A) The axon
B) The cell body or soma
C) The dendrites
D) The axon hillock
E) The Schwann cell
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Hydrocephaly is a condition whereby cerebrospinal fluid accumulates around the brain. Which supportive cells continue CSF production despite it backing up in the subarachnoid space?
A) Astrocytes
B) Microglia
C) Oligodendrocytes
D) Macrophages
E) Ependymal cells
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Gray matter on the surface of the brain is called ________.
A) the cortex
B) a nucleus
C) a ganglion
D) a tract
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
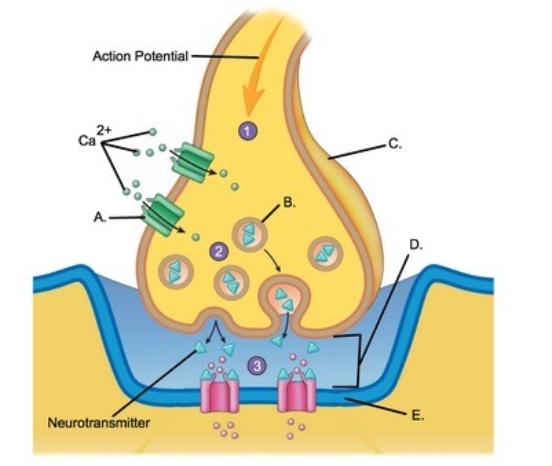 -Identify structure "E" on the neuron.
A) Schwann cell
B) Node of Ranvier
C) Neuron cell body (soma)
D) Dendrites
E) Axon
-Identify structure "E" on the neuron.
A) Schwann cell
B) Node of Ranvier
C) Neuron cell body (soma)
D) Dendrites
E) Axon
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the charge difference across the plasma membrane is decreased,
A) the potential difference across the plasma membrane does not change.
B) the membrane potential is more positive.
C) the change is called hyperpolarization.
D) negative proteins can leave the cell.
E) the membrane potential is more negative.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When two or more presynaptic neurons synapse with a single postsynaptic neuron in the CNS, a/an ________ pathway is formed.
A) convergent
B) divergent
C) reverberating
D) somatic
E) sensory
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In some cells, an afterpotential occurs because
A) the Na+ continue to enter the cell after depolarization is finished.
B) there is prolonged, elevated permeability to K+ during repolarization.
C) the sodium-potassium pump is actively exchanging ions across the membrane.
D) the extracellular Na+ concentration is reduced.
E) the permeability to Na+ continues longer than necessary.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When repolarization of a neuron is complete, the
A) neuron dies.
B) neuron regenerates.
C) cell no longer has a potential difference across its membrane.
D) original polarity of the neuron is restored.
E) neuron is no longer excitable.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of these is an example of an EPSP in a typical neuron?
A) A voltage change from 0 mV to +0.35 mV
B) A voltage change from -70 mV to -69.5 mV
C) A voltage change from -69.5 mV to -70 mV
D) A voltage change from +35 mV to 0 mV
E) A voltage change from -70 mV to -70.5 mV
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Low levels of ________ can have dire consequences on the functioning of neurons because of its role in membrane repolarization.
A) Na+
B) K+
C) Cl−
D) H+
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Match the following concerning concentration differences across the plasma membrane. -Higher concentration outside cell
A) Concentration of K+
B) Concentration of Na+ and Cl−
C) Negatively charged proteins
D) Sodium-potassium pump
E) Plasma membrane is more permeable to this ion because of leak ion channels
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If five action potentials arrive at the same synapse in very close succession, which of the following would occur?
A) The direction of the action potential is reversed.
B) Temporal summation occurs.
C) Spatial summation occurs.
D) Hyperpolarization occurs.
E) Depolarization always occurs.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
All of the following are typical characteristics of neurotransmitters except
A) they are synthesized by a presynaptic neuron.
B) they are released in response to stimulation.
C) they are released into the bloodstream before reaching the postsynaptic cell.
D) they bind to specific receptors on the postsynaptic cell.
E) they alter the physiology of the postsynaptic cell.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Nervous tissue of the CNS that is composed primarily of myelinated axons is often referred to as ________ matter.
A) white
B) gray
C) dark
D) light
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
________ are glial cells that are macrophages.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A person who has seizures might have a deficit of which of the following?
A) GABA
B) Dopamine
C) Glutamate
D) Serotonin
E) Histamine
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An inhibitory postsynaptic potential (IPSP) can result from the ________.
A) influx of Ca2+
B) influx of Na+
C) influx of Cl−
D) outflow of K+
E) Both "influx of Cl− and "outflow of K+" are correct.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Match the term with the correct definition. -Local potential
A) Small change in the resting membrane potential confined to a small area
B) Charge difference across the plasma membrane when the cell is in an unstimulated state
C) Larger change in resting membrane potential that spreads over entire surface of a cell
D) Membrane becomes more positive when Na+ diffuse into cell
E) Return to the resting membrane potential
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A substance is found to have the same effect as acetylcholinesterase, but acts at a much faster rate. What effect would this substance have at a cholinergic synapse?
A) It would greatly reduce synaptic communication by depleting ACh levels in the synaptic cleft.
B) It would enhance synaptic communication by concentrating ACh in the synaptic cleft.
C) It reduce synaptic communication by destroying ACh receptors on the post-synaptic membrane.
D) It would enhance synaptic communication by increasing the post-synaptic cells' sensitivity to ACh.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Receptor molecules in synapses
A) tend to concentrate on presynaptic terminals.
B) bind irreversibly with neurotransmitter.
C) have a high degree of specificity.
D) serve as channel proteins.
E) can bind to any molecule in the synapse.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 141 - 160 of 192
Related Exams