A) reduction of NADPH
B) release of oxygen
C) regeneration of the CO₂ acceptor
D) production of ATP
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A spaceship is designed to support animal life for a multiyear voyage to the outer planets of the solar system. Plants will be grown to provide oxygen and to recycle carbon dioxide. Since the spaceship will be too far from the sun for photosynthesis, an artificial light source will be needed. What wavelengths of light should be used to maximize plant growth with a minimum of energy expenditure?
A) full-spectrum white light
B) green light
C) a mixture of blue and red light
D) UV light
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In mechanism, photophosphorylation is most similar to
A) substrate-level phosphorylation in glycolysis.
B) oxidative phosphorylation in cellular respiration.
C) carbon fixation.
D) reduction of NADP⁺.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The mechanism of photophosphorylation is most similar to which of the following processes?
A) substrate-level phosphorylation in glycolysis
B) oxidative phosphorylation in cellular respiration
C) the Calvin cycle
D) reduction of NADP⁺
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which molecule is the final electron acceptor for electrons from photosystem I?
A) oxygen
B) chlorophyll in photosystem II
C) carbon dioxide
D) NADP⁺
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following events are associated with chemiosmosis in chloroplasts?
A) The pH of the stroma increases and ATP is synthesized.
B) The pH of the thylakoid space increases and ATP is synthesized.
C) The pH of the cytoplasm outside the chloroplast decreases and ATP is synthesized.
D) The pH of the stroma decreases and ATP is hydrolyzed.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Carotenoids are often found in foods that are considered to have antioxidant properties in human nutrition. What related function do they have in plants?
A) They serve as accessory pigments to increase light absorption.
B) They protect against oxidative damage from excessive light energy.
C) They shield the sensitive chromosomes of the plant from harmful ultraviolet radiation.
D) They reflect orange light and enhance red light absorption by chlorophyll.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In which of the following organisms did the process of photosynthesis most likely originate?
A) in plants
B) in prokaryotes
C) in fungi
D) three separate times during evolution
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The reducing power for Calvin cycle reactions is provided by which of the following molecules?
A) ATP
B) NADH
C) NADP⁺
D) NADPH
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Why are C₄ plants able to photosynthesize with no apparent photorespiration?
A) They do not participate in the Calvin cycle.
B) They use PEP carboxylase to initially fix CO₂.
C) They conserve water more efficiently.
D) They exclude oxygen from their tissues.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following events accompanies absorption of energy by chlorophyll molecules of the reaction-center complex?
A) ATP is synthesized from the energy absorbed.
B) An electron is excited.
C) NADP⁺ is reduced to NADPH.
D) A molecule of water is split.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which process is most directly driven by light energy?
A) creation of a pH gradient by pumping protons across the thylakoid membrane
B) reduction of NADP⁺ molecules
C) transfer of energy from pigment molecule to pigment molecule
D) ATP synthesis
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following processes is most directly driven by light energy?
A) creation of a pH gradient by pumping protons across the thylakoid membrane
B) carbon fixation in the stroma
C) reduction of NADP⁺ molecules
D) removal of electrons from chlorophyll molecules
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Theodor W. Engelmann illuminated a filament of algae with light that passed through a prism, thus exposing different segments of algae to different wavelengths of light. He added aerobic bacteria and then noted in which areas the bacteria congregated. He noted that the largest groups were found in the areas illuminated by the red and blue light. Which of the following statements describes a relationship that Engelmann's experiment helped to determine?
A) the relationship between wavelength of light and the rate of aerobic respiration
B) the relationship between wavelength of light and the amount of heat released
C) the relationship between wavelength of light and the rate of photosynthesis
D) the relationship between carbon dioxide concentration and the rate of photosynthesis
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements best describes the relationship between photosynthesis and cellular respiration?
A) Cellular respiration runs the biochemical pathways of photosynthesis in reverse.
B) Photosynthesis stores energy in complex organic molecules; cellular respiration releases energy from complex organic molecules.
C) Photosynthesis occurs only in plants; cellular respiration occurs only in animals.
D) Photosynthesis is catabolic; cellular respiration is anabolic.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Paper chromatography is a technique used to separate molecules based upon their size and solubility in a particular solvent. If pigments from a particular species of plant are extracted and subjected to paper chromatography, which of the following results is most likely?
A) Paper chromatography would produce a single band of pigment that is characteristic of that particular plant.
B) Paper chromatography would separate the pigments into two bands that appear green.
C) Paper chromatography would separate the pigments into several bands that appear green or yellow/orange.
D) Paper chromatography would separate the pigments into two bands, one that appears blue and one that appears red.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following processes would be most directly affected if a thylakoid membrane is punctured so that the interior of the thylakoid is no longer separated from the stroma?
A) splitting of water
B) flow of electrons from photosystem II to photosystem I
C) synthesis of ATP
D) reduction of NADP⁺
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In mitochondria, an electron transport chain pumps protons from the matrix into the intermembrane space, whereas in chloroplasts, an electron transport chain pumps protons from the ________.
A) matrix to the stroma
B) stroma to the thylakoid space
C) thylakoid space to the matrix
D) thylakoid space to the stroma
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
P680⁺ is said to be the strongest biological oxidizing agent. Given its function, why is this necessary?
A) It is the receptor for the most excited electron in either photosystem of photosynthesis.
B) It is the molecule that transfers electrons to plastoquinone (Pq) of the electron transfer system.
C) It transfers its electrons to reduce NADP⁺ to NADPH.
D) It obtains electrons from the oxygen atom in a water molecule, so it must have a stronger attraction for electrons than oxygen has.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Students conducted an experiment to determine the effect of light intensity on the rate of photosynthesis. They punched 40 leaf disks from spinach leaves and used a syringe partially filled with water to pull the gases from the leaf disks so that all leaf disks sunk to the bottom of the syringe. Ten leaf disks from the syringe were placed in each of four cups and covered with 50 ml of the solutions as indicated below. All leaf disks were resting on the bottom of the cups when the experiment began. The volume of liquid in each cup and the temperature of the solutions were held constant. All cups were placed 0.5 meters from the designated light source. A large beaker of water was placed between the light and the cups to act as a heat sink to prevent a change in temperature. At the end of 10 minutes, the number of disks floating in each cup was recorded.
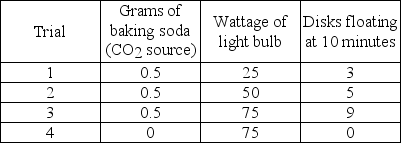 Use your knowledge of the mechanism of photosynthesis and the data presented in the chart to determine which of the statements is a correct explanation for the students' data.
Use your knowledge of the mechanism of photosynthesis and the data presented in the chart to determine which of the statements is a correct explanation for the students' data.
A) Cup 1 had a low rate of photosynthesis because 0.5 grams of baking soda did not provide a sufficient amount of CO₂.
B) Cup 2 had the highest rate of photosynthesis because it had the highest ratio of disks floating to wattage of light.
C) Cup 3 had the same rate of photosynthesis as Cup 1 because they had the same ratio of disks floating to wattage of light.
D) Cup 4 had the lowest rate of photosynthesis because it had the least CO₂.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 65
Related Exams