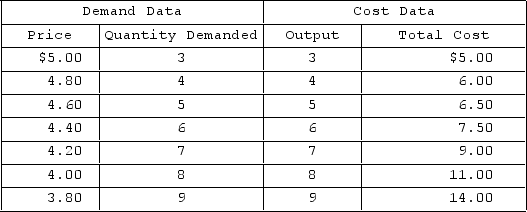 The profit-maximizing price for the monopolist will be
The profit-maximizing price for the monopolist will be
A) $4.60.
B) $4.40.
C) $4.20.
D) $4.00.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
"Big Data"
A) has completely eliminated the monopoly pricing power of online retailers.
B) is used by firms to price discriminate through personalized pricing.
C) is a significant barrier to entry to new Internet retailers.
D) makes it easier for government to regulate monopolistic industries.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The nondiscriminating pure monopolist must decrease price on all units of a product sold in order to sell more units. This explains why
A) there are barriers to entry in pure monopoly.
B) a monopoly has a perfectly elastic demand curve.
C) marginal revenue is less than average revenue.
D) total revenues are greater than total costs at the profit maximizing level of output.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
In a natural monopoly case, the socially optimal pricing policy rule will often result in negative economic profits for the firm.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the variable costs of a profit-maximizing pure monopolist decline, the firm should
A) produce more output and charge a higher price.
B) produce more output and charge a lower price.
C) reduce both output and price.
D) raise both output and price.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
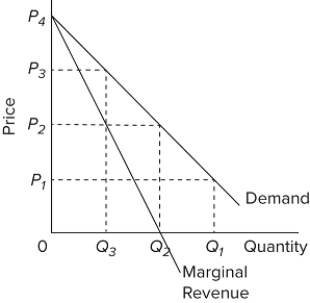 In the accompanying diagram, demand is relatively inelastic
In the accompanying diagram, demand is relatively inelastic
A) at price P₃.
B) at any price below P₂.
C) in the P₂ P₄ price range.
D) in the P₂ P₃ price range.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 407
Related Exams