A) 90 percent.
B) 95 percent.
C) 100 percent.
D) indeterminate because we don't know which four firms are included.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Answer the question on the basis of the following demand and cost data for a specific firm. 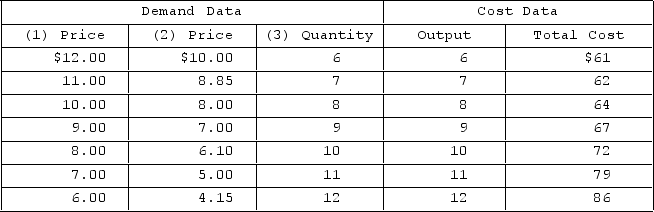 Suppose that entry into the industry changes this firm's demand schedule from columns (1) and (3) to columns (2) and (3) . Economic profit will
Suppose that entry into the industry changes this firm's demand schedule from columns (1) and (3) to columns (2) and (3) . Economic profit will
A) fall by $11.50.
B) fall to $8.
C) increase by $15.
D) decline to zero.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Firms in an industry will not earn long-run economic profits if
A) fixed costs are zero.
B) the number of firms in the industry is fixed.
C) there is free entry and exit of firms in the industry.
D) production costs for a given level of output are minimized.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which industry would be best characterized as monopolistically competitive?
A) smartphone manufacturing
B) Internet-search sites
C) web design consulting
D) business cloud-computing services
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The market situation of a monopolistic competitor is made more complex than our simple revenue-and-costs graphs would suggest, because the firm in reality juggles three decisions:
A) price, output quantity, and revenues.
B) revenue, costs, and profits.
C) advertising, resources, and product.
D) price, product, and advertising.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the long run, the economic profits for a monopolistically competitive firm will be
A) the same as the profits for a monopolist.
B) slightly less than the profits of a monopolist.
C) the same as the profits for a purely competitive firm.
D) slightly more than the profits of a purely competitive firm.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose the Herfindahl indexes for industries A, B, and C are 1,200, 5,000, and 7,500 respectively. These data imply that
A) market power is greatest in industry A.
B) market power is greatest in industry B.
C) market power is greatest in industry C.
D) industry A is more monopolistic than industry C.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A monopolistically competitive firm is operating at a short-run level of output where price is $30, average total cost is $27, marginal cost is $20, and marginal revenue is $25. In the short run this firm should
A) increase product price.
B) decrease the level of output.
C) not change the level of output.
D) increase the level of output.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Monopolistic competition resembles pure competition because
A) both industries emphasize nonprice competition.
B) in both instances firms will operate at the minimum point on their long-run average total cost curves.
C) both industries entail the production of differentiated products.
D) in both industries barriers to entry are either weak or nonexistent.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Monopolistically competitive firms
A) realize normal profits in the short run but losses in the long run.
B) incur persistent losses in both the short run and long run.
C) may realize either profits or losses in the short run but realize normal profits in the long run.
D) persistently realize economic profits in both the short run and long run.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Nonprice competition refers to
A) competition between products of different industries, for example, competition between aluminum and steel in the manufacture of automobile parts.
B) price increases by a firm that are ignored by its rivals.
C) advertising, product promotion, and changes in the real or perceived characteristics of a product.
D) reductions in production costs that are not reflected in price reductions.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
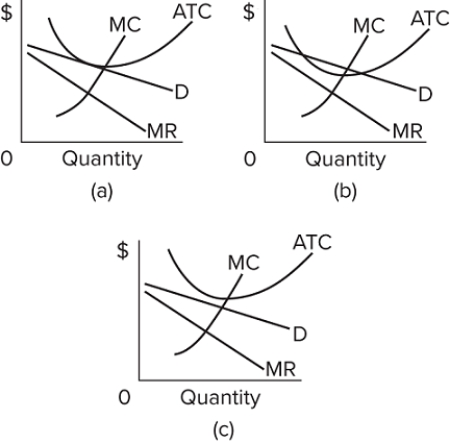 Refer to the diagrams, which pertain to monopolistically competitive firms. Long-run equilibrium is shown by
Refer to the diagrams, which pertain to monopolistically competitive firms. Long-run equilibrium is shown by
A) diagram a only.
B) diagram b only.
C) diagram c only.
D) none of these diagrams.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Answer the question based on the demand and cost schedules for a monopolistically competitive firm given in the table below. 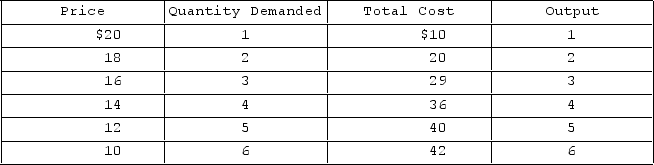 What price will this monopolistically competitive firm charge to maximize profits?
What price will this monopolistically competitive firm charge to maximize profits?
A) $18
B) $16
C) $12
D) $10
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is not true for a monopolistically competitive industry?
A) Firms tend to operate with excess capacity.
B) Each firm faces a downward-sloping demand curve.
C) These firms earn zero economic profits in the long run.
D) Firms operate at the lowest point of their ATC curves in the long run.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
We would expect the four-firm concentration ratio of the restaurant industry in a large metropolitan area to be about 0.80, or 80 percent, and higher.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The four-firm concentration ratio cannot have a value above 1.0, or 100 percent.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
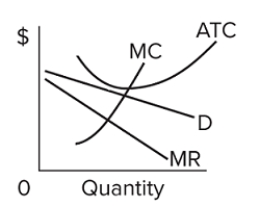 In short-run equilibrium, the monopolistically competitive firm shown will set its price
In short-run equilibrium, the monopolistically competitive firm shown will set its price
A) below ATC.
B) above ATC.
C) below MC.
D) below MR.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Answer the question on the basis of the following demand and cost data for a specific firm. 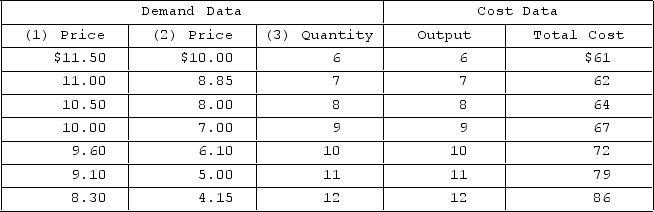 If columns (1) and (3) of the demand data shown are this firm's demand schedule, economic profit will be
If columns (1) and (3) of the demand data shown are this firm's demand schedule, economic profit will be
A) $72.
B) $24.
C) $23.
D) $21.1.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If you sum the squares of the market shares of each firm in an industry (as measured by percent of industry sales) , you are calculating the
A) four-firm concentration ratio.
B) Herfindahl index.
C) degree of collusion.
D) Lerner index.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Concentration ratios measure the
A) geographic location of the largest corporations in each industry.
B) degree to which product price exceeds marginal cost in various industries.
C) percentage of total industry sales accounted for by the largest firms in the industry.
D) number of firms in an industry.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 241 - 260 of 279
Related Exams