A) greater or equal to one.
B) less than one.
C) equal to one.
D) impossible to determine.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
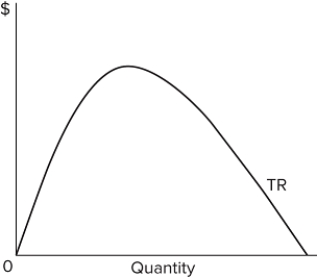 Refer to the graph, which shows a total revenue curve for a monopolist. If total revenue declines as output expands, demand is
Refer to the graph, which shows a total revenue curve for a monopolist. If total revenue declines as output expands, demand is
A) elastic.
B) inelastic.
C) perfectly inelastic.
D) perfectly elastic.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
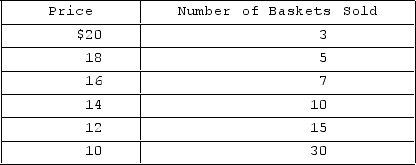 The table shows the demand schedule facing Nina, a monopolist selling baskets. What is the change in total revenue if she lowers the price from $20 to $18?
The table shows the demand schedule facing Nina, a monopolist selling baskets. What is the change in total revenue if she lowers the price from $20 to $18?
A) $10
B) $20
C) $30
D) $40
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
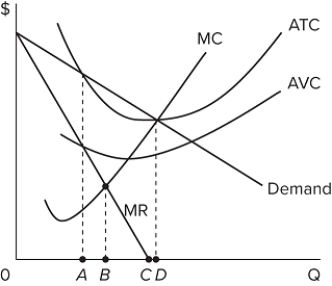 In the graph, what is the profit-maximizing level of output for this pure monopolist?
In the graph, what is the profit-maximizing level of output for this pure monopolist?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
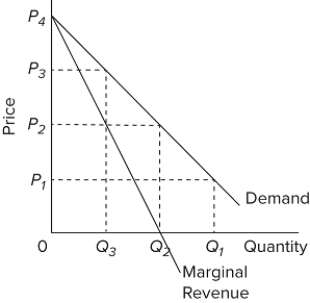 In the accompanying diagram, demand is relatively elastic
In the accompanying diagram, demand is relatively elastic
A) in the P₂ P₁ price range.
B) in the 0 P₁ price range.
C) in the P₂ P₄ price range.
D) only at price P₂.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Price discrimination occurs whenever a firm sells a good for two different prices.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
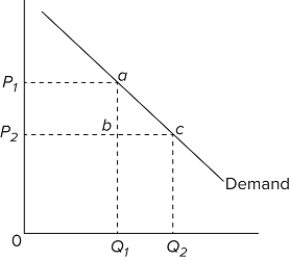 The quantitative difference between areas Q ₁ bcQ ₂ and P ₁ P ₂ ba in the diagram measures
The quantitative difference between areas Q ₁ bcQ ₂ and P ₁ P ₂ ba in the diagram measures
A) marginal cost.
B) total revenue.
C) marginal revenue.
D) average revenue.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Allocative inefficiency happens in a monopoly because at the profit-maximizing output level,
A) P > ATC.
B) P > MR.
C) P > MC.
D) P > AVC.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If you want to enjoy a Major League Baseball game at the stadium in St Louis, you must patronize the Cardinals. This makes the Cardinals organization a
A) purely competitive firm in St Louis.
B) monopoly firm in St Louis.
C) monopoly firm in Major League Baseball.
D) purely competitive firm in Major League Baseball.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which is not true of price discrimination?
A) Successful price discrimination requires that different segments of the market have different demand elasticities.
B) Successful price discrimination will provide the firm with more profit than if it does not discriminate.
C) Successful price discrimination implies that the producer can separate customers into easily identifiable groups.
D) Successful price discrimination will generally result in a lower level of output than would be the case under a single-price monopoly.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
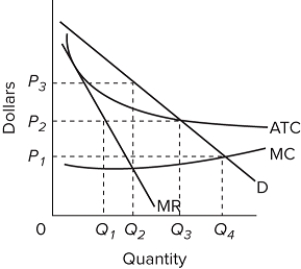 Refer to the diagram for a natural monopolist. If a regulatory commission were to set a maximum price of P3, the monopolist would
Refer to the diagram for a natural monopolist. If a regulatory commission were to set a maximum price of P3, the monopolist would
A) maximize profits.
B) increase output beyond the profit-maximizing level.
C) reduce output below the profit-maximizing level.
D) be unable to make a normal profit.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a nondiscriminating imperfectly competitive firm is selling its 100th unit of output for $35, its marginal revenue
A) may be either greater or less than $35.
B) will also be $35.
C) will be less than $35.
D) will be greater than $35.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
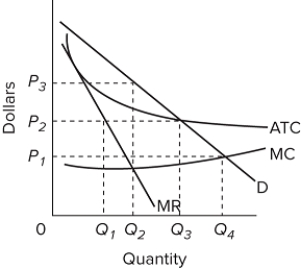 Refer to the diagram for a natural monopolist. If a regulatory commission set a maximum price of P ₁, the monopolist would produce output
Refer to the diagram for a natural monopolist. If a regulatory commission set a maximum price of P ₁, the monopolist would produce output
A) Q₂ and realize a normal profit.
B) Q₄ and realize a normal profit.
C) Q₃ and realize an economic profit.
D) Q₄ and realize a loss.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Under pure monopoly, a profit-maximizing firm will produce
A) in the inelastic range of its demand curve.
B) in the elastic range of its demand curve.
C) only where marginal costs are decreasing.
D) only where marginal revenue is increasing.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
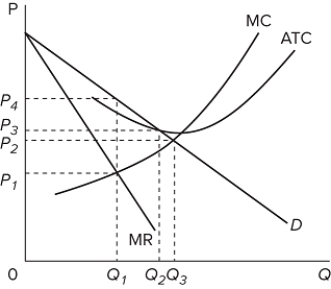 Refer to the graph for a pure monopoly. If the government regulated the monopoly and made the firm set a fair-return price, what price and quantity levels would we observe in the short run?
Refer to the graph for a pure monopoly. If the government regulated the monopoly and made the firm set a fair-return price, what price and quantity levels would we observe in the short run?
A) P₁ and Q₁
B) P₂ and Q₃
C) P₃ and Q₂
D) P₄ and Q₁
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
In order to maximize profits, the monopolist will produce the output level where MR = MC and charge a price equal to MR and MC.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
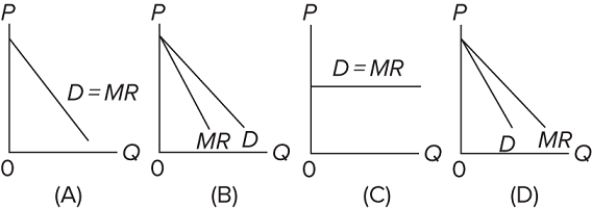 Which of the diagrams correctly portrays a nondiscriminating pure monopolist's demand (D) and marginal revenue (MR) curves?
Which of the diagrams correctly portrays a nondiscriminating pure monopolist's demand (D) and marginal revenue (MR) curves?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
One major barrier to entry under pure monopoly arises from
A) the availability of close substitutes for a product.
B) ownership of essential resources.
C) the price taking ability of the firm.
D) diseconomies of scale.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
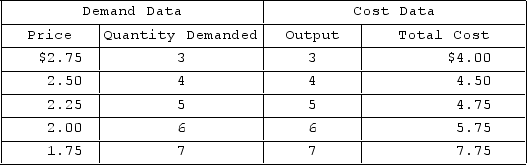 Answer the question on the basis of the demand and cost data for a pure monopolist. The profit-maximizing quantity of output for the monopolist will be
Answer the question on the basis of the demand and cost data for a pure monopolist. The profit-maximizing quantity of output for the monopolist will be
A) 4.
B) 6.
C) 5.
D) 7.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
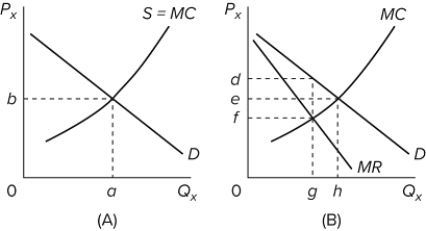 Refer to the diagrams. With the industry structures represented by diagram
Refer to the diagrams. With the industry structures represented by diagram
A) (A) , there will be only a normal profit in the long run, while in (B) an economic profit can persist.
B) (A) , price exceeds marginal cost, resulting in allocative inefficiency.
C) (B) , price equals marginal cost, resulting in allocative efficiency.
D) (B) , equilibrium price and quantity will be e and h, respectively.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 341 - 360 of 407
Related Exams