A) dehydrogenated
B) oxidized
C) reduced
D) redoxed
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
During which of the following metabolic processes is most of the CO₂ from the catabolism of glucose is released?
A) glycolysis
B) electron transport
C) oxidation of pyruvate to acetyl-CoA
D) the citric acid cycle
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In chemiosmosis, what is the most direct source of energy that is used to convert ADP +  ᵢ to ATP?
ᵢ to ATP?
A) energy released as electrons flow through the electron transport chain
B) energy released from substrate-level phosphorylation
C) energy released from movement of protons through ATP synthase, down their electrochemical gradient
D) energy released as electrons are transported across the inner mitochondrial membrane
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Water is one of the end products of aerobic respiration. What is the source of the oxygen atom used in formation of the water?
A) carbon dioxide (CO₂)
B) glucose (C₆H₁₂O₆)
C) molecular oxygen (O₂)
D) pyruvate (C₃H₃O₃⁻)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements describes a primary function of both alcohol fermentation and lactic acid fermentation?
A) reduction of NAD⁺ to NADH
B) reduction of FAD to FADH₂
C) oxidation of NADH to NAD⁺
D) hydrolysis of ATP to ADP + ![]() ᵢ
ᵢ
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What kinds of cells carry out ATP synthesis by chemiosmosis?
A) all cells, both prokaryotic and eukaryotic, exclusively using oxygen as the electron acceptor
B) only animal cells in mitochondria, exclusively using oxygen as the electron acceptor
C) only eukaryotic cells, both plant and animal, using either oxygen or other electron acceptors
D) all respiring cells, both prokaryotic and eukaryotic, using either oxygen or other electron acceptors
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Yeast cells that have defective mitochondria incapable of respiration will be able to grow by catabolizing which of the following carbon sources for energy?
A) glucose
B) cholesterol
C) fatty acids
D) amino acids
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The enzyme phosphofructokinase (PFK) catalyzes a key step in glycolysis. About 10% of Springer spaniels suffer from canine PFK deficiency. Given its critical role in glycolysis, which of the following conditions would be a likely consequence for dogs afflicted with this disorder?
A) They would die as embryos.
B) They would have elevated blood-glucose levels, which may result in a high incidence of diabetes.
C) They would be lethargic and readily tire from exercise.
D) They would carry out elevated levels of oxidative phosphorylation.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following processes generates a proton-motive force in mitochondria?
A) the flow of protons through ATP synthase down their concentration gradient
B) the reduction of NAD⁺ by the first electron carrier in the electron transport chain
C) lowering of pH in the mitochondrial matrix
D) pumping of hydrogen ions from the mitochondrial matrix across the inner membrane and into the intermembrane space
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following information to answer the question below.
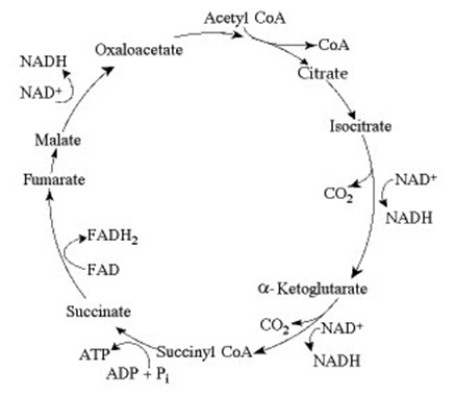 The citric acid cycle.
If pyruvate oxidation is blocked, what will happen to the levels of oxaloacetate and citric acid in the citric acid cycle shown in the accompanying figure?
The citric acid cycle.
If pyruvate oxidation is blocked, what will happen to the levels of oxaloacetate and citric acid in the citric acid cycle shown in the accompanying figure?
A) Oxaloacetate will decrease and citric acid will accumulate.
B) Oxaloacetate will accumulate and citric acid will decrease.
C) Both oxaloacetate and citric acid will decrease.
D) Both oxaloacetate and citric acid will accumulate.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the absence of oxygen, yeast cells can obtain energy by fermentation, which results in the production of which of the following sets of molecules?
A) ATP, CO₂, and ethanol (ethyl alcohol)
B) ATP, CO₂, and lactate
C) ATP, NADH, and ethanol
D) ATP, CO₂, and acetyl CoA
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Following glycolysis and the citric acid cycle, but before the electron transport chain and oxidative phosphorylation, the carbon skeleton of glucose has been broken down to CO₂ with some net gain of ATP. Most of the energy from the original glucose molecule at that point in the process, however, is stored in the form of which of the following molecules?
A) acetyl-CoA
B) NAD⁺
C) pyruvate
D) NADH
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If glucose is the sole energy source, what fraction of the carbon dioxide exhaled by animals is generated only by the reactions involved in oxidation of pyruvate to acetyl CoA?
A) 1/6
B) 1/3
C) 2/3
D) all of it
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In liver cells, the inner mitochondrial membranes are about five times the area of the outer mitochondrial membranes. What purpose must this serve?
A) It allows for an increased rate of glycolysis.
B) It allows for an increased rate of the citric acid cycle.
C) It increases the surface for oxidative phosphorylation.
D) It increases the surface for substrate-level phosphorylation.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the oxidizing agent in the following reaction? Pyruvate + NADH + H⁺ → Lactate + NAD⁺
A) NADH
B) NAD⁺
C) lactate
D) pyruvate
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Starting with one molecule of glucose, glycolysis results in the net production of which of the following sets of energy-containing products?
A) 2 NAD⁺, 2 pyruvate, and 2 ATP
B) 2 NADH, 2 pyruvate, and 2 ATP
C) 4 NADH, 2 pyruvate, and 4 ATP
D) 6 CO₂, 2 pyruvate, and 2 ATP
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Fatty acids usually have an even number of carbons in their structures. Catabolism of fatty acids produces two-carbon fragments that are converted to acetyl CoA molecules. What is the most likely way in which these acetyl CoA molecules would be metabolized in aerobic cellular respiration?
A) They would directly enter the electron transport chain.
B) They would directly enter the energy-yielding phase of glycolysis.
C) They would be converted to pyruvate and then undergo pyruvate oxidation upon transport into mitochondria.
D) They would directly enter the citric acid cycle.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which kind of metabolic poison would most directly interfere with glycolysis?
A) an agent that reacts with oxygen and depletes its concentration in the cell
B) an agent that binds to pyruvate and inactivates it
C) an agent that closely mimics the structure of glucose but is not metabolized
D) an agent that reacts with NADH and oxidizes it to NAD⁺
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following information to answer the question below.
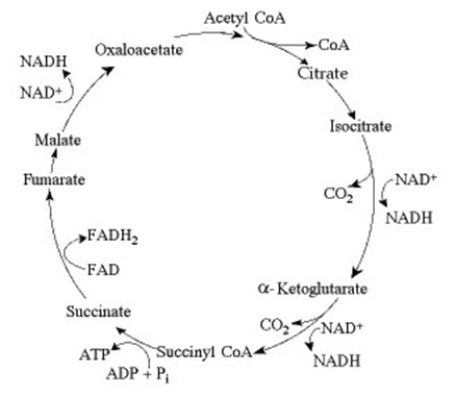 The citric acid cycle.
If you were to add one of the eight citric acid cycle intermediates to the culture medium of yeast growing in the laboratory, what do you think would happen to the rates of ATP and carbon dioxide production?
The citric acid cycle.
If you were to add one of the eight citric acid cycle intermediates to the culture medium of yeast growing in the laboratory, what do you think would happen to the rates of ATP and carbon dioxide production?
A) There would be no change in ATP production, but the rate of carbon dioxide production would increase.
B) The rates of ATP production and carbon dioxide production would both increase.
C) The rate of ATP production would increase, but the rate of carbon dioxide production would decrease.
D) The rates of ATP and carbon dioxide production would both decrease.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which metabolic pathway is common to both fermentation and cellular respiration of a glucose molecule?
A) the citric acid cycle
B) the electron transport chain
C) glycolysis
D) reduction of pyruvate to lactate
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 68
Related Exams