A) yolk sac.
B) chorion.
C) amnion.
D) allantois.
E) embryo.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the 1920s, two German embryologists, Hans Spemann and Hilde Mangold, demonstrated that a small patch of cells, called the dorsal lip of the blastopore, would
A) become the neural tube.
B) form the chorion.
C) become the digestive tract.
D) induce the surrounding cells to differentiate.
E) lack the genes necessary to develop the embryo.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which extraembryonic membrane lies immediately beneath the shell of a reptile embryo?
A) Allantois
B) Chorion
C) Amnion
D) Placenta
E) Yolk sac
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The birth defect spina bifida results in part of the spinal cord lying outside of the body. This defect is due to abnormal development of the
A) placenta.
B) neural tube.
C) gill grooves.
D) allantois.
E) embryonic disk.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The nervous system forms from the
A) ectoderm.
B) mesoderm.
C) chorion.
D) yolk.
E) endoderm.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
is the developmental event that results in the formation of a primitive gut and the three tissue layers.
A) Metamorphosis
B) Gastrulation
C) Blastulation
D) Induction
E) Cleavage
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Your biceps muscle is derived from the
A) ectoderm.
B) amnion.
C) mesoderm.
D) endoderm.
E) blastopore.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Mitotic cell divisions of the zygote are collectively called cleavage.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
At which stage is the human embryo most susceptible to toxic substances?
A) During organogenesis
B) Just before birth
C) During the last trimester
D) During cleavage
E) During the fourth and fifth months
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The extraembryonic membrane that sends blood vessels into the endometrium is the chorion.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Essay
A human embryo has webbed fingers. Why are human babies not usually born with webbed fingers?
Correct Answer

verified
During development, ...View Answer
Show Answer
Correct Answer
verified
View Answer
Short Answer
A _ is a fertilized egg.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
If a cell lacks transcription factors, will never be transcribed.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The cells of an aging animal function less efficiently because
A) organelles and cellular components decline.
B) cells can no longer mitotically divide.
C) cell metabolism is slower.
D) protein synthesis ceases.
E) damaged DNA cannot be repaired.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The structure produced by cleavage of a human zygote is called a(n)
A) embryonic disk.
B) blastopore.
C) blastocyst.
D) chorion.
E) gastrula.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Prior to birth, stretching of the cervix by the baby's head stimulates the release of
A) oxytocin.
B) progesterone.
C) estrogen.
D) colostrum.
E) prolactin.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
Newborn animals that closely resemble the adults of their species undergo development.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
During development, some cells , or specialize in both structure and function.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
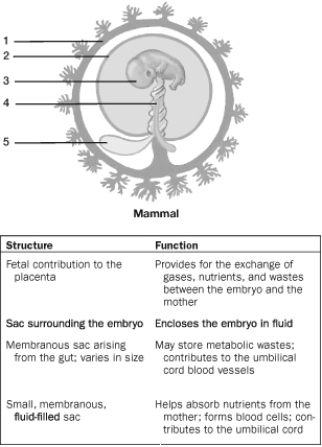 -The fluid the embryo floats in is produced by structure
-The fluid the embryo floats in is produced by structure
A) 1.
B) 2.
C) 3.
D) 4.
E) 5.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The most rapid differentiation in an embryo occurs during the first 2 months of pregnancy.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 122
Related Exams