A) It generates ATP.
B) It involves the Krebs cycle.
C) It involves glycolysis only.
D) It requires cytochromes.
E) It involves the reduction of nitrate.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Beggiatoa bacteria get energy by oxidizing S2- to S6+. This means they take (1) for their (2) .
A) 1- protons; 2- NAD+
B) 1- electrons; 2- electron transport chain
C) 1- glucose; 2- glycolysis
D) 1- electrons; 2- fermentation
E) 1- sulfur; 2- photophosphorylation
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
All the following are true about substrate- level phosphorylation except
A) It occurs in glycolysis.
B) The oxidation of intermediate metabolic compounds releases energy that is used to generate ATP.
C) No final electron acceptor is required.
D) It involves the direct transfer of a high- energy phosphate group from an intermediate metabolic compound to ADP.
E) All of the above are true.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 5.4
 -An enzyme, citrate synthase, in the Krebs cycle is inhibited by ATP; this is an example of all of the following except
-An enzyme, citrate synthase, in the Krebs cycle is inhibited by ATP; this is an example of all of the following except
A) Noncompetitive inhibition.
B) Competitive inhibition.
C) Feedback inhibition.
D) Allosteric inhibition.
E) None of the above.
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to the chemiosmotic mechanism, ATP is generated when
A) Protons are moved across a membrane.
B) Cells lyse in a hypotonic environment.
C) Chlorophyll liberates an electron.
D) A high- energy phosphate group is transferred from an intermediate metabolite to ADP.
E) Electrons are transferred between carrier molecules.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Assume you are working for a chemical company and you are responsible for growing a yeast culture that produces ethyl alcohol. The yeasts are growing well on the maltose medium but are not producing alcohol. The most likely explanation is
A) Yeasts don't produce ethyl alcohol.
B) O₂ is in the medium.
C) Not enough protein is provided.
D) The maltose is toxic.
E) None of the above.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
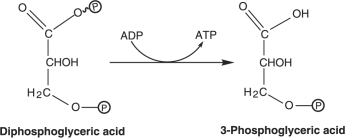
How is ATP generated in the reaction in Figure 5.4?
A) Fermentation
B) Glycolysis
C) Oxidative phosphorylation
D) Substrate- level phosphorylation
E) Photophosphorylation
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A strictly fermentative bacterium produces energy
A) By aerobic respiration only.
B) Only in the absence of oxygen.
C) Only in the presence of oxygen.
D) By glycolysis only.
E) By fermentation or aerobic respiration.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 5.7
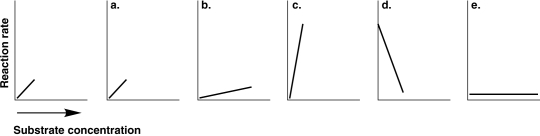 -The graph at the left of Figure 5.7 shows the reaction rate for an enzyme at its optimum temperature. Which graph shows enzyme activity at a higher temperature?
-The graph at the left of Figure 5.7 shows the reaction rate for an enzyme at its optimum temperature. Which graph shows enzyme activity at a higher temperature?
A) a
B) b
C) c
D) d
E) e
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In green and purple bacteria, electrons to reduce CO2come from
A) C6H12O6
B) H2O
C) Sunlight
D) Chlorophyll
E) CO2
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Assume you are growing bacteria on a lipid medium that started at pH 7. The action of bacterial lipases should cause the pH of the medium to
A) Increase.
B) Decrease.
C) Stay the same.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Uses CO₂ for carbon and H₂ for energy.
A) Chemoheterotroph
B) Photoheterotroph
C) Photoautotroph
D) Chemoautotroph
E) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 5.3
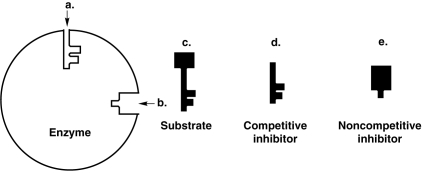 -How would a noncompetitive inhibitor interfere with a reaction involving the enzyme in Figure 5.3?
-How would a noncompetitive inhibitor interfere with a reaction involving the enzyme in Figure 5.3?
A) It would bind to a.
B) It would bind to b.
C) It would bind to c.
D) It would bind to d.
E) Can't tell.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When oxygen is unavailable, Halobacterium produce ATP by
A) Substrate- level phosphorylation.
B) Fermentation.
C) The Krebs cycle.
D) Photophosphorylation.
E) Oxidative phosphorylation.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 5.1
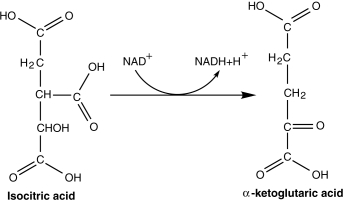 -Which compound is being reduced in the reaction in Figure 5.1?
-Which compound is being reduced in the reaction in Figure 5.1?
A) Isocitric acid and a- ketoglutaric acid
B) NADH
C) NADH and isocitric acid
D) NAD+
E) a- ketoglutaric acid and NAD+
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is not true about photophosphorylation?
A) The oxidation of carrier molecules releases energy.
B) It occurs in photosynthesizing cells.
C) Energy from oxidation reactions is used to generate ATP from ADP.
D) Light liberates an electron from chlorophyll.
E) It requires CO₂.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 5.5
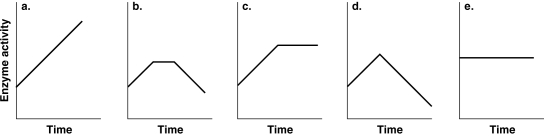 -Which of the graphs in Figure 5.5 best illustrates the activity of an enzyme that is saturated with substrate?
-Which of the graphs in Figure 5.5 best illustrates the activity of an enzyme that is saturated with substrate?
A) a
B) b
C) c
D) d
E) e
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Aerobic respiration differs from anaerobic respiration in which of the following respects?
A) The final electron acceptors are different.
B) Anaerobic respiration is glycolysis.
C) Aerobic respiration requires the electron transport chain.
D) Aerobic respiration gets electrons from the Krebs cycle.
E) Aerobic respiration produces more ATP.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following compounds is not an enzyme?
A) Cellulase
B) fi- galactosidase
C) Dehydrogenase
D) Coenzyme A
E) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 5.2
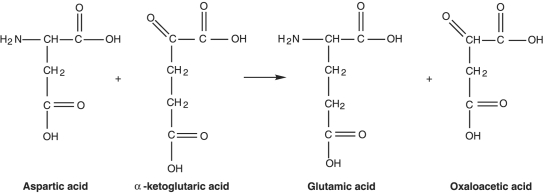 -What type of reaction is in Figure 5.2?
-What type of reaction is in Figure 5.2?
A) Reduction
B) Decarboxylation
C) Dehydrogenation
D) Oxidation
E) Transamination
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 38
Related Exams