A) resource prices are a major determinant of money incomes.
B) resource prices allocate scarce resources among alternative uses.
C) resource prices, along with resource productivity, are important to firms in minimizing their costs.
D) of all these reasons.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The demand curve for labor would shift leftward as the result of
A) an increase in the price of the product labor is producing.
B) a decrease in the productivity of labor.
C) an increase in the price of labor.
D) a decrease in the price of capital, provided the output effect exceeds the substitution effect.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Employers will hire more units of a resource if the
A) price of the resource increases.
B) productivity of the resource increases.
C) price of the good being produced declines.
D) price of a complementary resource rises.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a firm is selling in an imperfectly competitive product market, then
A) average product will be less than marginal product for any number of workers hired.
B) the marginal products of successive workers must be sold at lower prices.
C) the marginal products of successive workers can be sold at higher prices.
D) the marginal products of successive workers can be sold at a constant price.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
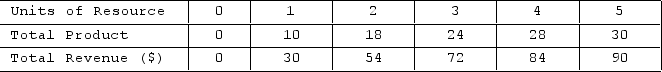 Refer to the table. The resource demand data indicate that the firm is
Refer to the table. The resource demand data indicate that the firm is
A) buying its resource in an imperfectly competitive market.
B) buying its resource in a perfectly competitive market.
C) selling its product in a perfectly competitive market.
D) selling its product in an imperfectly competitive market.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Assume a firm purchases resources a and b under purely competitive conditions and combines these resources to produce X. Product X is sold in a purely competitive market. The MPs of a and b are 6 and 3, respectively, and the prices of a and b are $12 and $6, respectively. If profit-maximizing equilibrium exists, the price of X will be
A) $1.
B) $0.5.
C) $2.
D) $5.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Hiring the least-costly combination of resources ensures that profits will be maximized.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the price of labor falls relative to the price of capital, and as a result the quantity of capital employed decreases, then it can be concluded that
A) the substitution effect is greater than the output effect.
B) the output effect is greater than the substitution effect.
C) the income effect is greater than the output effect.
D) labor cannot be easily substituted for capital.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The demand for telephone operators is expected by the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics to decline from 2016 to 2026, largely due to
A) "labor-saving" technological change.
B) a decline in the wages paid to this type of labor.
C) an increase in the cost per unit of this type of labor.
D) weakening demand for machine-sewn products.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A farmer who has fixed amounts of land and capital finds that total product is 24 for the first worker hired, 32 when two workers are hired, 37 when three are hired, and 40 when four are hired. The farmer's product sells for $3 per unit, and the wage rate is $13 per worker. What is the farmer's profit-maximizing output?
A) 20
B) 32
C) 40
D) 37
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When the elasticity coefficient for resource demand is less than one, resource demand is
A) inelastic.
B) elastic.
C) unit-elastic.
D) infinitely elastic.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A farmer who has fixed amounts of land and capital finds that total product is 24 for the first worker hired, 32 when two workers are hired, 37 when three are hired, and 40 when four are hired. The farmer's product sells for $3 per unit, and the wage rate is $13 per worker. How many workers should the farmer hire?
A) $1
B) $2
C) $4
D) $3
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
We say that the demand for labor is a derived demand because
A) labor is a necessary input in the production of every good or service.
B) we demand the product that labor helps produce rather than labor service per se.
C) the forces of supply and demand do not apply directly to labor markets.
D) labor is hired using the MRP = MRC rule.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
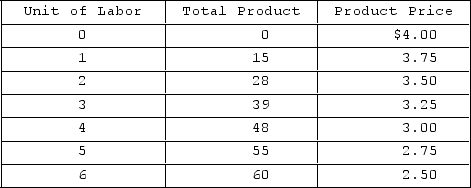 Refer to the table, which gives data for a firm that is hiring labor in a purely competitive market. If the wage rate is $56, how many workers will the firm choose to employ?
Refer to the table, which gives data for a firm that is hiring labor in a purely competitive market. If the wage rate is $56, how many workers will the firm choose to employ?
A) 3
B) 2
C) 0
D) 1
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose there is a decline in the demand for the product labor is producing. Furthermore, the price of capital, which is complementary to labor, increases. Thus, the demand for labor
A) will increase.
B) will decrease.
C) may either increase or decrease.
D) will not change.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The marginal revenue product of an input in a competitive market decreases as a firm increases the quantity of the input employed because of the
A) law of diminishing returns.
B) law of diminishing marginal utility.
C) homogeneity of the product.
D) free mobility of resources.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose the demand for strawberries rises sharply, resulting in an increased price for strawberries. As it relates to strawberry pickers, we could expect the
A) MRP curve to shift to the right.
B) MRP curve to shift to the left.
C) MRC curve to shift downward.
D) MP curve to shift downward.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which would result in a decrease in the elasticity of demand for a particular resource?
A) a decrease in the rate at which the marginal product of that resource declines
B) an increase in the elasticity of demand for the product that the resource helps to produce
C) a decrease in the percentage of the firm's total costs accounted for by the resource
D) an increase in the substitutability of other resources for the particular resource
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A major criticism of the marginal productivity theory of income distribution is that
A) the demand for labor resources is price inelastic.
B) achieving equality in incomes will take time.
C) imperfectly competitive firms are only interested in profit maximization.
D) property resources like land are unevenly distributed, which leads to income inequality.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose a firm is hiring resources l and m under purely competitive conditions to produce product Y, which sells for $2 in a purely competitive market. The prices of l and m are $10 and $4, respectively. In equilibrium, the MPs of l and m, respectively, are
A) 1 and 1.
B) 2 and 5.
C) 10 and 4.
D) 5 and 2.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 141 - 160 of 359
Related Exams