A) 0
B) 6.1
C) 7.5
D) 13
E) 15
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 10-g bullet moving horizontally with a speed of 2.0 km/s strikes and passes through a 4.0-kg block moving with a speed of 4.2 m/s in the opposite direction on a horizontal frictionless surface. If the block is brought to rest by the collision, what is the kinetic energy of the bullet as it emerges from the block?
A) 0.51 kJ
B) 0.29 kJ
C) 0.80 kJ
D) 0.13 kJ
E) 20 kJ
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 1.6-kg block is attached to the end of a 2.0-m string to form a pendulum. The pendulum is released from rest when the string is horizontal. At the lowest point of its swing when it is moving horizontally, the block is hit by a 10-g bullet moving horizontally in the opposite direction. The bullet remains in the block and causes the block to come to rest at the low point of its swing. What was the magnitude of the bullet's velocity just before hitting the block?
A) 1.0 km/s
B) 1.6 km/s
C) 1.2 km/s
D) 1.4 km/s
E) 1.8 km/s
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A rocket engine consumes 450 kg of fuel per minute. If the exhaust speed of the ejected fuel is 5.2 km/s, what is the thrust of the rocket?
A) 42 kN
B) 39 kN
C) 45 kN
D) 48 kN
E) 35 kN
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
A U-238 nucleus (mass = 238 units) decays, transforming into an alpha particle (mass = 4.00 units) and a residual thorium nucleus (mass = 234 units). If the uranium nucleus was at rest, and the alpha particle has a speed of 1.50 × 107 m/s, determine the recoil speed of the thorium nucleus.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 10-g bullet moving 1000 m/s strikes and passes through a 2.0-kg block initially at rest, as shown. The bullet emerges from the block with a speed of 400 m/s. To what maximum height will the block rise above its initial position? 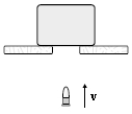
A) 78 cm
B) 66 cm
C) 56 cm
D) 46 cm
E) 37 cm
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An 80-g particle moving with an initial speed of 50 m/s in the positive x direction strikes and sticks to a 60-g particle moving 50 m/s in the positive y direction. How much kinetic energy is lost in this collision?
A) 96 J
B) 89 J
C) 175 J
D) 86 J
E) 110 J
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Three particles are placed in the xy plane. A 30-g particle is located at (3, 4) m, and a 40-g particle is located at (−2, −2) m. Where must a 20-g particle be placed so that the center of mass of the three-particle system is at the origin?
A) (−3, −1) m
B) (+1, +3) m
C) (+3, −1) m
D) (−1, −3) m
E) (−0.5, −2) m
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 2.0-kg object moving with a velocity of 5.0 m/s in the positive x direction strikes and sticks to a 3.0-kg object moving with a speed of 2.0 m/s in the same direction. How much kinetic energy is lost in this collision?
A) 2.4 J
B) 9.6 J
C) 5.4 J
D) 0.6 J
E) 6.0 J
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 2.0-kg object moving 5.0 m/s collides with and sticks to an 8.0-kg object initially at rest. Determine the kinetic energy lost by the system as a result of this collision.
A) 20 J
B) 15 J
C) 30 J
D) 25 J
E) 5.0 J
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Two cars start at the same point, but travel in opposite directions on a circular path of radius R, each at speed v. While each car travels a distance less than 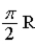 , one quarter circle, the center of mass of the two cars
, one quarter circle, the center of mass of the two cars
A) remains at the initial point.
B) travels along a diameter of the circle at speed v' < v.
C) travels along a diameter of the circle at speed v' = v.
D) travels along a diameter of the circle at speed v' > v.
E) remains at the center of the circle.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 1.0-kg ball is attached to the end of a 2.5-m string to form a pendulum. This pendulum is released from rest with the string horizontal. At the lowest point in its swing when it is moving horizontally, the ball collides elastically with a 2.0-kg block initially at rest on a horizontal frictionless surface. What is the speed of the block just after the collision?
A) 2.3 m/s
B) 4.7 m/s
C) 3.5 m/s
D) 3.0 m/s
E) 7.0 m/s
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Refer to Exhibit 9-1. What is the magnitude of their velocity, in m/s, immediately after the collision?
A) 0
B) 13
C) 15
D) 26
E) 30
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 1.5-kg playground ball is moving with a velocity of 3.0 m/s directed 30° below the horizontal just before it strikes a horizontal surface. The ball leaves this surface 0.50 s later with a velocity of 2.0 m/s directed 60° above the horizontal. What is the magnitude of the average resultant force on the ball?
A) 14 N
B) 11 N
C) 18 N
D) 22 N
E) 3.0 N
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
A uniform thin wire has a length 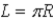 and is bent into a semicircular arc of radius R. If the wire starts at (x, y) = (R, 0) and curves counterclockwise to (x, y) = (−R, 0), what is the y coordinate of its center of mass?
and is bent into a semicircular arc of radius R. If the wire starts at (x, y) = (R, 0) and curves counterclockwise to (x, y) = (−R, 0), what is the y coordinate of its center of mass?
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The linear density of a rod, in g/m, is given by 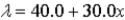 . The rod extends from the origin to x = 0.400 m. What is the mass of the rod?
. The rod extends from the origin to x = 0.400 m. What is the mass of the rod?
A) 0.213 g
B) 3.50 g
C) 3.84 g
D) 18.4 g
E) 20.8 g
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 3.0-kg mass is released from rest at point A of a circular frictionless track of radius 0.40 m as shown in the figure. The mass slides down the track and collides with a 1.4-kg mass that is initially at rest on a horizontal frictionless surface. If the masses stick together, what is their speed after the collision? 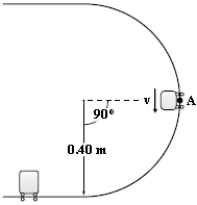
A) 2.1 m/s
B) 1.7 m/s
C) 1.9 m/s
D) 1.5 m/s
E) 2.3 m/s
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
At an instant when a particle of mass 50 g has an acceleration of 80 m/s2 in the positive x direction, a 75-g particle has an acceleration of 40 m/s2 in the positive y direction. What is the magnitude of the acceleration of the center of mass of this two-particle system at this instant?
A) 60 m/s2
B) 56 m/s2
C) 40 m/s2
D) 50 m/s2
E) 46 m/s2
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The value of the momentum of a system is the same at a later time as at an earlier time if there are no
A) collisions between particles within the system.
B) inelastic collisions between particles within the system.
C) changes of momentum of individual particles within the system.
D) internal forces acting between particles within the system.
E) external forces acting on particles of the system.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A steel ball bearing of mass m1 and speed of magnitude v1 has a head-on elastic collision with a steel ball bearing of mass m2 at rest. Rank the speed v1 of m1 relative to v2, the magnitude of the speed of m2, after the collision when i) m1 > m2; ii) m1 = m2; and iii) m1 < m2.
A) v1 < v2; v1 < v2; v1 < v2
B) v1 < v2; v1 = v2; v1 > v2
C) v1 < v2; v1 > v2; v1 > v2
D) v1 > v2; v1 = v2; v1 < v2
E) v1 > v2; v1 > v2; v1 > v2
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 89
Related Exams