A) short run; full employment level of output
B) long run; potential output
C) short run; market gluts
D) short run; money supply
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following groups of economists perceive the economy as essentially stable and self-correcting?
A) Keynesians, monetarists, and classical economists
B) Classical economists, monetarists, and new classical economists.
C) Monetarists, classical economists, and socialists
D) Classical economists, Keynesians, monetarists, and new classical economists.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
New classical economics contends that policy activism is
A) not warranted, because we don't know enough about the workings of the economy to stabilize it.
B) not warranted; the public defeats discretionary policies because everyone expects them, and therefore, their effectiveness is thwarted.
C) warranted, because discretionary policies have a strong effect on real output.
D) warranted, because expectations are rational only in the short run.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Prior to the Great Depression of the 1930s, macroeconomics was dominated by
A) Keynesian economics.
B) monetarism.
C) classical economics.
D) supply-side economics.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is true about classical economists?
A) They represent a large and cohesive group of economists who agreed with David Ricardo concerning wage and price flexibility in both the short run and the long run.
B) They may have shared some ideas in common, but their views were far from uniform.
C) They did not believe in the neutrality of money.
D) Their theories shed little insight on the economy today because modern issues and concerns are so different from those described in their earlier writings.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In developing his macroeconomic theory, Keynes
A) focused primarily on how potential GDP can change over time.
B) focused on how fiscal policy can change potential output.
C) was concerned with output gaps and how they could be eliminated.
D) was primarily concerned with the supply-side of the economy and how producer behavior led to output gaps.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following to answer questions
Exhibit: Economic Adjustments 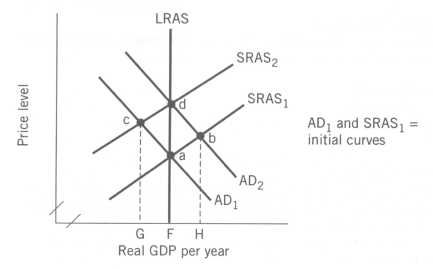 -(Exhibit: Economic Adjustments)
Suppose the economy is at point c.A Keynesian economist would advocate
-(Exhibit: Economic Adjustments)
Suppose the economy is at point c.A Keynesian economist would advocate
A) allowing the economy's self-correcting mechanism to move the economy to point a.
B) pursuing expansionary fiscal policies to move the economy to point a.
C) pursuing expansionary fiscal policies to move the economy to point b.
D) pursuing expansionary fiscal policies to move the economy to point d.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is true about new Keynesian economics? I.It incorporates monetarist ideas about the importance of monetary policy. II.It incorporates new classical ideas about the importance of aggregate supply. III.It includes a greater use of microeconomic analysis in macroeconomic analysis than Keynesian economics. IV.Unlike Keynesian economics, it is opposed to active stabilization policies.
A) I and III only
B) II and III only
C) I, II, and III only
D) I, II, III, and IV
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Writing in 1752, David Hume's essay, "Of Money,"
A) showed that changes in the money supply were unrelated to short-run fluctuations in output.
B) suggested that an increase in the money supply would be favorable to industry in the long-run.
C) echoed John Maynard Keynes' view that sticky prices would lead to short-run deviations of output from the level of potential real GDP.
D) was unable to unravel the nature and role of money in the economy because he ignored sticky prices.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
During the 1960s, Keynesian economic policies led to lower unemployment rates and higher prices.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The experience of the Great Depression led to the widespread acceptance of classical economics.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to the monetarists, after an initial increase in aggregate demand,
A) short-run aggregate supply curve will tend to shift leftward, reflecting the effect of higher wages adjusting in the long run.
B) short-run aggregate supply curve will tend to shift leftward, reflecting the effect of lower wages adjusting in the long run.
C) aggregate demand curve will tend to shift rightward, reflecting the effect of income adjusting in the long run.
D) aggregate demand curve will tend to shift lower, reflecting the effect of price level adjusting in the long run.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A policy implication of Keynesian economics is that
A) full employment will always be maintained.
B) countercyclical policies have no effect on the economy.
C) constant growth of the money supply is better than discretionary policies.
D) countercyclical monetary and fiscal policies can be used to achieve full employment.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following to answer questions
Exhibit: Economic Adjustments  -(Exhibit: Economic Adjustments)
Suppose the economy is at point c.A classical economist would advocate
-(Exhibit: Economic Adjustments)
Suppose the economy is at point c.A classical economist would advocate
A) allowing the economy's self-correcting mechanism to move the economy to point a.
B) pursuing expansionary fiscal policies to move the economy to point a.
C) pursuing expansionary fiscal policies to move the economy to point b.
D) pursuing expansionary fiscal policies to move the economy to point d.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
John Maynard Keynes argued that _______
A) flexibility in wages and prices could block adjustments to full employment.
B) stickiness in wages and prices could block adjustments to full employment.
C) wage and price rigidities were caused by producer and consumer expectations about future prices.
D) wage and price rigidities could be eliminated by government wage and price setting.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose the economy is initially in long-run equilibrium.Now suppose oil prices rise sharply and at the same time, policymakers pursue expansionary monetary and fiscal policies.Which of the following will occur as a result of these two events, given that supply-side effects dominate demand-side effects?
A) The price level will necessarily rise but the effect on output is indeterminate.
B) Real GDP must necessarily fall but the effect on the price level is indeterminate.
C) The price level and real GDP must rise.
D) The price level must rise and real GDP must fall.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the initial stages of the Great Depression, fiscal authorities responded to the decline in Output by
A) increasing government purchases to stimulate aggregate demand.
B) raising taxes to increase government revenue.
C) lowering taxes to encourage spending.
D) subsidizing private production to create jobs.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Keynesian theory was a response to the prevailing
A) classical theory that held that the economy could suffer from a period of sustained unemployment.
B) classical theory that held that the economy is self-correcting.
C) monetarist theory that held that the economy is self-correcting.
D) monetarist theory that held that monetary policy should be used to return the economy to its potential output.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
In the U.S., the Great Recession was fought with traditional monetary and fiscal policies,
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following policies would supply-side economists favor?
A) Lowering taxes to increase work effort and investment tax credits to stimulate investments
B) Lowering taxes to increase work effort and lowering interest rates to stimulate investment
C) Eliminating welfare programs to increase employment and investment tax credits to encourage firms to provide on-the-job training programs
D) Investment tax credits and increasing government spending on applied research to increase productivity
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 120
Related Exams