A) an intermediary that sells only to other intermediaries.
B) any intermediary between a manufacturer and industrial markets.
C) an intermediary that sells to other distributors.
D) an intermediary that takes possession of a product, alters it in some way, and then sells it to the ultimate consumer.
E) an intermediary that sells to consumers.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Bentley Motors makes one of the world's most prestigious automobile brands, targeting the ultra-luxury segment. Which type of market coverage does Bentley most likely use?
A) intensive distribution
B) extensive distribution
C) selective distribution
D) exclusive distribution
E) private label distribution
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
You probably own several pairs of shoes. Further, it is likely you purchased those shoes at retail stores located in a shopping mall and not directly from the manufacturer. In fact, most products are brought to you from a series of other individuals or firms known as a
A) marketing network.
B) distribution hierarchy.
C) marketing chain.
D) distribution matrix.
E) marketing channel.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An administered vertical marketing system is a marketing system
A) that achieves coordination at successive stages of production and distribution by contractual agreements between channel members.
B) that achieves coordination at successive stages of production and distribution by cooperation and consensus among all members of the marketing chain.
C) that achieves coordination at successive stages of production and distribution by the size and influence of one channel member rather than through ownership.
D) in which a channel member (producer, wholesaler, or retailer) is elected to coordinate, direct, and support all other channel members.
E) that is run and coordinated completely outside the traditional chain of distribution by a firm that specializes in that industry's specific logistics needs.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Allowing consumers to buy products by interacting with various advertising media without a face-to-face meeting with a salesperson is referred to as
A) an indirect marketing channel.
B) a direct to consumer marketing channel.
C) a multimarketing channel.
D) channel bypass marketing.
E) personal selling.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the first step in choosing the right supply chain?
A) Understand the supply chain.
B) Develop a list of qualified channel members.
C) Enumerate logistics specifications.
D) Compare multiple-channel alternatives.
E) Understand the customer.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In some instances, firms pair multiple channels with a multibrand strategy. The purpose of this strategy is to ________ of the firm's family brand and differentiate its marketing channels.
A) create greater perceived value
B) maximize channel profits
C) minimize cannibalization
D) generate awareness
E) create a "backup" channel
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
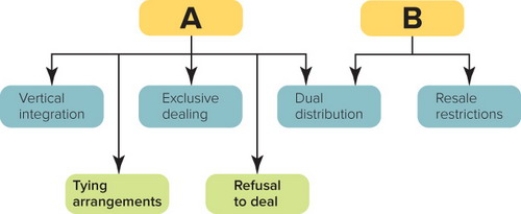 Figure 15-7
-Figure 15-7 above shows six channel practices that restrain competition, create monopolies, or otherwise represent unfair methods of competition. Box A represents which federal legislation meant to curb them?
Figure 15-7
-Figure 15-7 above shows six channel practices that restrain competition, create monopolies, or otherwise represent unfair methods of competition. Box A represents which federal legislation meant to curb them?
A) Sherman Act
B) Robinson-Patman Act
C) Federal Trade Commission Act
D) Consumer Goods Pricing Act
E) Clayton Act
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Extending credit to customers is an example of a ________ function performed by channel intermediaries.
A) transactional
B) logistical
C) facilitating
D) buying
E) risk-taking
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A large company produces paint and other home decorating products. Its goal is to choose the marketing channel arrangement that will give it the most control over supply sources. Which marketing channel system should this company choose?
A) a contractual vertical marketing system
B) an administered vertical marketing system
C) a corporate vertical marketing system
D) an integrated marketing system
E) a corporate horizontal marketing system
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Risk taking as a transactional function refers to
A) unpredictable costs of transportation because of fuel prices.
B) product liability from poorly produced products that become defective.
C) the need to stock merchandise in anticipation of sales.
D) trying new promotional campaigns.
E) investments in new-product development.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Nestlé and General Mills have ________ to distribute General Mills products like Cheerios under the Nestlé brand name in about 140 markets worldwide.
A) multichannel distribution
B) a direct marketing channel
C) a cooperative distribution channel
D) a strategic channel alliance
E) a dual distribution agreement
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The various firms involved in performing the activities required to create and deliver a product or service to ultimate consumers or industrial users are referred to as
A) strategic distribution.
B) distribution management.
C) a supply chain.
D) value chain optimization.
E) logistics.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A fast-food franchisee is required by its franchisor to buy unmarked plastic eating utensils from the franchisor if the franchisee wants to use the cups, napkins, and other paper products with the franchise logo. The franchisee can buy the identical utensils from a local supplier for half the price. This requirement would be an example of
A) a dual distribution network.
B) a refusal to deal.
C) an exclusive dealing.
D) a tying arrangement.
E) a resale restriction.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The three basic functions intermediaries perform are
A) planning, implementing, and evaluating functions.
B) implementation, accommodating, and contractual functions.
C) contractual, facilitating, and logistical functions.
D) transactional, logistical, and facilitating functions.
E) facilitating, accommodating, and implementation functions.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A supply chain refers to
A) the various firms involved in performing the activities required to create and deliver a product or service to ultimate consumers or industrial users.
B) an inventory management system where the supplier determines the product amount and assortment a retailer needs and automatically delivers the appropriate items.
C) mathematical formulas and calculations used in determining product volume and demand in order to generate the greatest revenue at the lowest cost.
D) activities that focus on getting the right amount of the right products to the right place at the right time at the lowest possible cost.
E) a specialized intermediary in the distribution chain responsible for the coordination of all production schedules.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A retailer-sponsored cooperative involves
A) small, independent retailers forming an organization that operates a wholesale facility cooperatively.
B) a vertical marketing system that uses a contractual relationship between a wholesaler and small independent retailers to standardize and coordinate buying practices, merchandising programs, and inventory management.
C) an agreement among small, privately owned manufacturers to pool their resources by sharing installations, heavy equipment, and warehousing they would be unable to afford on their own.
D) an agreement among retailers to pool their resources by purchasing services such as signage, snow removal, and trash removal that affects the physical space (strip mall, etc.) they all share.
E) small, independent retailers that pool their resources to finance store expansion programs.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The objective of logistics management in a customer-driven supply chain is to minimize logistics costs while
A) satisfying suppliers.
B) maximizing profits.
C) maximizing supply chain membership.
D) delivering the appropriate level of customer service.
E) maximizing supply chain inefficiency.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Franchising refers to
A) a contractual agreement between multiple retailers sharing the same business mission to operate with a consistent business model to not only achieve enhanced buying power but also increase customer loyalty.
B) a contractual arrangement between a parent company and an individual or firm that allows the latter to operate a certain type of business under an established name and according to specific rules.
C) purchasing the name, branding, and raw materials from one organization and transferring it to another.
D) a practice whereby one firm's marketing channel is used to sell another firm's product.
E) selling an idea to a larger company and letting it do all the manufacturing, distribution, and marketing.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In choosing the appropriate marketing channel, a firm should consider the interests that buyers might want fulfilled. These interests fall into four broad categories, one of which is
A) profitability.
B) information.
C) quality.
D) brand-name recognition.
E) availability.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 121 - 140 of 304
Related Exams