A) $1.
B) $6.
C) $10.
D) $60.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Refer to the information provided in Figure 6.5 below to answer the question(s) that follow. 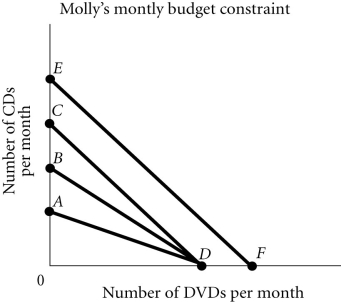 Figure 6.5
-Refer to Figure 6.5. Molly's budget constraint is AD. If her income decreases, her new budget constraint is
Figure 6.5
-Refer to Figure 6.5. Molly's budget constraint is AD. If her income decreases, her new budget constraint is
A) CD.
B) BD.
C) EF.
D) not shown on this graph.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Refer to the information provided in Figure 6.1 below to answer the question(s) that follow. 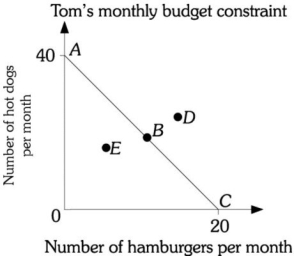 Figure 6.1
-Refer to Figure 6.1. Tom's budget constraint is AC. His choice set includes all points
Figure 6.1
-Refer to Figure 6.1. Tom's budget constraint is AC. His choice set includes all points
A) to the right of budget constraint AC.
B) bounded by the area OAC.
C) along budget constraint AC.
D) along the vertical and horizontal axes.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Refer to the information provided in Figure 6.13 below to answer the question(s) that follow. 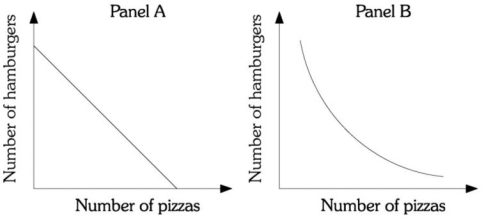
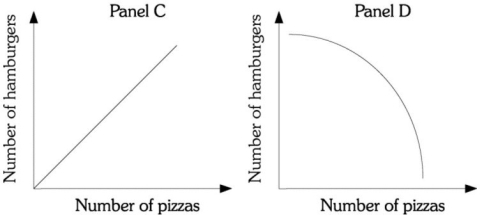 Figure 6.13
-Refer to Figure 6.13. Assume Megan has two products available, pizza and hamburgers. Megan must be compensated with more hamburgers as she gives up more pizzas. The curve in Panel ________ represents her indifference curve.
Figure 6.13
-Refer to Figure 6.13. Assume Megan has two products available, pizza and hamburgers. Megan must be compensated with more hamburgers as she gives up more pizzas. The curve in Panel ________ represents her indifference curve.
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a household's income rises by 30%, its budget constraint will
A) shift out parallel to the old one.
B) pivot at the Y-intercept.
C) shift in parallel to the old one.
D) be unaffected.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Refer to the information provided in Figure 6.7 below to answer the question(s) that follow.  Figure 6.7
-Refer to Figure 6.7. Along budget constraint AB, the price of good X is $10 and the price of good Y is $12. If the price of X increases to $15, the budget constraint will
Figure 6.7
-Refer to Figure 6.7. Along budget constraint AB, the price of good X is $10 and the price of good Y is $12. If the price of X increases to $15, the budget constraint will
A) pivot in at point B.
B) pivot out at point A.
C) shift in parallel to AB.
D) pivot in at point A.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Refer to the information provided in Table 6.4 below to answer the question(s) that follow. Table 6.4 -Refer to Table 6.4. The total utility of five donuts per day is
A) 230.
B) 240.
C) 260.
D) indeterminate from this information.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Related to the Economics in Practice on page 125: A reduction in the salience of prices should make demand for those products
A) more elastic.
B) less elastic.
C) perfectly inelastic.
D) perfectly elastic.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Refer to the information provided in Figure 6.2 below to answer the question(s) that follow. 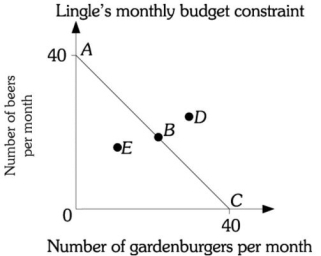 Figure 6.2
-Refer to Figure 6.2. Assume Mr. Lingle is on budget constraint AC. If the price of a gardenburger is $5, Mr. Lingleʹs monthly income is
Figure 6.2
-Refer to Figure 6.2. Assume Mr. Lingle is on budget constraint AC. If the price of a gardenburger is $5, Mr. Lingleʹs monthly income is
A) $8.
B) $150.
C) $200.
D) $240.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
An indifference curve is a set of points, each point representing a combination of two goods, all of which represent the same total utility.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Harry tells you that he prefers Pepsi to Coke, Coke to 7-UP, and 7-UP to Pepsi. This violates what assumption made when analyzing consumer preferences?
A) that more is better
B) that there is a diminishing marginal rate of substitution
C) that consumers are rational
D) that consumers are able to choose among all the combinations of goods and services available
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Refer to the information provided in Figure 6.14 below to answer the question(s) that follow. 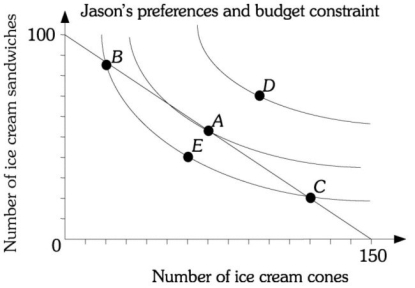 Figure 6.14
-Refer to Figure 6.14. Jason maximizes utility at point
Figure 6.14
-Refer to Figure 6.14. Jason maximizes utility at point
A) A.
B) B.
C) C.
D) D.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Assuming that charitable giving is a normal good, the income effect of a decrease in personal tax rates would lead to
A) less giving because giving to charity would become more expensive relative to other goods.
B) more giving because giving to charity would become less expensive relative to other goods.
C) more giving because households would have more disposable income.
D) less giving because households would spend that money on luxury goods.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A consumer satisfies the condition MUx/Px = MUy/Py when his indifference curve ________ his budget constraint.
A) is completely above
B) is completely below
C) is just tangent to
D) crosses
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
When the price of a good decreases, the budget constraint shifts out parallel to the original budget constraint.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the price of a normal good falls, the income effect will result in households buying ________ of the good and the substitution effect will result in households buying ________ of the good.
A) more; more
B) more; less
C) less; more
D) less; less
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Refer to the information provided in Figure 6.1 below to answer the question(s) that follow.  Figure 6.1
-Refer to Figure 6.1. Along budget constraint AC, the opportunity cost of one hamburger
Figure 6.1
-Refer to Figure 6.1. Along budget constraint AC, the opportunity cost of one hamburger
A) is 1/4 of a hot dog.
B) is 1/2 of a hot dog.
C) is 2 hot dogs.
D) changes as you move down along the budget constraint.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Refer to the information provided in Figure 6.3 below to answer the question(s) that follow. 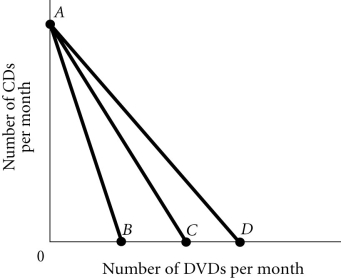 Figure 6.3
-Refer to Figure 6.3. Mollyʹs budget constraint is AD. It would swivel to AB if the price of
Figure 6.3
-Refer to Figure 6.3. Mollyʹs budget constraint is AD. It would swivel to AB if the price of
A) DVDs increased.
B) DVDs decreased.
C) CDs increased.
D) CDs decreased.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Juanita is spending her entire income on goods X and Y. Her marginal utility from the last unit of X is 50 and the marginal utility from the last unit of Y that she consumes is 100. Juanita's utility is only maximized if
A) the prices of X and Y are the same.
B) the price of good X is twice that of good Y.
C) the price of good Y is twice that of good X.
D) We cannot determine whether Juanita is maximizing her utility.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Refer to the information provided in Figure 6.5 below to answer the question(s) that follow.  Figure 6.5
-Refer to Figure 6.5. Molly's budget constraint is BD. Molly's income is $400, the price of a DVD is $15 and the price of a CD is $20. At point B she is buying ________ DVDs and ________ CDs.
Figure 6.5
-Refer to Figure 6.5. Molly's budget constraint is BD. Molly's income is $400, the price of a DVD is $15 and the price of a CD is $20. At point B she is buying ________ DVDs and ________ CDs.
A) 0; 20
B) 20; 0
C) 20; 15
D) 40; 30
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 272
Related Exams