A) a decline in GDP and rising unemployment.
B) inflation.
C) an increase in consumption.
D) an offsetting increase in planned investment.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
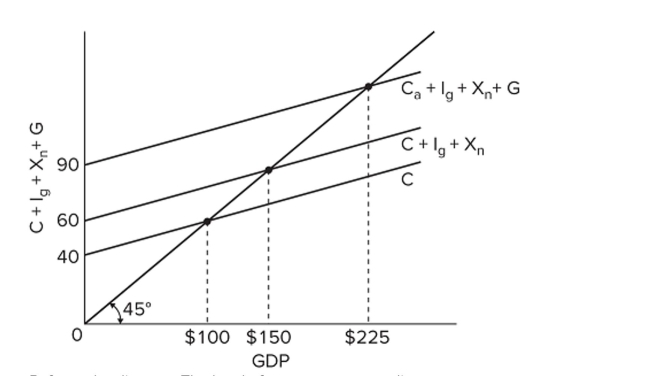 Refer to the diagram. The level of government spending
Refer to the diagram. The level of government spending
A) is equal to tax collections at each level of GDP.
B) is the same at all levels of GDP.
C) varies inversely with the level of GDP.
D) varies directly with the level of GDP.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is incorrect?
A) Given the economy's MPS, a $15 billion reduction in government spending will reduce the equilibrium GDP by more than would a $15 billion increase in taxes.
B) Other things unchanged, a tax reduction of $10 billion will increase the equilibrium GDP by $25 billion when the MPS is 0.4.
C) If the MPC is 0.8 and GDP has declined by $40 billion, this was caused by a decline in aggregate expenditures of $8 billion.
D) A government surplus is anti-inflationary; a government deficit is expansionary.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Refer to the tables of information for a private closed economy. If the real interest rate is 9 percent, the equilibrium GDP will be
A) $600.
B) $500.
C) $400.
D) $300.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Other things equal, an increase in an economy's exports will
A) lower the marginal propensity to import.
B) have no effect on domestic GDP because imports will change by an offsetting amount.
C) decrease its domestic aggregate expenditures and therefore decrease its equilibrium GDP.
D) increase its domestic aggregate expenditures and therefore increase its equilibrium GDP.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the aggregate expenditures model, it is assumed that investment
A) automatically changes in response to changes in real GDP.
B) changes by less in percentage terms than changes in real GDP.
C) does not respond to changes in interest rates.
D) does not change when real GDP changes.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 121 - 126 of 126
Related Exams