A) O2 < Ne < Ar < H2
B) O2 < Ar < Ne < H2
C) H2 < Ne < Ar < O2
D) H2 < Ne < O2 < Ar
E) Ar < O2 < Ne < H2
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements regarding intermolecular forces is incorrect?
A) Hydrogen bonding is the strongest of the intermolecular forces for substances of similar molar mass.
B) London dispersion forces are present in all atoms and molecules.
C) Dipole-dipole forces increase with increasing molecular size.
D) Bonding forces are much stronger than intermolecular forces.
E) Hydrogen bonding is the reason for the abnormally high boiling point of water.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following molecules experience dipole-dipole forces?
A) NO2
B) CO2
C) CBr4
D) SO3
E) all of these choices are correct
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The forces that hold CO2 together in the solid state are:
A) ionic bonds.
B) dipole-dipole forces.
C) London dispersion forces only.
D) covalent bonds.
E) attractions between nuclei and delocalized valence electrons.
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Arrange the following substances in order of increasing boiling point: N2, H2, NH3, PH3
A) H2 < N2 < PH3 < NH3
B) N2 < H2 < PH3 < NH3
C) H2 < N2 < NH3 < PH3
D) N2 < PH3 < NH3 < H2
E) NH3 < PH3 < N2 < H2
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The physical properties of a substance influenced by the strength of intermolecular forces include all of the following except:
A) density.
B) boiling point.
C) surface tension.
D) melting point.
E) mass.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Rank the following substances in order of increasing boiling point: F2, Ne, He, Cl2
A) F2 < Ne < He < Cl2
B) F2 < He < Ne < Cl2
C) F2 < Cl2 < He < Ne
D) He < Ne < F2 < Cl2
E) Cl2 < F2 < Ne < He
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The pictured change of state occurs at constant temperature even though heat is being removed.Where does this change of state occur on the cooling curve? 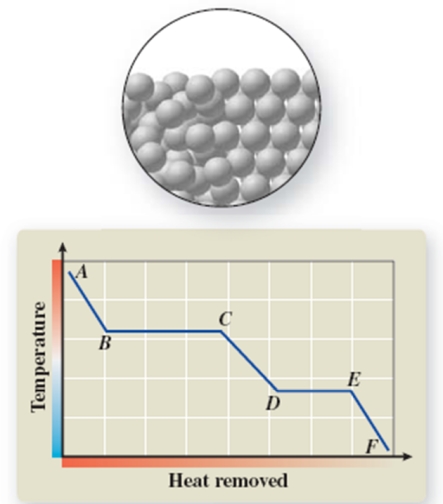
A) AB
B) BC
C) CD
D) DE
E) EF
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which choice correctly lists the intermolecular forces present in CH3NH2?
A) London forces only
B) dipole-dipole forces only
C) London forces, dipole-dipole forces, and hydrogen bonding
D) dipole-dipole forces and hydrogen bonding
E) hydrogen bonding only
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A solid substance has a moderate melting point, is fairly soft, and is a nonconductor.This substance is probably a(n) ________ solid.
A) metallic
B) ionic
C) network
D) nonpolar molecular
E) polar molecular
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Three phases of water are shown in the figure.List the terms used to identify the phase changes indicated by the arrows. 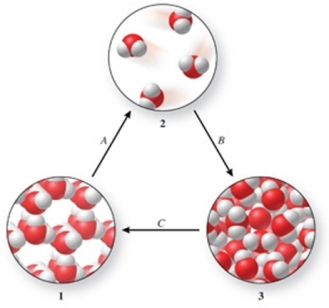
A) A = sublimation, B = vaporization, C = freezing
B) A = vaporization, B = condensation, C = melting
C) A = vaporization, B = deposition, C = melting
D) A = sublimation, B = condensation, C = freezing
E) A = condensation, B = sublimation, C = freezing
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Rank the following substances in order of increasing intermolecular forces: He, HF, F2, Ne
A) He < HF < F2 < Ne
B) He < HF < Ne < F2
C) He < Ne < F2 < HF
D) He < F2 < Ne < HF
E) HF < Ne < F2 < He
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Identify the type of solid shown in the image. 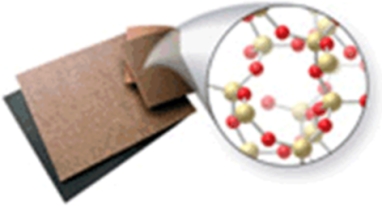
A) metallic
B) ionic
C) network
D) nonpolar molecular
E) polar molecular
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following substances can participate in hydrogen bonding?
A) CH4
B) HF
C) CH3COCH3
D) SiH4
E) all of these choices are correct
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Calculate the amount of heat energy required to convert 55.0 g of water at 62.5oC to steam at 124.0 C.(Cwater = 4.18 J/g C; Csteam = 2.02 J/g C; molar heat of vaporization of liquid water = 4.07 x 104 J/mol)
A) 2.25 x 103 kJ
B) 1.23 x 102 kJ
C) 0.862 kJ
D) 1.35 x 102 kJ
E) 2.67 kJ
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is correct?
A) At the melting point of a substance, the solid, liquid, and gas phases are all in equilibrium.
B) The freezing point and the melting point of a substance are the same.
C) There is no fundamental difference in the melting process for covalent substances and ionic substances.
D) When iodine vapor cools at atmospheric pressure, it condenses to the liquid state.
E) In order for a substance to go from the liquid phase to the gas phase, it must give off energy to the surroundings.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Calculate the amount of heat energy required to melt 25.0 g of ice at 0.0 C.(molar heat of fusion of ice = 6.01 x 103 J/mol)
A) 1.50 x 102 kJ
B) 8.34 kJ
C) 4.33 kJ
D) 7.50 x 102 kJ
E) 1.50 x 10-1 kJ
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What phase transition is occurring between points D and E on the heating curve? 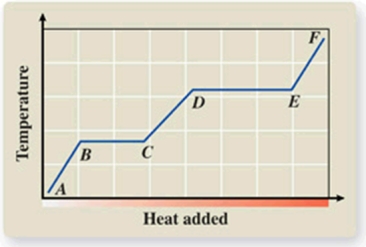
A) melting
B) freezing
C) evaporation
D) sublimation
E) deposition
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A solid substance has a high melting point, is hard, brittle, and conducts electricity when molten.This substance is probably a(n) ________ solid.
A) metallic
B) ionic
C) network
D) nonpolar molecular
E) polar molecular
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Identify the type of solid shown in the image. 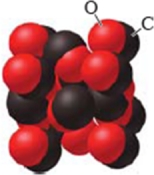
A) metallic
B) ionic
C) network
D) molecular
E) amorphous
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 107
Related Exams