A) 5.23 years
B) 4.86 years
C) 4.00 years
D) 6.12 years
E) 4.35 years
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The post-audit two main purposes are to improve forecasts and to improve operations.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An investment project has an initial cost, and then generates inflows of R50 a year for the next five years.The project has a payback period of 3.6 years.What is the project's internal rate of return?
A) 11.18%
B) 12.05%
C) 13.47%
D) 14.66%
E) 15.89%
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Tara is evaluating two mutually exclusive capital budgeting projects that have the following characteristics: 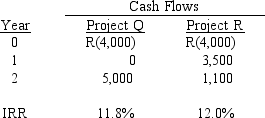 If the firm's required rate of return (r) is 10 percent, which project should be purchased?
If the firm's required rate of return (r) is 10 percent, which project should be purchased?
A) Both projects should be purchased, because the IRRs for both projects exceed the firm's required rate of return.
B) Neither project should be accepted, because the IRRs for both projects exceed the firm's required rate of return.
C) Project Q should be accepted, because its net present value (NPV) is higher than Project R's NPV.
D) Project R should be accepted, because its net present value (NPV) is higher than Project Q's NPV.
E) None of the above is a correct answer.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Michigan Mattress Company is considering the purchase of land and the construction of a new plant.The land, which would be bought immediately (at t = 0) , has a cost of R100,000 and the building, which would be erected at the end of the first year (t = 1) , would cost R500,000.It is estimated that the firm's after-tax cash flow will be increased by R100,000 starting at the end of the second year, and that this incremental flow would increase at a 10 percent rate annually over the next 10 years.What is the approximate payback period?
A) 2 years
B) 4 years
C) 6 years
D) 8 years
E) 10 years
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is correct?
A) Because discounted payback takes account of the required rate of return, a project's discounted payback is normally shorter than its regular payback.
B) The NPV and IRR methods use the same basic equation, but in the NPV method the discount rate is specified and the equation is solved for NPV, while in the IRR method the NPV is set equal to zero and the discount rate is found.
C) If the required rate of return is less than the crossover rate for two mutually exclusive projects' NPV profiles, a NPV/IRR conflict will not occur.
D) If you are choosing between two projects which have the same life, and if their NPV profiles cross, then the smaller project will probably be the one with the steeper NPV profile.
E) If the required rate of return is relatively high, this will favor larger, longer-term projects over smaller, shorter-term alternatives because it is good to earn high rates on larger amounts over longer periods.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The present value of the expected net cash inflows for a project will most likely exceed the present value of the expected net profit after tax for the same project because
A) Income is reduced by taxes paid, but cash flow is not.
B) There is a greater probability of realising the projected cash flow than the forecasted income.
C) Income is reduced by dividends paid, but cash flow is not.
D) Income is reduced by depreciation charges, but cash flow is not.
E) Cash flow reflects any change in net working capital, but sales do not.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Given the following net cash flows, determine the IRR of the project: 
A) 36%
B) 32%
C) 28%
D) 24%
E) 20%
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The internal rate of return is that discount rate which equates the present value of the cash outflows (or costs) with the present value of the cash inflows.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
When considering two mutually exclusive projects, the financial manager should always select that project whose internal rate of return is the highest provided the projects have the same initial cost.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Small businesses probably make less use of the DCF capital budgeting techniques than large businesses.This may reflect a lack of knowledge on the part of small firms' managers, but it may also reflect a rational conclusion that the costs of using DCF analysis outweigh the benefits of these methods for those firms.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
International Transport Company is considering building a new facility in Johannesburg.If the company goes ahead with the project, it will spend R2 million immediately (at t = 0) and another R2 million at the end of Year 1(t = 1) .It will then receive net cash flows of R1 million at the end of Years 2-5, and it expects to sell the property for R2 million at the end of Year 6.The company's required rate of return is 12 percent, and it uses the modified IRR criterion for capital budgeting decisions.Which of the following statements is most correct?
A) The project should be rejected because the modified IRR is less than the regular IRR.
B) The project should be accepted because the modified IRR is greater than the required rate of return.
C) The regular IRR is less than the required rate of return.Under this condition, the modified IRR will also be less than the regular IRR.
D) If the regular IRR is less than the required rate of return, then the modified IRR will be greater than the regular IRR.
E) Given the data in the problem, the NPV is negative.This demonstrates that the modified IRR criterion is not always a valid decision method for projects such as this one.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Your assistant has just completed an analysis of two mutually exclusive projects.You must now take her report to a board of directors meeting and present the alternatives for the board's consideration.To help you with your presentation, your assistant also constructed a graph with NPV profiles for the two projects.However, she forgot to label the profiles, so you do not know which line applies to which project.Of the following statements regarding the profiles, which one is most reasonable?
A) If the two projects have the same investment cost, and if their NPV profiles cross once in the upper right quadrant, at a discount rate of 40 percent, this suggests that a NPV versus IRR conflict is not likely to exist.
B) If the two projects' NPV profiles cross once, in the upper left quadrant, at a discount rate of minus 10 percent, then there will probably not be a NPV versus IRR conflict, irrespective of the relative sizes of the two projects, in any meaningful, practical sense (that is, a conflict which will affect the actual investment decision) .
C) If one of the projects has a NPV profile which crosses the X-axis twice, hence the project appears to have two IRRs, your assistant must have made a mistake.
D) Whenever a conflict between NPV and IRR exist, then, if the two projects have the same initial cost, the one with the steeper NPV profile probably has less rapid cash flows.However, if they have identical cash flow patterns, then the one with the steeper profile probably has the lower initial cost.
E) If the two projects both have a single outlay at t = 0, followed by a series of positive cash inflows, and if their NPV profiles cross in the lower left quadrant, then one of the projects should be accepted, and both would be accepted if they were not mutually exclusive.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Beyond some point, a further increase in the size of the firm's total capital budget may lead to a decrease in the NPVs of all the investments being considered.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is correct?
A) In general, the NPVs of riskier cash flows should be found using relatively high discount rates.However, if a cash flow is negative, it should be evaluated using a low discount rate.
B) If a project has only costs (no revenues) as would certain environmental projects, then the project is likely to have two regular IRRs.
C) If the NPV and IRR methods give conflicting rankings for two mutually exclusive projects, the payback period should be used to choose the project that should be purchased.
D) It is better to use the NPV method to evaluate independent projects, but for mutually exclusive projects, especially if projects vary greatly in size, the IRR method is better.
E) None of the above is a correct statement.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The main reason that the NPV method is regarded as being conceptually superior to IRR method for evaluating mutually exclusive investments is that multiple IRRs may exist.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A college intern working at Anderson Paints evaluated potential investments-that is, capital budgeting projects-using the firm's average required rate of return (WACC) , and he produced the following report for the capital budgeting manager: 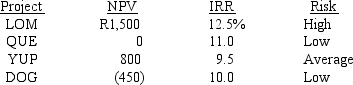 The capital budgeting manager usually considers the risks associated with capital budgeting projects before making her final decision.If a project has a risk that is different from average, she adjusts the average required rate of return by adding or subtracting 2 percentage points.If the four projected listed above are independent, which one(s) should the capital budgeting manager recommend be purchased?
The capital budgeting manager usually considers the risks associated with capital budgeting projects before making her final decision.If a project has a risk that is different from average, she adjusts the average required rate of return by adding or subtracting 2 percentage points.If the four projected listed above are independent, which one(s) should the capital budgeting manager recommend be purchased?
A) Project LOM only, because it has both the highest NPV and the higher IRR.
B) Projects LOM, QUE, and YUP, because they all have positive NPVs and their IRRs.
C) Projects DOG and QUE, because their IRRs are greater than their risk-adjusted discount the projects returns are higher than the rates of return that capital budgeting manager uses to evaluate them.
D) Projects QUE, YUP, and DOG, because their IRRs are greater than their risk-adjusted discount rates-that is, the projects returns are higher than the rates of return that capital budgeting manager uses to evaluate them.
E) There is not enough information to answer this question, because the firm's average required rate of return cannot be determined.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Los Angeles Lumber Company (LALC) is considering a project with a cost of R1,000 at t = 0 and inflows of R300 at the end of Years 1-5.LALC's cost of capital is 10 percent.What is the project's modified IRR (MIRR) ?
A) 10.0%
B) 12.9%
C) 15.2%
D) 18.3%
E) 20.7%
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Your company is choosing between following non-repeatable, equally risky, mutually exclusive projects with the cash flows shown below.Your required rate of return is 10 percent.How much value will your firm sacrifice if it selects the project with the higher IRR? 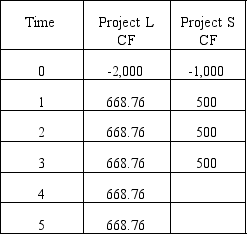
A) R243.43
B) R291.70
C) R332.50
D) R481.15
E) R535.13
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is correct?
A) One can find the "cross-over rate," or the discount rate at which two normal projects have the same NPV, by finding the IRR of the differences in the projects' yearly cash flows.
B) If you calculate a project's MIRR and find it to be the same as the regular IRR, you can be sure you made a mistake.
C) If a project's IRR is less than its required rate of return, then the discounted payback period will be less than the regular payback period.
D) If a project has a cash outflow at t = 0 followed by a single cash inflow at t = 10, then the MIRR will be less than the regular IRR.
E) If a project has a cash outflow at t = 0 followed by a single cash inflow at t = 10, then the MIRR will be greater than the regular IRR.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 94
Related Exams