A) heat does not involve a transfer of energy.
B) cells do not have much thermal energy; they are relatively cool.
C) temperature is usually uniform throughout a cell.
D) heat can never be used to do work.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Living organisms increase in complexity as they grow, resulting in a decrease in the entropy of an organism. How does this relate to the second law of thermodynamics?
A) Living organisms do not obey the second law of thermodynamics, which states that the entropy of an organism increases with each energy transformation.
B) The decrease in entropy is associated with growth of an organism. As a consequence of growth, organisms cause a greater increase in entropy in their environment than the decrease in entropy associated with their increased complexity.
C) As a consequence of growth, the decrease in entropy of the organism is associated with a corresponding decrease in the entropy of the universe.
D) Living organisms are able to transform chemical energy into entropy.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following terms most precisely describes the cellular process of breaking down large molecules into smaller ones?
A) catabolism (catabolic pathways)
B) metabolism
C) anabolism (anabolic pathways)
D) dehydration
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements describes a central role that ATP plays in cellular metabolism?
A) Hydrolysis of ATP provides an input of free energy for exergonic reactions.
B) ATP provides energy coupling between exergonic and endergonic reactions.
C) Hydrolysis of the terminal phosphate group stores free energy that is used for cellular work.
D) Its terminal phosphate bond is stronger than most covalent bonds in other biological macromolecules.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements about the evolution of life on Earth, from simple prokaryote-like cells to multicellular eukaryotic organisms, is true?
A) By resulting in such diversity and complexity of life, it is an exception to the second law of thermodynamics.
B) It has occurred in accordance with the laws of thermodynamics and resulted in a substantial increase in the entropy of the planet.
C) It has occurred in accordance with the laws of thermodynamics and resulted in a substantial increase in the total energy in the universe.
D) It has occurred in accordance with the laws of thermodynamics and resulted in a substantial decrease in the entropy of the planet.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Most cells cannot harness heat to perform work because ________.
A) heat is not a form of energy
B) temperature is usually uniform throughout a cell
C) heat can never be used to do work
D) heat must remain constant during work
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Some bacteria are metabolically active in hot springs because
A) they are able to maintain a lower internal temperature.
B) high temperatures make catalysis unnecessary.
C) their enzymes have high optimal temperatures.
D) their enzymes are completely insensitive to temperature.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
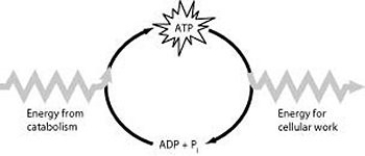 How do cells use the ATP cycle illustrated in the figure?
How do cells use the ATP cycle illustrated in the figure?
A) Cells use the cycle to recycle ADP and phosphate.
B) Cells use the cycle to recycle energy released by ATP hydrolysis.
C) Cells use the cycle to recycle ADP, phosphate, and the energy released by ATP hydrolysis.
D) Cells use the cycle primarily to generate heat.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Zinc, an essential trace element for most organisms, is present in the active site of the enzyme carboxypeptidase. The zinc most likely functions as ________.
A) a noncompetitive inhibitor of the enzyme
B) an allosteric activator of the enzyme
C) a cofactor necessary for enzyme activity
D) a coenzyme derived from a vitamin
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The relationship between catabolism and anabolism is most similar to the relationship between which of the following pairs of terms?
A) exergonic; spontaneous
B) exergonic; endergonic
C) free energy; entropy
D) work; free energy
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following information to answer the question below.
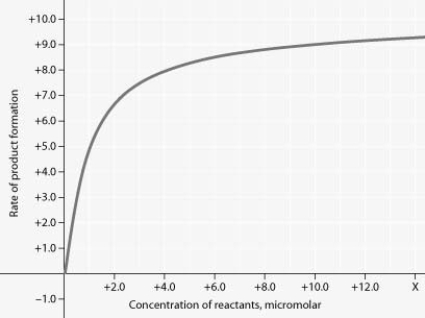 Rate of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction as a function of varying reactant concentration, with the concentration of enzyme constant
In the figure, why does the reaction rate plateau at higher reactant concentrations?
Rate of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction as a function of varying reactant concentration, with the concentration of enzyme constant
In the figure, why does the reaction rate plateau at higher reactant concentrations?
A) Feedback inhibition by product occurs at high reactant concentrations.
B) Most enzyme molecules are occupied by substrate at high reactant concentrations.
C) The reaction nears equilibrium at high reactant concentrations.
D) The rate of the reverse reaction increases at high reactant concentrations.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following information to answer the question below.
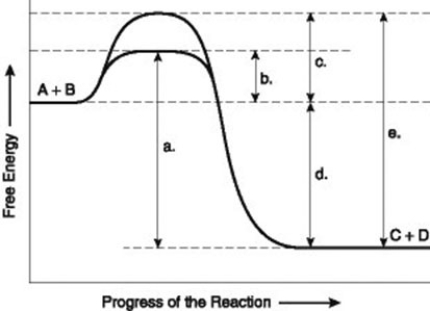 The figure illustrates the energy states associated with the reaction A + B ↔ C + D. Which of the following in the figure would be the same in either an enzyme-catalyzed or a noncatalyzed reaction?
The figure illustrates the energy states associated with the reaction A + B ↔ C + D. Which of the following in the figure would be the same in either an enzyme-catalyzed or a noncatalyzed reaction?
A) a
B) b
C) c
D) d
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is true of metabolism in its entirety in all organisms?
A) Metabolism depends on a constant supply of energy from food.
B) Metabolism uses all of an organism's resources.
C) Metabolism consists of all the energy transformation reactions in an organism.
D) Metabolism manages the increase of entropy in an organism.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is an important consequence of the first law of thermodynamics for a living organism?
A) The energy content of an organism is constant.
B) An organism ultimately must obtain all of the necessary energy for life from its environment.
C) The entropy of an organism decreases with time as the organism grows in complexity.
D) Organisms grow by converting energy into organic matter.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following characteristics is most likely to be associated with an enzyme that catalyzes two different chemical reactions?
A) The enzyme contains α-helices and β-pleated sheets.
B) The enzyme is subject to competitive inhibition and allosteric regulation.
C) The enzyme is composed of at least two subunits.
D) Either the enzyme has two distinct active sites or the substrates involved in the two reactions have very similar structures.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following conditions may be overcome by increasing the substrate concentration in an enzymatic reaction with a fixed amount of enzyme?
A) the need for a coenzyme
B) allosteric inhibition
C) noncompetitive inhibition
D) competitive inhibition
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following information to answer the question below.
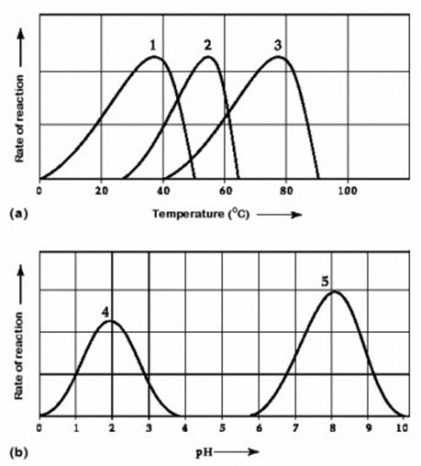 Activity of various enzymes at various temperatures (a) and at various pH (b)
Which curves on the graphs may represent the temperature and pH profiles of an enzyme taken from a bacterium that lives in a mildly alkaline hot springs at temperatures of 70°C or higher?
Activity of various enzymes at various temperatures (a) and at various pH (b)
Which curves on the graphs may represent the temperature and pH profiles of an enzyme taken from a bacterium that lives in a mildly alkaline hot springs at temperatures of 70°C or higher?
A) curves 1 and 5
B) curves 2 and 5
C) curves 3 and 4
D) curves 3 and 5
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is a primary function of the active site of an enzyme?
A) It binds allosteric regulators of the enzyme.
B) It binds noncompetitive inhibitors of the enzyme.
C) It catalyzes the reaction associated with the enzyme.
D) It is activated by the presence of the end product of the metabolic pathway in which the enzyme is involved.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following information to answer the question below.
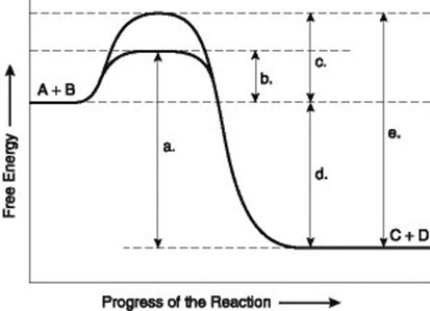 The figure illustrates the energy states associated with the reaction A + B ↔ C + D. Which of the following represents the activation energy required for the enzyme-catalyzed reaction in the figure?
The figure illustrates the energy states associated with the reaction A + B ↔ C + D. Which of the following represents the activation energy required for the enzyme-catalyzed reaction in the figure?
A) a
B) b
C) c
D) d
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the name of the thermodynamic barrier that must be overcome before products are formed in a spontaneous reaction?
A) entropy
B) activation energy
C) the equilibrium point
D) free energy
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 67
Related Exams