A) 8
B) 12.5
C) 14
D) 25
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The immediate energy source that drives ATP synthesis by ATP synthase during oxidative phosphorylation is the ________.
A) oxidation of glucose and other organic compounds
B) flow of electrons down the electron transport chain
C) H+ concentration gradient across the membrane holding ATPsynthase
D) transfer of phosphate to ADP
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following types of metabolic poison would most directly interfere with glycolysis?
A) an agent that reacts with oxygen and depletes its concentration in the cell
B) an agent that binds to pyruvate and inactivates it
C) an agent that closely mimics the structure of glucose but is not metabolized
D) an agent that reacts with NADH and oxidizes it to NAD+
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following sequences describes the path by which electrons move from high-energy to lower-energy molecules in aerobic respiration?
A) glucose → NADH → electron transport chain → oxygen
B) glucose → pyruvate → ATP → oxygen
C) glucose → pyruvate → electron transport chain → NADH → ATP
D) food → glycolysis → citric acid cycle → NADH → ATP
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is one of the molecules formed by the removal of a carboxyl group (as CO2) from a molecule of pyruvate?
A) ATP
B) acetyl CoA
C) citrate
D) water
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Exposing inner mitochondrial membranes to ultrasonic vibrations will fragment the membranes and pieces will reseal to form small vesicles that contain the intermembrane space. These vesicles can transfer electrons from NADH to oxygen and synthesize ATP. Which of the following statements best describes what will happen to the vesicles when NADH is added?
A) The inside of the vesicles will become acidic.
B) The inside of the vesicles will become alkaline.
C) ATP will be produced from ADP and ![]() i in the interior of the vesicle.
i in the interior of the vesicle.
D) Protons will be pumped out of the interior of the vesicle to the exterior using energy from ATP hydrolysis.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
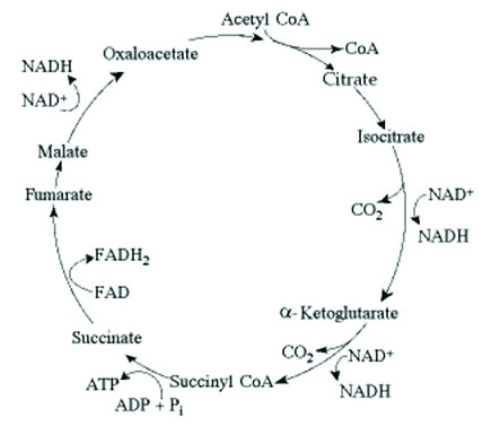 The citric acid cycle.
If pyruvate oxidation is blocked, what is the most likely effect on the levels of oxaloacetate and citrate in the citric acid cycle shown in the accompanying figure?
The citric acid cycle.
If pyruvate oxidation is blocked, what is the most likely effect on the levels of oxaloacetate and citrate in the citric acid cycle shown in the accompanying figure?
A) Oxaloacetate will decrease and citrate will accumulate.
B) Oxaloacetate will accumulate and citrate will decrease.
C) Both oxaloacetate and citrate will decrease.
D) Both oxaloacetate and citrate will accumulate.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In mitochondria, exergonic redox reactions ________.
A) are the source of energy driving prokaryotic ATP synthesis
B) provide the energy that establishes the proton gradient
C) reduce carbon atoms to carbon dioxide
D) are coupled via phosphorylated intermediates to endergonic processes
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following reactions produces the majority of the CO2 released by the complete oxidation of glucose?
A) glycolysis
B) electron transport
C) oxidation of pyruvate to acetyl-CoA
D) the citric acid cycle
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the proteins of the electron transport chain were labeled with a fluorescent tag, the fluorescence observed by microscopy will be localized to which of the following regions of the mitochondria?
A) outer membrane
B) inner membrane
C) intermembrane space
D) matrix
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the summary statements below best describes the results of the following reaction? C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy
A) C6H12O6 is oxidized and O2 is reduced.
B) O2 is oxidized and H2O is reduced.
C) CO2 is reduced and O2 is oxidized.
D) O2 is reduced and CO2 is oxidized.
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The enzyme phosphofructokinase (PFK) catalyzes a key step in glycolysis. About 10% of Springer spaniels suffer from canine PFK deficiency. Dogs affected with this disorder most likely display which of the following symptoms?
A) They die as embryos.
B) They constantly have low blood sugar.
C) They are lethargic and readily tire from exercise.
D) They carry out elevated levels of oxidative phosphorylation.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In chemiosmosis, the most direct source of energy used to convert ADP + 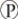 i to ATP is energy released ________.
i to ATP is energy released ________.
A) as electrons flow through the electron transport chain
B) from substrate-level phosphorylation
C) from movement of protons through ATP synthase, down their electrochemical gradient
D) as electrons are transported across the inner mitochondrial membrane
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The enzyme phosphofructokinase (PFK) catalyzes a key step in glycolysis and is inhibited by high levels of which of the following molecules?
A) glucose and NAD+
B) AMP and ATP
C) ATP and citrate
D) citrate and CO2
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the oxidizing agent in the following reaction? Pyruvate + NADH + H+ → Lactate + NAD+
A) oxygen
B) NADH
C) lactate
D) pyruvate
Correct Answer

verified
D
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements best describes the primary role played by oxygen in cellular respiration?
A) It yields energy in the form of ATP as it is passed down the electron transport chain.
B) It oxidizes glucose to form two molecules of pyruvate.
C) It serves as an acceptor for carbon, forming CO2 in the citric acid cycle.
D) It serves as the final acceptor for electrons from the electron transport chain.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
New biosensors, applied like a temporary tattoo to the skin, can alert endurance athletes that they are about to "hit the wall" and will find it difficult to continue exercising. These biosensors monitor lactate present in sweat during strenuous exercise. Which of the statements below best explains the use of lactate as an indicator of exercise capacity?
A) During aerobic respiration, muscle cells cannot produce enough lactate to fuel muscle cell contractions, and muscles begin to cramp, thus athletic performance suffers.
B) During anaerobic respiration, lactate levels increase when muscles cells need more energy; however, muscles cells eventually fatigue, thus athletes should modify their activities to increase aerobic respiration.
C) During aerobic respiration, muscles cells produce too much lactate, which causes a rise in the pH of the muscle cells, thus athletes must consume increased amounts of sports drinks, high in electrolytes, to buffer the pH.
D) During anaerobic respiration, muscle cells receive too little oxygen and begin to convert lactate to pyruvate (pyruvic acid) , thus athletes experience cramping and fatigue.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements best explains why carbohydrates and fats may be considered high-energy foods?
A) They contain many protons associated with oxygen atoms.
B) They contain no low-energy nitrogen atoms.
C) They contain many electrons associated with hydrogen atoms.
D) They are strong oxidizing molecules.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Substrate-level phosphorylation accounts for approximately what percent of the ATP formed by the reactions of glycolysis?
A) 0%
B) 2%
C) 38%
D) 100%
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements best describes a characteristic of NAD+?
A) NAD+ is reduced to NADH in glycolysis, pyruvate oxidation, and the citric acid cycle.
B) NAD+ stores more chemical energy than NADH.
C) NAD+ may donate electrons for use in oxidative phosphorylation.
D) NAD+ is oxidized in glycolysis to produce ATP.
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 68
Related Exams