A) unicellular chytrid.
B) unicellular yeast.
C) multicellular algae.
D) multicellular fungus.
E) flagellated protist.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Whatever its ultimate cause(s) , the Cambrian explosion is a prime example of
A) mass extinction.
B) evolutionary stasis.
C) adaptive radiation.
D) All three of the responses are correct.
E) Only two of the responses are correct.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Evidence of which structure or characteristic would be most surprising to find among fossils of the Ediacaran fauna?
A) true tissues
B) hard parts
C) bilateral symmetry
D) cephalization
E) embryos
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
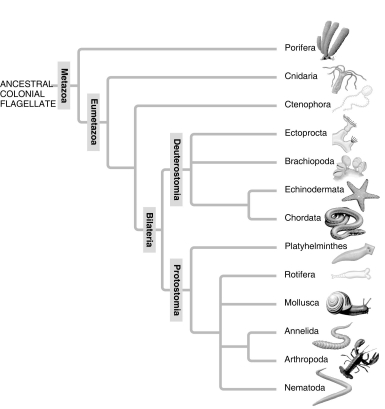 A: Morphological phylogeny.
A: Morphological phylogeny.
 B: Molecular phylogeny.
-In the traditional phylogeny (A) , the phylum Platyhelminthes is depicted as a sister taxon to the rest of the protostome phyla, and as having diverged earlier from the lineage that led to the rest of the protostomes. In the molecular phylogeny (B) , Platyhelminthes is depicted as a lophotrochozoan phylum. What probably led to this change?
B: Molecular phylogeny.
-In the traditional phylogeny (A) , the phylum Platyhelminthes is depicted as a sister taxon to the rest of the protostome phyla, and as having diverged earlier from the lineage that led to the rest of the protostomes. In the molecular phylogeny (B) , Platyhelminthes is depicted as a lophotrochozoan phylum. What probably led to this change?
A) Platyhelminthes ceased to be recognized as true protostomes.
B) The removal of the acoel flatworms (Acoela) from the Platyhelminthes allowed the remaining flatworms to be clearly tied to the Lophotrochozoa.
C) All Platyhelminthes must have a well-developed lophophore as their feeding apparatus.
D) Platyhelminthes' close genetic ties to the arthropods became clear as their Hox gene sequences were studied.
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What do animals as diverse as corals and monkeys have in common?
A) body cavity between body wall and digestive system
B) number of embryonic tissue layers
C) type of body symmetry
D) presence of Hox genes
E) degree of cephalization
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which statement is most consistent with the hypothesis that the Cambrian explosion was caused by the rise of predator-prey relationships?
A) increased incidence of worm burrows in the fossil record
B) increased incidence of larger animals in the fossil record
C) increased incidence of organic material in the fossil record
D) increased incidence of fern galls in the fossil record
E) increased incidence of hard parts in the fossil record
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following was probably the least important factor in bringing about the Cambrian explosion?
A) the emergence of predator-prey relationships among animals
B) the accumulation of diverse adaptations, such as shells and different modes of locomotion
C) the movement of animals onto land
D) the origin of Hox genes and other genetic changes affecting the regulation of developmental genes
E) the accumulation of sufficient atmospheric oxygen to support the more active metabolism of mobile animals
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is (are) unique to animals?
A) cells that have mitochondria
B) the structural carbohydrate, chitin
C) nervous conduction and muscular movement
D) heterotrophy
E) Two of these responses are correct.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
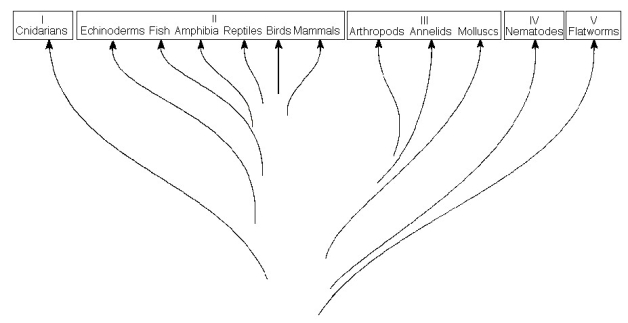 The previous figure shows a chart of the animal kingdom set up as a modified phylogenetic tree. Use the diagram to answer the following questions.
-Which two groups have members that undergo ecdysis?
The previous figure shows a chart of the animal kingdom set up as a modified phylogenetic tree. Use the diagram to answer the following questions.
-Which two groups have members that undergo ecdysis?
A) I and II
B) II and III
C) III and IV
D) III and V
E) IV and V
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The blastopore is a structure that first becomes evident during
A) fertilization.
B) gastrulation.
C) the eight-cell stage of the embryo.
D) coelom formation.
E) cleavage.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
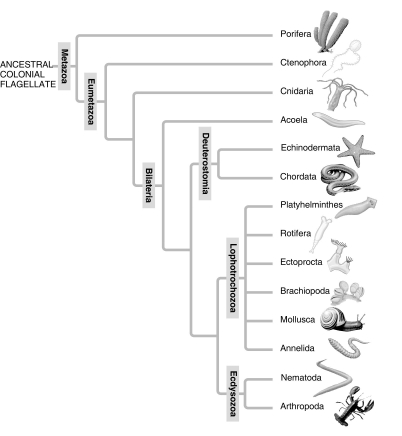
 A: Morphological phylogeny.
A: Morphological phylogeny.
 B: Molecular phylogeny.
-What is true of the deuterostomes in the molecular phylogeny (B) that is not true in the traditional phylogeny (A) ?
B: Molecular phylogeny.
-What is true of the deuterostomes in the molecular phylogeny (B) that is not true in the traditional phylogeny (A) ?
A) Deuterostomia is a clade.
B) To maintain Deuterostomia as a clade, some phyla had to be removed from it.
C) Deuterostomia now includes the Acoela.
D) It is actually a grade, rather than a clade.
E) It diverged from the rest of the Bilateria earlier than did the Acoela.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A student encounters an animal embryo at the eight-cell stage. The four smaller cells that comprise one hemisphere of the embryo seem to be rotated 45 degrees and to lie in the grooves between larger, underlying cells (i.e., spiral cleavage) . -If we were to separate these eight cells and attempt to culture them individually, then what is most likely to happen?
A) All eight cells will die immediately.
B) Each cell may continue development, but only into a nonviable embryo that lacks many parts.
C) Each cell may develop into a full-sized, normal embryo.
D) Each cell may develop into a smaller-than-average, but otherwise normal, embryo.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In individual insects of some species, whole chromosomes that carry larval genes are eliminated from the genomes of somatic cells at the time of metamorphosis. A consequence of this occurrence is that
A) we could not clone a larva from the somatic cells of such an adult insect.
B) such species must reproduce only asexually.
C) the descendents of these adults do not include a larval stage.
D) metamorphosis can no longer occur among the descendents of such adults.
E) Two of these responses are correct.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Arthropods invaded land about 100 million years before vertebrates did so. This most clearly implies that
A) arthropods evolved before vertebrates did.
B) extant terrestrial arthropods are better adapted to terrestrial life than are extant terrestrial vertebrates.
C) ancestral arthropods must have been poorly adapted to aquatic life, and thus experienced a selective pressure to invade land.
D) vertebrates evolved from arthropods.
E) arthropods have had more time to coevolve with land plants than have vertebrates.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which distinction is given more emphasis by the morphological phylogeny than by the molecular phylogeny?
A) metazoan and eumetazoan
B) radial and bilateral
C) true coelom and pseudocoelom
D) protostome and deuterostome
E) molting and lack of molting
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
At which developmental stage should one be able to first distinguish a protostome embryo from a deuterostome embryo?
A) fertilization
B) cleavage
C) gastrulation
D) coelom formation
E) metamorphosis
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is descriptive of protostomes?
A) spiral and indeterminate cleavage, blastopore becomes mouth
B) spiral and determinate cleavage, blastopore becomes mouth
C) spiral and determinate cleavage, blastopore becomes anus
D) radial and determinate cleavage, blastopore becomes anus
E) radial and determinate cleavage, blastopore becomes mouth
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Hox genes came to regulate each of the following in what sequence, from earliest to most recent? 1) identity and position of paired appendages in protostome embryos 2) anterior-posterior orientation of segments in protostome embryos 3) positioning of tentacles in cnidarians 4) anterior-posterior orientation in vertebrate embryos
A) 4 → 1 → 3 → 2
B) 4 → 2 → 3 → 1
C) 4 → 2 → 1 → 3
D) 3 → 2 → 1 → 4
E) 3 → 4 → 1 → 2
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
 The previous figure shows a chart of the animal kingdom set up as a modified phylogenetic tree. Use the diagram to answer the following questions.
-Which group contains diploblastic organisms?
The previous figure shows a chart of the animal kingdom set up as a modified phylogenetic tree. Use the diagram to answer the following questions.
-Which group contains diploblastic organisms?
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 32.1. Proposed Number of Hox Genes in Various Extant and Extinct Animals
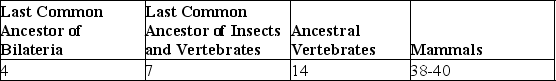 -What conclusion is apparent from the data in the table?
-What conclusion is apparent from the data in the table?
A) Land animals have more Hox genes than do those that live in water.
B) All bilaterian phyla have had the same degree of expansion in their numbers of Hox genes.
C) Acoel flatworms should be expected to contain seven Hox genes.
D) The expansion in number of Hox genes throughout vertebrate evolution cannot be explained merely by three duplications of the ancestral vertebrate Hox cluster.
E) Extant insects all have seven Hox genes.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 74
Related Exams