A) pulmonary ventilation.
B) internal respiration.
C) external respiration.
D) expiration.
E) inspiration.
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Where is the uvula? 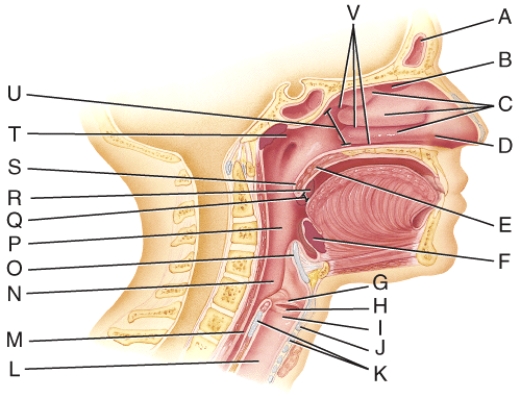
A) E
B) F
C) Q
D) S
E) U
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What line is pointing to the left terminal bronchiole? 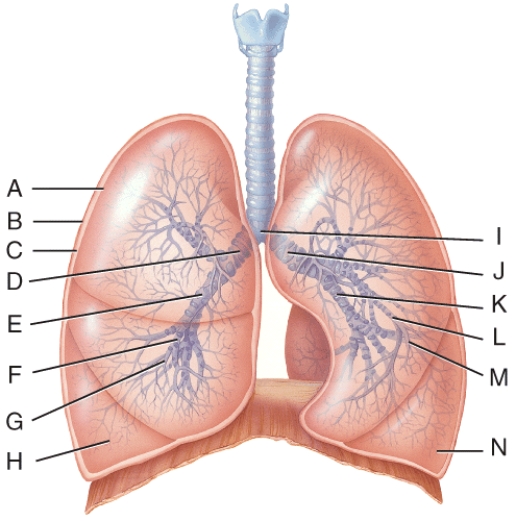
A) G
B) N
C) H
D) A
E) None of these choices
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The basic rhythm of respiration is controlled by the
A) pons.
B) medulla oblongata.
C) hypothalamus.
D) pneumotaxic area.
E) apneustic area.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the below tissues maintains open airways in the lower respiratory system?
A) stratified squamous epithelium with keratin
B) ciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelium with goblet cells
C) hyaline cartilage
D) mucus membrane
E) bone
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Exhalation begins when
A) inspiratory muscles relax.
B) the diaphragm contracts.
C) blood circulation is the lowest.
D) inspiratory muscles relax and the diaphragm contracts.
E) All of these choices.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Where are the nasal conchae? 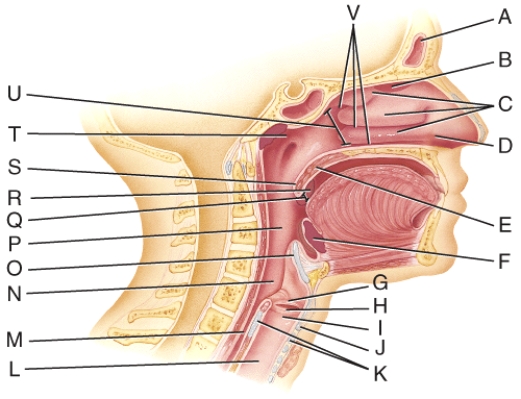
A) A
B) C
C) T
D) U
E) V
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Identify the alveolar sac. 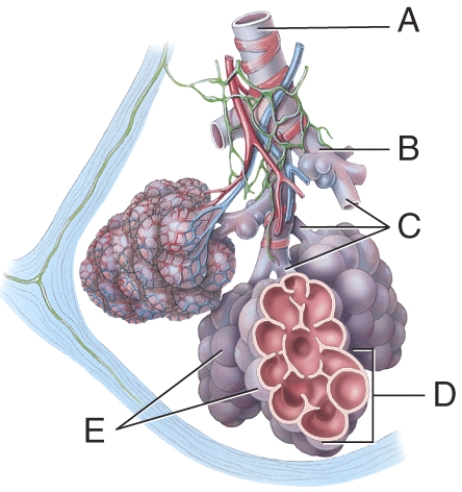
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
This is located anterior to the esophagus and carries air to the bronchi.
A) trachea
B) larynx
C) nasopharynx
D) pharynx
E) None of these choices.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is a passageway for air and food?
A) pharynx
B) larynx
C) paranasal sinuses
D) trachea
E) esophagus
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
This means the lungs and the chest wall expand easily.
A) high surface tension
B) low surface tension
C) high compliance
D) low compliance
E) None of these choices
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is line D pointing to? 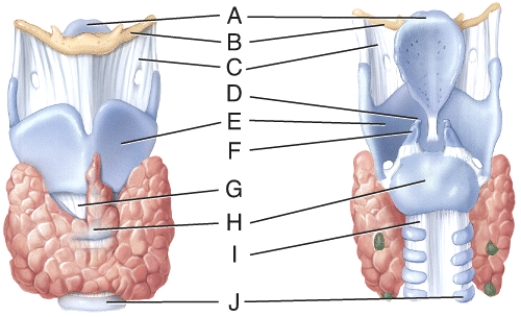
A) thyrohyoid membrane
B) arytenoid cartilage
C) cricothyroid ligament
D) cricoid cartilage
E) tracheal cartilage
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
These are cells of the alveoli that produce surfactant.
A) type I alveolar cells
B) type II alveolar cells
C) type III alveolar cells
D) surface cells
E) macrophages
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The conducting airways with the air that does not undergo gas exchange are known as the
A) inspiratory volume.
B) expiratory reserve volume.
C) minimal volume.
D) residual volume.
E) anatomic dead space.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When blood pH drops then the amount of oxyhemoglobin ___ and oxygen delivery to the tissue cells ___.
A) increases, increases
B) increases, decreases
C) decreases, increases
D) decreases, decreases
E) does not change, does not change
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is not a factor that the rate of pulmonary and systemic gas exchange depends on?
A) partial pressure difference of the gases
B) surface area for gas exchange
C) diffusion distance
D) molecular weight and solubility of the gases
E) force of contraction of diaphragm
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For air to enter the lungs during inhalation
A) the pressure inside the lungs must become lower than the atmospheric pressure.
B) the pressure inside the lungs must be higher than the atmospheric pressure.
C) the pressure inside the lungs must be equal to the atmospheric pressure.
D) the size of the lungs must be decreased.
E) the diaphragm has to be relaxed.
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which is the dominant method of carbon dioxide transport?
A) bound to hemoglobin
B) bound to oxygen
C) dissolved in plasma as a gas
D) dissolved in plasma as bicarbonate ions
E) diffusion
Correct Answer

verified
D
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is not part of the upper respiratory system?
A) nose
B) oral cavity
C) pharynx
D) trachea
E) nasal meatuses
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which cells are the main sites of gas exchange? 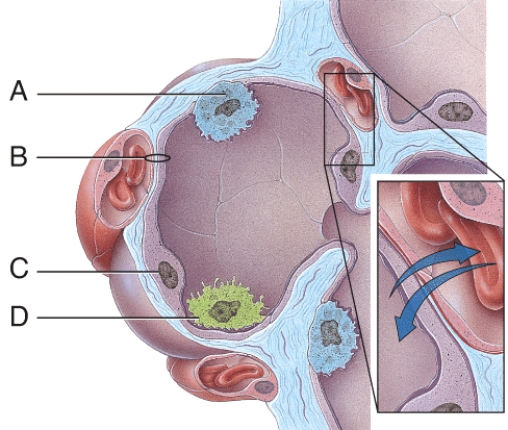
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) All of these choices
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 56
Related Exams