A) encode transcription factors that control the expression of genes responsible for specific anatomical structures.
B) are found only in Drosophila and other arthropods.
C) are the only genes that contain the homeobox domain.
D) encode proteins that form anatomical structures in the fly.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A sequence database such as GenBank could be used to carry out which of the following processes?
A) Determine the expression pattern for specific human genes.
B) Construct a tree to determine the evolutionary relationships between various bird species.
C) Search for genes that have not yet been identified in eukaryotic genomes.
D) Compare patterns of gene expression in cancerous and non-cancerous cells.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is metagenomics?
A) genomics as applied to a species that most typifies the average phenotype of its genus
B) the sequencing of one or two representative genes from several species
C) the sequencing of only the most highly conserved genes in a lineage
D) sequencing DNA from a group of species from the same ecosystem
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements defines proteomics?
A) It is the linkage of each gene to a particular protein.
B) It is the study of the full protein set and its properties.
C) It is the totality of the functional possibilities of a single protein.
D) It is the study of how amino acids are ordered in a protein.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Comparisons of DNA sequences within the human species have revealed many variations. Which of the following variations involves duplication of relatively long stretches of DNA?
A) CNVs
B) SNPs
C) STRs
D) Transposable elements
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following techniques would be most appropriate to test the hypothesis that humans and chimps differ in the expression of a large set of shared genes?
A) DNA microarray analysis
B) polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
C) DNA sequencing
D) protein-protein interaction assays
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A microarray is a tool used in genetic research to determine the mRNAs being produced in a particular tissue, and their relative level of expression. Known genes can therefore be assayed for their expression in different situations. One use of the technology is in cancer diagnosis and treatment. If a known gene functions as a tumor suppressor, predict which of the following pieces of evidence would be most useful in diagnosis of a cancer due to a mutation in this tumor-suppressor gene.
A) The tissue sample shows a high level of gene expression relative to a control (noncancerous) sample.
B) The tissue sample responds to treatment with a mitosis-promoting compound.
C) The mRNAs for the targeted tumor suppressor sequence are not being produced.
D) The mRNAs for cyclins and kinases show unusually high levels of expression.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following processes is an early step in the whole-genome shotgun approach to sequencing?
A) break genomic DNA at random sites
B) map the position of cloned DNA fragments
C) randomly select DNA primers and hybridize these to random positions of chromosomes in preparation for sequencing
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Why is sequencing of eukaryotic genomes more difficult than sequencing genomes of bacteria or archaea?
A) It is due to the large size of eukaryotic proteins.
B) Eukaryotic genomes contain sequences for hard-to-find proteins.
C) There is a high proportion of G-C base pairs in eukaryotic DNA, which makes sequencing difficult to complete.
D) The large size of eukaryotic genomes and the large amount of eukaryotic repetitive DNA make sequencing difficult.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements correctly describes one characteristic of a multigene family?
A) A multigene family includes multiple genes whose products must be coordinately expressed.
B) A multigene family includes genes whose sequences are very similar and that probably arose by duplication.
C) A multigene family includes a gene whose exons can be spliced in a number of different ways.
D) A multigene family includes a highly conserved gene found in a number of different species.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When gene duplication occurs to its ultimate extent by doubling all genes in a genome, which of the following results has occurred?
A) pseudogene creation
B) creation of a gene cluster
C) creation of a polyploid
D) creation of a diploid
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
During which of the following processes does exon shuffling occur?
A) splicing of DNA
B) DNA replication
C) meiotic recombination
D) translation
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Fragments of DNA have been extracted from the remnants of extinct woolly mammoths, amplified, and sequenced. How can these fragments of DNA now be used?
A) to introduce certain mammoth traits into relatives, such as elephants
B) to clone live woolly mammoths
C) to understand the reasons why mammoths went extinct
D) to better understand the evolutionary relationships among members of related taxa
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Unequal crossing over during prophase I can result in one sister chromosome with a deletion and another with a duplication. A mutated form of hemoglobin, so-called hemoglobin Lepore, exists in the human population. Hemoglobin Lepore has a deleted series of amino acids. If this mutated form was caused by unequal crossing over, what would be an expected consequence?
A) There should also be persons whose hemoglobin contains two copies of the series of amino acids that is deleted in hemoglobin Lepore.
B) Each of the genes in the hemoglobin gene family must show the same deletion.
C) The deleted gene must have undergone exon shuffling.
D) The deleted region must be located in a different area of the individual's genome.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following information to answer the question.
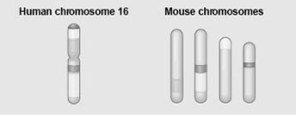 The figure shows a diagram of blocks of genes on human chromosome 16 and the locations of blocks of similar genes on four chromosomes of the mouse.
Which of the following statements describes the result of the movement of these blocks?
The figure shows a diagram of blocks of genes on human chromosome 16 and the locations of blocks of similar genes on four chromosomes of the mouse.
Which of the following statements describes the result of the movement of these blocks?
A) During evolutionary time, these sequences have separated and have returned to their original positions.
B) DNA sequences within these blocks have become increasingly divergent.
C) Sequences represented have duplicated at least three times.
D) Chromosomal translocations have moved blocks of sequences to other chromosomes.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Based on the data in the Amino Acid Sequence Identity Table, which two members of the human globin gene family are the most divergent?
A) α1 and ß
B) Αγ and ß
C) α1 and a2
D) α1 and G?
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In humans, the embryonic and fetal forms of hemoglobin have a higher affinity for oxygen than that of adults. Why is this the case?
A) Nonidentical genes produce different versions of globins during development.
B) Pseudogenes interfere with gene expression in adults.
C) The attachment of methyl groups to cytosine following birth changes the type of hemoglobin produced.
D) Histone proteins change shape during embryonic development.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following types of genes or gene families may be created by mutations that occur in one member of a gene pair that arose from gene duplication?
A) only a pseudogene
B) only a gene with a new function
C) only a gene family with two distinct but related members
D) a pseudogene, a gene with a new function, and a gene family with two distinct but related members
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Using modern techniques of sequencing by synthesis and the shotgun approach, sequences are assembled into chromosomes by ________.
A) placing them on previously generated genetic maps
B) cloning them into plasmid vectors
C) computer analysis looking for sequence overlaps
D) cloning them into plasmid vectors, placing them on previously generated genetic maps, followed by computer analysis looking for sequence overlaps
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements correctly describes one of the characteristics of alternative splicing in vertebrate genomes?
A) Vertebrate genomes can produce more than one polypeptide from a single gene.
B) Vertebrate genomes can produce only one polypeptide from a single gene.
C) Vertebrate genomes are always smaller than other organisms.
D) Alternative splicing leaves introns in vertebrate genes after they are transcribed.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 44
Related Exams