A) both rival in consumption and excludable.
B) nonrival in consumption and excludable.
C) both nonrival in consumption and nonexcludable.
D) rival in consumption and nonexcludable.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure: Demand and Marginal Revenue 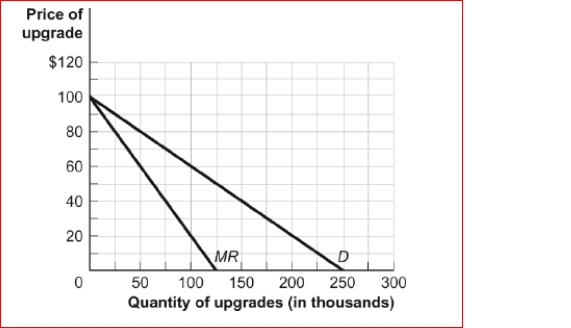 (Figure: Demand and Marginal Revenue) The figure Demand and Marginal Revenue refers to a software upgrade.The producer incurred fixed costs of $10 million to produce the upgrade; the marginal cost of allowing consumers to download the upgrade is zero.What is the efficient level of output for the upgrade?
(Figure: Demand and Marginal Revenue) The figure Demand and Marginal Revenue refers to a software upgrade.The producer incurred fixed costs of $10 million to produce the upgrade; the marginal cost of allowing consumers to download the upgrade is zero.What is the efficient level of output for the upgrade?
A) 0
B) 80,000
C) 125,000
D) 250,000
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Some public goods would not be provided without government intervention because:
A) the marginal cost of the good exceeds an individual's marginal benefit.
B) the marginal cost of the good is less than an individual's marginal benefit.
C) the socially optimal price of the good would be zero (i.e., there is no chance of making a profit) .
D) the marginal cost of the good exceeds an individual's marginal benefit and the socially optimal price of the good would be zero (i.e., there is no chance of making a profit) .
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A common resource is a good or service for which exclusion is:
A) possible and which is rival in consumption.
B) possible and which is nonrival in consumption.
C) not possible and which is rival in consumption.
D) not possible and which is nonrival in consumption.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Scenario: Ben and Nick Two individuals, Ben and Nick, are the only members of a hypothetical community.They have revealed the marginal private benefits they each receive from a public good whose marginal social benefit is known.In addition, the marginal social cost (MSC) of the public good is known and is constant. (Scenario: Ben and Nick) Refer to the information and figure in the scenario Ben and Nick.At all levels of public good provision:
A) Ben places a higher value on the public good than Nick.
B) the MSC is less than the MSB.
C) the optimal level is not attained.
D) the private marginal benefits cannot be determined.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure: Market Failure 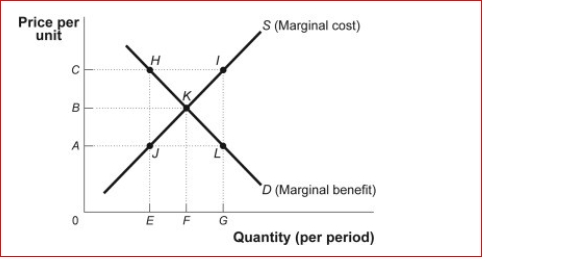 (Figure: Market Failure) Look at the figure Market Failure.Suppose it represents the demand and marginal cost of pounds of shrimp in the bay.The additional cost of the shrimp due to the depletion of the common resource is equal to AC.The efficient price of shrimp is
(Figure: Market Failure) Look at the figure Market Failure.Suppose it represents the demand and marginal cost of pounds of shrimp in the bay.The additional cost of the shrimp due to the depletion of the common resource is equal to AC.The efficient price of shrimp is
A) 0
B) A
C) B
D) C
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The best example of a good whose consumption is not excludable is:
A) a yard.
B) a house.
C) a bicycle.
D) national defense.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
For a public good, the marginal social benefit will be higher than any individual's marginal benefit of consumption.False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Scenario: Ben and Nick Two individuals, Ben and Nick, are the only members of a hypothetical community.They have revealed the marginal private benefits they each receive from a public good whose marginal social benefit is known.In addition, the marginal social cost (MSC) of the public good is known and is constant. 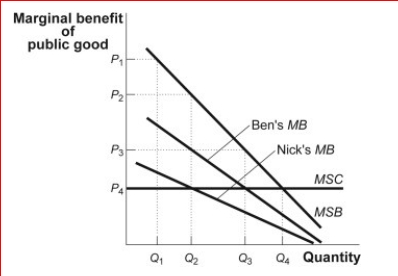
 (Scenario: Ben and Nick) Refer to the information and figure in the scenario Ben and Nick.Q4:
(Scenario: Ben and Nick) Refer to the information and figure in the scenario Ben and Nick.Q4:
A) is the socially optimal level of public good provision.
B) is equal to P₄ + P₃ in marginal social benefits.
C) represents an amount at which the MSB is greater than the MSC.
D) will not be produced, since neither Ben nor Nick finds benefit in it at this level.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
One way the government of Alaska could prevent an inefficiently large production of crab fishing would be to:
A) subsidize fishermen to create more competition.
B) sell exclusive licenses for the right to fish.
C) offer tax breaks for more efficient boats.
D) allow competition from foreign fishermen.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following goods is most likely a public good?
A) the Internet
B) a public park
C) a pair of pants
D) fire protection provided by the local fire department
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure: An Individual's Marginal Benefit from a Public Good (Figure: An Individual's Marginal Benefit from a Public Good) Look at the figure An Individual's Marginal Benefit from a Public Good.Assume that two individuals will share consumption of a public good; each individual has the same marginal benefit curve as the one shown in the figure.If the marginal cost of the good is $24, what is the level of this public good that would maximize society's welfare?
A) 0 units
B) 8 units
C) 12 units
D) 16 units
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The tendency of people to avoid paying for a good's benefits when the benefits can be obtained free is called the:
A) free-cost problem.
B) free-rider problem.
C) free-goods problem.
D) free-market problem.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Common resource goods are similar to:
A) public goods because they are both nonexcludable and nonrival in consumption.
B) goods with negative externalities because not all users take into account the external costs imposed on society.
C) private goods because they are both excludable and rival.
D) artificially scarce goods because they are both are excludable and nonrival in consumption.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When the allocation of resources is such that a different allocation would increase society's welfare, economists say:
A) there is market failure.
B) the efficiency condition is met.
C) decision makers have faced the marginal benefits and marginal costs of their decisions.
D) producers have maximized total cost.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Whether or not they pay for them, people cannot be excluded from receiving the benefits of:
A) private goods.
B) public goods.
C) common resources.
D) either public goods or common resources.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a good is nonrival in consumption and a positive price is charged by the supplier, then:
A) more people want to use this good at the supplier's price.
B) there is inefficiently low consumption of this good.
C) free-riding occurs in this market.
D) there is a socially optimal level of consumption.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Public goods should be produced up to the point at which the marginal cost of production equals:
A) the maximum price any individual is willing to pay for that unit.
B) the sum of the individual marginal benefits from all consumers of that unit.
C) zero, which is the marginal cost of allowing another individual to consume the good.
D) the highest marginal benefit from any individual consumer of the good.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
(Table: Marginal Benefit, Cost, and Consumer Surplus) The table Marginal Benefit, Cost, and Consumer Surplus shows six consumers' willingness to pay (his or her individual marginal benefit) for one iTunes download of a Jack Johnson song.If the marginal social cost is constant at ________, then consumers will purchase this good and consumer Surplus is _.
A) $5; three; $30
B) $4; four; $18
C) $5; two; $37
D) $4; four; $34
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Airplane seats are rival in consumption. False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 81 - 100 of 237
Related Exams