A) It allows firms to tie goods that are highly valued together with goods that are not highly valued, hence increasing profits for firms.
B) It is a way to force consumers to buy more than what they would without tying.
C) It is a subtle way to raise prices for those consumers who have a low willingness to pay.
D) It is a subtle way to charge higher prices to those consumers with a high willingness to pay, and a lower price to consumers with a low willingness to pay.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is TRUE?
A) Bundling in the cable industry is required by the government.
B) There is little benefit in bundling varied TV channels, though there are added costs in doing so.
C) Bundling has come under attack in the cable TV industry, but not in other industries.
D) Bundling is rarely practiced by firms in the cable TV industry.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following would be an effective method for firms to ensure profit from price discrimination when the possibility of arbitrage exists?
A) set a single price for all markets
B) supply products only to one market
C) make products sold to each market have an exclusive feature
D) request law enforcement to eliminate the possibility of arbitrage
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
To maximize profit GlaxoSmithKline sets a higher price for Combivir in Europe than in Africa because demand curve in Africa is:
A) lower and more inelastic.
B) lower and more elastic.
C) higher and more inelastic.
D) higher and more elastic.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The difference between tying and bundling in pricing strategies is that:
A) they both are strategies that firms use to maximize profit.
B) tying does not require the purchase of both goods, but bundling does.
C) tying involves the combination of goods that are complements, whereas bundling involves the combination of substitutes.
D) tying does not lead to as much profit as bundling does.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Perfect price discrimination results in zero dollars of consumer surplus.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In general, price discrimination exists because:
A) higher prices are required when costs are higher.
B) lower prices are possible when profits are not a goal of the entrepreneur.
C) higher prices are charged because some customers are willing to pay more.
D) lower prices encourage arbitrage.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
 Reference: Ref 14-6 (Table: Willingness to Pay) Refer to the table. If the firm were to engage in bundling, total surplus is:
Reference: Ref 14-6 (Table: Willingness to Pay) Refer to the table. If the firm were to engage in bundling, total surplus is:
A) $65.
B) $50.
C) $160.
D) $225.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
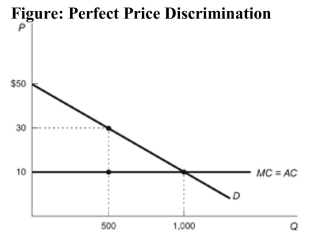 Reference: Ref 14-4 (Figure: Perfect Price Discrimination) Refer to the figure. For a firm practicing perfect price discrimination, calculate the dollar amount of consumer surplus in this market.
Reference: Ref 14-4 (Figure: Perfect Price Discrimination) Refer to the figure. For a firm practicing perfect price discrimination, calculate the dollar amount of consumer surplus in this market.
A) $15,000
B) $20,000
C) $0
D) $5,000
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose that GSK sells one of its drugs for $25/pill in the United States and $13/pill in Canada. Which of the following statements is true? I. The price discrimination benefits the Canadians since they pay a lower price. II. The price discrimination benefits the Americans since GSK's larger profits means more research and development of new drugs for Americans. III. Price discrimination is beneficial in industries with large fixed costs, since price discrimination increases the size of the market, helping to spread large costs over a greater number of consumers.
A) I only
B) I and II only
C) I and III only
D) I, II, and III
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
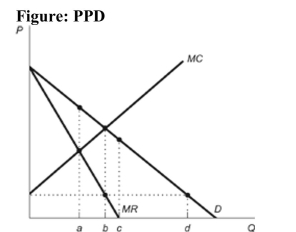 Reference: Ref 14-3 (Figure: PPD) Refer to the figure. Which of the following statements best explains why a firm that perfectly price discriminates would sell additional units beyond a units of output?
Reference: Ref 14-3 (Figure: PPD) Refer to the figure. Which of the following statements best explains why a firm that perfectly price discriminates would sell additional units beyond a units of output?
A) A firm will not sell beyond a units of output. The firm will only sell exactly a, as it is the profit-maximizing rate of output for this firm.
B) The marginal cost is less than consumers' willingness to pay for these units.
C) The marginal cost is greater than consumers' willingness to pay for these units.
D) A firm will not sell beyond a units of output, since the marginal cost is greater than the marginal revenue for these units.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is NOT an example of tying?
A) game consoles and game cartridges
B) cell phones and phone calls
C) printers and print cartridges
D) automobiles and engines
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 141 - 152 of 152
Related Exams