A) high r, small offspring.
B) low r, small offspring.
C) low r, large offspring.
D) high r, large offspring.
E) low r, large population size.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
All of the following may be involved in feedback mechanisms in natural communities when populations become too dense EXCEPT
A) density-dependent factors.
B) limiting factors.
C) biotic potential.
D) physical factors.
E) biotic factors.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Population size is related to
A) deaths.
B) births.
C) migration.
D) immigration.
E) all of these.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A population of wolf spiders exemplifies a __________ population distribution.
A) clumped
B) random
C) uniform
D) constant
E) homogeneous
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Biotic potential is controlled by all of the following factors EXCEPT
A) the age of individuals within the population.
B) the resources available for each individual.
C) fecundity rate.
D) environmental disturbances.
E) all of these control biotic potential.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is NOT true for a population growing exponentially?
A) The number of individuals added to the population in a year is greater than it was the previous year.
B) The population growth rate increases year after year.
C) Its r remains constant in the short-run.
D) The doubling time remains constant.
E) All of these are NOT true.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Reznick and Endler were interested in the effects of __________ on guppy evolution.
A) predation
B) competition
C) population density
D) density-independent factors
E) mating rituals
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The distribution of highly competitive animals is likely to be
A) clumped.
B) random.
C) uniform.
D) constant.
E) homogeneous.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The effect of resource availability on population size determines
A) the carrying capacity of the environment.
B) exponential growth.
C) the doubling time of a population.
D) the population's biotic potential.
E) all of these.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The size of a population is affected by all of the following EXCEPT
A) biotic potential.
B) trophic level.
C) carrying capacity of the environment.
D) death rate.
E) birth rate.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The average number of individuals in a specified portion of habitat is the population's
A) distribution.
B) carrying capacity.
C) density.
D) size.
E) birth rate.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A J-shaped population growth curve becomes an S-shaped one
A) as more resources become available.
B) if the data are plotted on semi-log graph paper.
C) as the carrying capacity is reached.
D) if reproduction stops.
E) if any of these occur.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
As population density increases, the chance of __________ also increases.
A) parasitism
B) disease
C) predation
D) competition
E) all of these
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Limiting factors
A) produce more pronounced effects as a population grows.
B) prevent indefinite, exponential population growth.
C) can be either density-dependent or density-independent.
D) acting together constitute environmental resistance to population growth.
E) include all of these.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is NOT true regarding biotic potential? It
A) varies from one species to another.
B) is related to the timing of the first reproduction.
C) is related to the frequency of reproduction.
D) is related to the number of offspring produced.
E) increases as population density increases.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Questions refer to the figure above illustrating logistic growth.
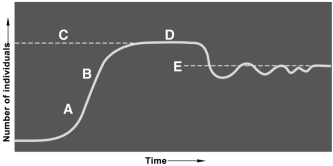 -The effect of population growth limiting factors begin to become evident at about
-The effect of population growth limiting factors begin to become evident at about
A) A.
B) B.
C) C.
D) D.
E) E.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The work of Reznick and Endler with guppies shows all of the following EXCEPT that
A) life history traits can be inherited.
B) life history traits evolve.
C) life history traits can be altered over a short period of time.
D) predation does not influence the modification of life history traits.
E) life history traits are coded for in DNA.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A cohort is
A) a group of individuals of the same species born during the same time interval.
B) any member of the same species.
C) a group of individuals with the same parents.
D) a group of individuals of the same sex.
E) any group of closely related individuals.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is true regarding quadrats?
A) A full population count is usually impractical.
B) Quadrats are plots of land of the same size and shape that can be used to randomly count a single non-migrating species.
C) Once several quadrats are counted, an estimate of number of a particular organism can be extrapolated for a given land mass.
D) Sampling error is common if the size of the quadrats is not large.
E) All of these are correct.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The distribution of social animals is likely to be
A) clumped.
B) random.
C) uniform.
D) constant.
E) homogeneous.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 62
Related Exams