A) 1568.429.
B) 1.4853.
C) 0.1689.
D) 7.8147.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In a χ2 test for homogeneity, the test statistic is 18.6732 and the critical value is 12.8325.What is the proper conclusion for the test?
A) The sample provides sufficient evidence to state that the distribution of the categorical variable in question is similar for all populations considered.
B) The sample does not provide sufficient evidence to state that the distribution of the categorical variable in question is similar for all populations considered.
C) The sample does not provide sufficient evidence to state that the distribution of the categorical variable in question is different for at least one of the populations considered.
D) The sample provides sufficient evidence to state that the distribution of the categorical variable in question is different for at least one of the populations considered.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A chi-square test for homogeneity applies to:
A) data from a single random sample where two variables are recorded on each sample.
B) data from samples from two or more populations where each sample is classified by values of a single categorical variable.
C) data from a single random sample where three or more variables are recorded on each sample.
D) data from samples from two or more populations where each sample is classified by values of two categorical variables.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In a test of homogeneity of proportions, if the null hypothesis is not rejected, then:
A) we have proven homogeneity.
B) we have proven nonhomogeneity.
C) we would decide that the category proportions for at least one population are different from the rest.
D) we have insufficient evidence to reject homogeneity.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If two categorical observations are made on the same individual or object, the data set is said to be:
A) binumeral.
B) bivariate.
C) bifurcated.
D) bicategorical.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In a χ2 goodness-of-fit test, the decision to reject H₀ can be interpreted as:
A) all of the proportions stated in the null hypothesis appear to be incorrect.
B) most of the proportions stated in the null hypothesis appear to be incorrect.
C) none of the proportions stated in the null hypothesis appears to be incorrect.
D) at least one of the proportions stated in the null hypothesis appears to be incorrect.
Correct Answer

verified
D
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In a χ2 goodness-of-fit test, 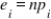 is:
is:
A) the exponentially distributed random variable.
B) the expected value for the ith cell assuming H₀ is false.
C) the expected value for the ith cell assuming H₀ is true.
D) the expectation for the average value function expressed as a product of sample size and proportion.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A chi-square test for independence is appropriate for:
A) data from a single random sample where two variables are recorded on each sample.
B) data from samples from two or more populations where each sample is classified by values of a categorical variable.
C) data from a single random sample where three or more variables are recorded on each sample.
D) data from samples from two or more populations where each sample is classified by values of two categorical variables.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A marketing research firm runs a well-designed survey to see if the color on the face of a golf club affects a golfer's preference.Golfers can choose one of three club face colors: gold (G) , black (B) , and tan (T) .When 120 golfers are randomly sampled and asked to indicate their preference, 25 prefer the gold, 55 prefer the black, and 40 prefer the tan.The firm reports that it did a chi-square goodness-of-fit test on the data and decided there is enough statistical evidence, at 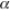 = 0.01, to reject the idea that color does not matter to golfers.As the head of production for the golf club manufacturer that commissioned the study, you might:
= 0.01, to reject the idea that color does not matter to golfers.As the head of production for the golf club manufacturer that commissioned the study, you might:
A) disregard the survey and continue to produce equal numbers of each color of club because the sample was too small.
B) ask your sales people why they had not reported this trend before now.
C) begin to change the product mix to reflect the survey, checking on sales of each type of club as you go.
D) immediately change all production to reflect the survey because of the high level of certainty at a 0.01 level.
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In a chi-square test for homogeneity, the variables under consideration are:
A) the different populations and a single categorical variable.
B) the different populations and two or more categorical variables.
C) two or more categorical variables from the same population.
D) one categorical variable from a single population.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A chi-square test for independence of two categorical variables is appropriate if:
A) ![]() .
.
B) ![]() for all i and all j.
for all i and all j.
C) ![]() for all i and all j.
for all i and all j.
D) ![]() and
and ![]() for all i and all j.
for all i and all j.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In a two-way frequency table, suppose one cell has a row total of 200 and a column total of 75, with a total sample size of 1000.What would that cell's expected count be?
A) 25
B) 20
C) 15
D) 10
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A chi-square test for homogeneity can support a conclusion that:
A) two variables are somehow dependent.
B) two variables are linearly dependent.
C) the distribution of a single categorical variable is similar for two or more disparate populations.
D) the distribution of two categorical variables is similar for two or more disparate populations.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In a goodness-of-fit test with 4 degrees of freedom, the chi-square test statistic is 10.25.Which of the following is true about the p-value?
A) p < 0.025
B) 0.025 < p < 0.05
C) 0.05 < p < 0.10
D) 0.1 < p < 0.2
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A chi-square test of independence for a two-way frequency table with rows and columns results in a test statistic of 20.18.What can you conclude about the p-value for this test?
A) p < 0.025
B) 0.025 < p < 0.05
C) 0.05 < p < 0.10
D) p > 0.10
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Psychologists conduct a study to see if right-handed people have a greater tendency to turn right.In the study, 220 right-handed people are sent down an unfamiliar hallway that offers the possibility of turning left, turning right, or continuing straight.They are told that each direction will take them to the desired destination.It is postulated that right-handed people will turn right 75% of the time, turn left 5% of the time, and go straight 20% of the time.In the experiment, 165 of the people turn right, 11 turn left, and 44 go straight.Conduct a χ2 goodness-of-fit test to see if the data provide sufficient evidence to refute the postulated percentages.Select the appropriate critical value (CV) , test statistic (TS) , and decision.(Use α = 0.05.)
A) CV = 5.9915, TS = 0.00, fail to reject H₀; handedness does not seem to affect which way people turn
B) CV = 5.9915, TS = 353.1, reject H₀; handedness does seem to affect which way people turn
C) CV = 7.8147, TS = 353.1, reject H₀; handedness does seem to affect which way people turn
D) CV = 5.9915, TS = 1.225, fail to reject H₀; handedness does not seem to affect which way people turn
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In a goodness-of-fit test, one sample showed that the observed frequency and the expected frequency eiwere quite different for each cell.We can conclude that:
A) the null hypothesis is likely not true.
B) the null hypothesis is likely true.
C) the alternative hypothesis is likely true.
D) the chi-square distribution is likely invalid in this situation.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In a chi-square goodness-of-fit test, what does the following mathematical statement yield? 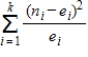
 where
where 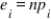 .
.
A) the critical value
B) the test statistic
C) the distribution center
D) the expected value
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The target grade distribution for a particular course is 10% A, 30% B, 40% C, 15% D, 5% F.Students complain that a particular professor who teaches this course grades "too hard." The present students survey 250 former students of this professor's class and then do a χ2 goodness-of-fit test to see if the data provide sufficient evidence to support their complaint.They find a critical value of 14.7 and a test statistic of 9.8, with α = 0.10.What is the take-away conclusion from this survey?
A) The professor's grades do not conform to the target.
B) The professor's grades conform to the target.
C) There is not sufficient statistical evidence to reject the idea that the professor's grades conform to the target.
D) There is sufficient statistical evidence to reject the idea that the professor's grades conform to the target.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A two-way frequency table:
A) classifies data with respect to two categorical variables.
B) divides the outcomes of each variable into two or more categories.
C) shows the frequencies for all possible combinations of categories.
D) All of the above.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 23
Related Exams