A) It may be used to estimate inventories for interim statements.
B) It may be used to estimate inventories for annual statements.
C) It may be used by auditors.
D) It may be used to provide a rough check on the accuracy of the physical inventory count.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Under ASPE, agricultural produce, forest products, and mineral products inventories may be accounted for at net realizable value if
A) there is a well-established industry practice of doing so.
B) arbitrary cost allocation would be too costly.
C) costs to bring them to market are expected to be minimal.
D) the company's financial results appear more favourable by doing so.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The following inventory transactions took place for NPR Corporation for the month of May: 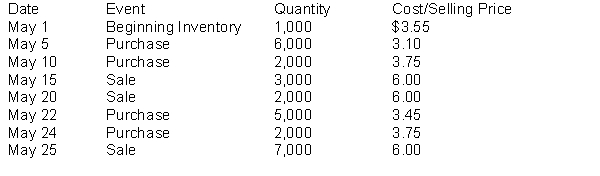 The ending inventory balance for NPR Corporation, assuming the company uses a perpetual inventory system, and a first-in, first-out (FIFO) cost formula is
The ending inventory balance for NPR Corporation, assuming the company uses a perpetual inventory system, and a first-in, first-out (FIFO) cost formula is
A) $15,000.
B) $14,400.
C) $12,850.
D) $13,800.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following information for questions.
Shanti Inc.is a calendar-year corporation.Its financial statements for the years 2018 and 2017 contained errors as follows:  -Assume that no correcting entries were made at December 31, 2017.Ignoring income taxes, by how much will retained earnings at December 31, 2018 be overstated or understated?
-Assume that no correcting entries were made at December 31, 2017.Ignoring income taxes, by how much will retained earnings at December 31, 2018 be overstated or understated?
A) $2,000 understated
B) $18,000 understated
C) $10,000 overstated
D) $18,000 overstated
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following inventories may NOT be valued at fair value less costs to sell?
A) grain and livestock futures
B) biological assets
C) farm equipment
D) agricultural produce
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following information for questions.
The following information was available from the inventory records of Key Company for January: 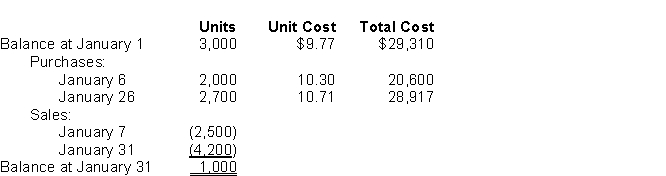 -Assuming that Key uses the perpetual inventory system, what should the inventory be at January 31, using the moving-average inventory method, rounded to the nearest dollar?
-Assuming that Key uses the perpetual inventory system, what should the inventory be at January 31, using the moving-average inventory method, rounded to the nearest dollar?
A) $10,237
B) $10,260
C) $10,360
D) $10,505
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Washington Distribution Co.has determined its December 31, 2017 inventory on a FIFO basis at $240,000.Information pertaining to that inventory follows: 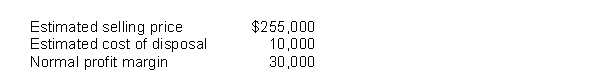 Washington records losses that result from applying the lower of cost and net realizable value rule.At December 31, 2017, the loss that Washington should recognize is
Washington records losses that result from applying the lower of cost and net realizable value rule.At December 31, 2017, the loss that Washington should recognize is
A) $0.
B) $5,000.
C) $15,000.
D) $25,000.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The following information was reported by Montana Inc.for 2017: 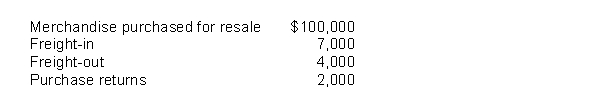 Based on this data, Montana's 2017 inventoriable cost was
Based on this data, Montana's 2017 inventoriable cost was
A) $113,000.
B) $111,000.
C) $105,000.
D) $100,000.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An inventory cost formula in which the oldest costs incurred rarely have an effect on the ending inventory valuation is
A) FIFO.
B) moving-average cost.
C) LIFO.
D) weighted average.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A manufacturing company typically maintains the following inventory account(s) :
A) Merchandise Inventory.
B) Raw Materials and Work in Process only.
C) Raw Materials, Work in Process and Finished Goods.
D) Work in Process and Merchandise Inventory.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An inventory method which is designed to approximate inventory valuation at the lower of average cost and market is
A) last-in, first-out.
B) weighted average.
C) conventional retail method.
D) specific identification.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When using the moving-average cost formula with a perpetual system,
A) a weighted-average cost is calculated at year end.
B) a new unit cost is calculated each time a sale is made.
C) a new unit cost is calculated each time a purchase is made.
D) a new unit cost is calculated both when a sale is made and when a purchase is made.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
To produce an inventory valuation which approximates the lower of average cost and market using the conventional retail inventory method, the calculation of the ratio of cost to retail should
A) include markups but not markdowns.
B) include markups and markdowns.
C) ignore both markups and markdowns.
D) include markdowns but not markups.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Conversion costs include
A) all materials plus direct labour.
B) all materials plus variable overhead allocated.
C) direct labour plus variable and fixed overhead allocated.
D) direct labour plus fixed overhead allocated.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
All of the following costs should be charged to expense in the period in which they are incurred EXCEPT for
A) manufacturing overhead costs for a product manufactured and sold in the same accounting period.
B) costs which will not benefit any future period.
C) costs from idle manufacturing capacity resulting from an unexpected plant shutdown.
D) costs of normal shrinkage and scrap incurred for the manufacture of a product in ending inventory.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Tennessee Ltd.'s accounting records reported the following information: 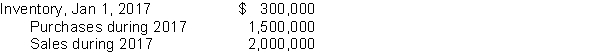 A physical inventory taken on December 31, 2017 resulted in an ending inventory of $350,000.Tennessee's gross profit on sales has remained constant at 30% in recent years.Tennessee suspects some inventory may have been taken by a new employee.At December 31, 2017, what is the estimated cost of the missing inventory?
A physical inventory taken on December 31, 2017 resulted in an ending inventory of $350,000.Tennessee's gross profit on sales has remained constant at 30% in recent years.Tennessee suspects some inventory may have been taken by a new employee.At December 31, 2017, what is the estimated cost of the missing inventory?
A) $400,000
B) $100,000
C) $75,000
D) $50,000
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Tehran Ltd.uses FIFO to cost its inventory.The following information is available for Tehran's inventory of product # 101: Beginning inventory: 120 units @ $3.14 per unit March 1: Purchase of 250 units @ $3.50 per unit April 10: Sale of 100 units @ $5.10 per unit Assuming Tehran uses the perpetual inventory system, the second entry to account for the April 10 sale is
A) debit Cost of Goods Sold and credit Inventory, $350.
B) debit Cost of Goods Sold and credit Purchases, $350.
C) debit Cost of Goods Sold and credit Inventory, $314.
D) debit Cost of Goods Sold and credit Purchases, $314.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following does NOT correctly describe the concept of net realizable value (NRV) ?
A) Estimates of NRV are based on the best evidence available at and shortly after the balance sheet date.
B) NRV generally does not change over time.
C) NRV generally changes over time.
D) A new estimate of NRV is required at each balance sheet date.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Portland Ltd.estimates the cost of its physical inventory at March 31 for use in interim financial statements.The rate of markup on cost is 25%.The following account balances are available: 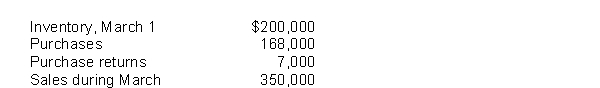 What is the estimated dollar value of the inventory at March 31?
What is the estimated dollar value of the inventory at March 31?
A) $18,000
B) $175,000
C) $81,000
D) $368,000
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following information for questions.
Giselle Ltd.is a calendar-year corporation.Its financial statements for the years 2018 and 2017 contained errors as follows:  -Assume that the proper correcting entries were made at December 31, 2017.By how much will 2018 pre-tax income be overstated or understated?
-Assume that the proper correcting entries were made at December 31, 2017.By how much will 2018 pre-tax income be overstated or understated?
A) $2,000 understated
B) $2,000 overstated
C) $6,000 overstated
D) $8,000 overstated
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 101 - 120 of 127
Related Exams