A) He determined the proper motion of globular clusters in the outer disk of the galaxy.
B) He found the distances to individual variables free floating in the halo.
C) He found the distances to open clusters found throughout the disk of the galaxy.
D) He found the distances to globular clusters distributed about the center of the galaxy.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Not Answered
Why are Cepheid variable stars important in our study of the Milky Way galaxy?
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The period-luminosity relation is useful in determining
A) the mass of a star for which the distance is known.
B) the temperature of a star for which we know the luminosity.
C) the radius of the bulge of our galaxy.
D) the distance to globular clusters that contain Cepheid variables.
E) the mass of the Milky Way galaxy.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What behavior do galactic rotation curves exhibit to suggest the existence of dark matter in an extended halo?
A) Small velocities are seen at large distances from the galactic center.
B) Small velocities are seen at distances close to the galactic center.
C) Large velocities are seen at large distances from the galactic center.
D) Large velocities are seen at distances close to the galactic center.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Not Answered
Why are all spiral tracers young?
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
CO observations of the galaxy reveal
A) the location of dense neutral hydrogen clouds.
B) the location of population II stars.
C) the location of population I stars.
D) the location of the galactic corona.
E) the location of giant molecular clouds.
Correct Answer

verified
E
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How does the traditional theory of the formation of the galaxy explain the origin of globular clusters?
A) They formed in the disk and later were ejected to the halo.
B) They formed in other galaxies and were captured by close interactions.
C) They build over time from the collision of stars in the halo.
D) They formed early on during the free-fall collapse of the proto-galactic material.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The nuclear bulge of our galaxy
A) contains stars that are primarily population I stars.
B) is primarily composed of gas and dust.
C) contains stars primarily associated with the spherical component of our galaxy.
D) contains stars primarily associated with the disk component of our galaxy.
E) a, b and d
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Who first calibrated the Cepheid variable stars for use in determining distance?
A) Henrietta Leavitt
B) Edwin Hubble
C) John Glenn
D) Carl Sagan
E) Harlow Shapley
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The center of our galaxy lies in the direction of (but far beyond) the stars in the constellation of
A) Ursa Minor.
B) Ursa Major.
C) Sagittarius.
D) Orion.
E) Monoceros.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Old stars are poor in heavy atoms because there were very few previous generations of stars before the old stars formed.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
____ of the Milky Way contains mostly old (population II) stars and globular clusters.
A) The disk component
B) The spherical halo component
C) The hydrogen gas in the disk
D) The spiral arms
E) Sgr A *
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The density wave theory explains spurs and branches along the spiral arms.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The traditional theory states that the galaxy formed
A) as a large spherical cloud of gas that was rotating very slowly.
B) from a large cloud of material that broke off a larger galaxy.
C) from material that had been ejected in the violent explosion of a dying galaxy.
D) as a result of mergers between several smaller groups of gas, dust, and stars.
E) as two massive galaxies collided.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
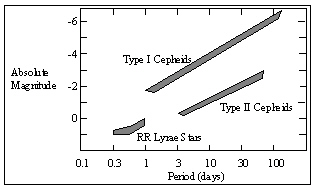 Refer to the figure. A Type I Cepheid has been located in an open cluster. The period of the Cepheid variable is 30 days and the variables apparent visual magnitude m is 10. First, use 12-1 to estimate the absolute visual magnitude, M . Calculate the distance to this open cluster? Hint: dpc = 10(m - M + 5) /5 using a scientific calculator.
Refer to the figure. A Type I Cepheid has been located in an open cluster. The period of the Cepheid variable is 30 days and the variables apparent visual magnitude m is 10. First, use 12-1 to estimate the absolute visual magnitude, M . Calculate the distance to this open cluster? Hint: dpc = 10(m - M + 5) /5 using a scientific calculator.
A) 100 pc
B) 10,000 pc
C) 20 pc
D) 300 pc
E) 2500 pc
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
____ in other galaxies should contain luminous O and B stars if they are like the Milky Way.
A) The halos
B) The bulges
C) The spiral arms
D) The globular clusters
E) The coronas
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Sgr A* is believed to be the center of the Milky Way galaxy because I. It lies in the general direction of the center of the galaxy based on observations of globular clusters in the plane of the Milky Way. II. Long wavelength dust penetrating images show it to be a region crowded with stars III. Orbits of stars around it indicate a mass several million times that of the Sun within a volume a few light hours in size IV. Radio observations show it is a concentrated source at the center of swirling clouds of gas
A) I II only
B) II III only
C) I, IV only
D) II IV only
E) All of I, II, III, IV
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The orbits of population I stars I. are confined to disk of the galaxy. II. are very elliptical. III. are nearly circular. IV. are randomly inclined to the disk of the galaxy.
A) I
B) IV
C) I, IV
D) II IV
E) I,III
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Not Answered
Discuss how Harlow Shapley determined the structure of the Milky Way galaxy from his study of globular clusters.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Not Answered
Compare and contrast the properties of disk and halo stars.
Correct Answer

verified
Answer not provided.
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 70
Related Exams