A) Pareto optimal.
B) not productively efficient.
C) allocatively efficient.
D) one at which P = MC for all goods.
E) productively efficient.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The economic efficiency of a natural monopoly can be improved with the use of two- part tariffs because it allows the monopoly to
A) charge users according to their willingness to pay.
B) lower its total costs.
C) charge residential users different rates than business users.
D) charge users according to their ability to pay.
E) charge users separately for fixed and variable costs.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the absence of market failures, allocative efficiency is achieved in a perfectly competitive industry because
A) firms do not need to maximize profits.
B) the industry produces a level of output such that there are increasing returns to scale.
C) the industry produces a level of output such that the marginal cost to producers equals the marginal benefit to consumers.
D) there are barriers to entry.
E) the industry produces a level of output such that the marginal cost of production is minimized.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An economy with no market failures and all industries are in a competitive long- run equilibrium is one where 1. allocative efficiency is achieved; 2. the economy is on the production possibilities boundary; 3. there is no incentive for firms to enter or leave industries.
A) 1 and 3
B) 2 and 3
C) 1 and 2
D) 1, 2, and 3
E) 2 only
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider three firms, A, B and C, all producing kilos of potatoes (per year) in a perfectly competitive market. The diagrams below show marginal cost curves for each of the three firms. 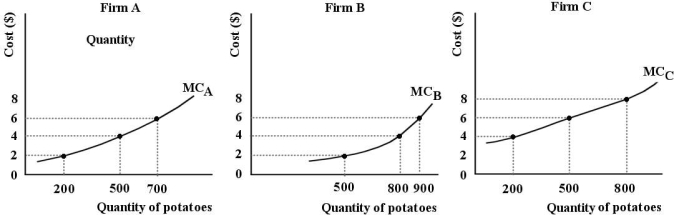 FIGURE 12- 1
-Refer to Figure 12- 1. Suppose each of Firms A, B, and C are producing 500 kilos of potatoes. Is this industry allocatively efficient?
FIGURE 12- 1
-Refer to Figure 12- 1. Suppose each of Firms A, B, and C are producing 500 kilos of potatoes. Is this industry allocatively efficient?
A) It is not possible to say whether this industry is allocatively efficient because we do not know the market price for kilos of potatoes.
B) Yes, because output is equated for all firms.
C) It is not possible to say whether this industry is allocatively efficient because we do not know the average costs for each firm.
D) No, since marginal costs are not equated for all firms, the industry is not productively efficient, and thus cannot be allocatively efficient.
E) No, because the marginal cost curve for each firm has a different slope.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The objective of government regulation and competition policy is best described as a means to
A) promote economic efficiency.
B) reduce inequality in the economy.
C) make at least one person better off at the expense of others.
D) increase fairness in economic activities.
E) eliminate all market power.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Allocative efficiency is actively sought
A) only by profit- maximizing imperfectly- competitive firms.
B) by none of the firms in any market.
C) only by perfectly- competitive firms.
D) by all firms in all markets.
E) by profit- maximizing firms in all market structures.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consumer surplus represents
A) the marginal value that consumers place on the last unit consumed of a good.
B) the value that consumers place on the last unit consumed of a good.
C) the quantity consumed in excess of the allocatively efficient amount.
D) the total value that consumers place on the quantity consumed of some good.
E) the difference between the value that consumers place on a good and the payment they make to buy the good, summed over the quantity consumed.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider two firms, A and B, that are producing the same product but with different marginal costs. In this case,
A) neither firm is producing its output at the lowest attainable cost.
B) each firm is being wasteful.
C) a reallocation of output between the firms can lower the industry's total cost.
D) one firm is not maximizing profits.
E) some resources must be unemployed.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For an entire economy, allocative efficiency requires that
A) MRP is equated for all factors of production.
B) goods are allocated equitably across markets.
C) MC = P for all goods.
D) price is greater than marginal cost for all goods.
E) price equals average cost for all goods.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The diagram below shows supply, demand, and quantity exchanged of Monday matinee movie tickets. Assume it is a perfectly competitive market. 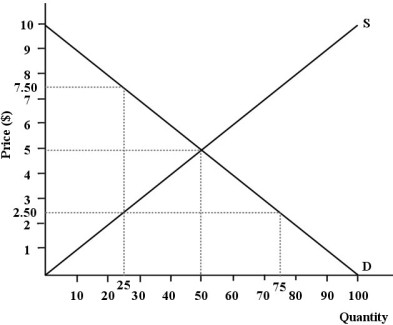 FIGURE 12- 4
-Refer to Figure 12- 4. Suppose a disequilibrium price of $7.50 per movie ticket is imposed on this market. The total economic surplus is now _ , which is than the total economic surplus generated at the allocatively efficient level of output.
FIGURE 12- 4
-Refer to Figure 12- 4. Suppose a disequilibrium price of $7.50 per movie ticket is imposed on this market. The total economic surplus is now _ , which is than the total economic surplus generated at the allocatively efficient level of output.
A) $187.50; $62.50 less
B) $125; $250 less
C) $62.50; $125 less
D) $125; $125 less
E) $187.50; $187.50 less
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The diagram below shows the demand and supply curves in a perfectly competitive market. 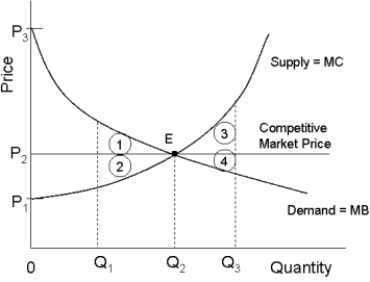 FIGURE 12- 5
-Refer to Figure 12- 5. If output in this market were Q3, and the price was still equal to its
Free- market level, the loss in producer surplus relative to the competitive equilibrium would be illustrated by area
FIGURE 12- 5
-Refer to Figure 12- 5. If output in this market were Q3, and the price was still equal to its
Free- market level, the loss in producer surplus relative to the competitive equilibrium would be illustrated by area
A) 3 + 4.
B) 4.
C) 1.
D) 2.
E) 3.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the absence of market failures, allocative efficiency is achieved only under perfect competition because only this market structure results in
A) productive efficiency.
B) P = MC.
C) complete freedom of entry and exit.
D) zero long- run profits.
E) maximization of profits through competition.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The diagram below shows cost and revenue curves for a natural monopoly producing electricity. Price is dollars per kilowatt hour and quantity is kilowatt hours per day. 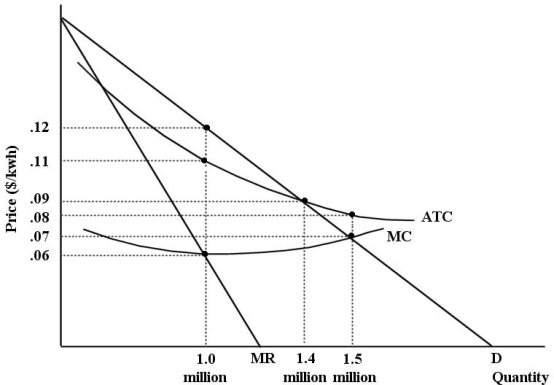 FIGURE 12- 7
-Refer to Figure 12- 7. Suppose this firm is being regulated using a policy of marginal- cost pricing. The resulting price and output would be per kwh and kwh per day.
FIGURE 12- 7
-Refer to Figure 12- 7. Suppose this firm is being regulated using a policy of marginal- cost pricing. The resulting price and output would be per kwh and kwh per day.
A) $0.09; 1.4 million
B) $0.06; 1 million
C) $0.08; 1.5 million
D) $0.07; 1.5 million
E) $0.12; 1 million
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a perfectly competitive industry was suddenly monopolized without any change in cost conditions,
A) price would increase and quantity produced would decrease.
B) price would decrease and quantity produced would increase.
C) there would be no change in either price or quantity produced.
D) both price and quantity produced would decrease.
E) both price and quantity produced would increase.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Allocative efficiency occurs when
A) the sum of consumer and producer surplus is maximized.
B) deadweight loss is achieved.
C) the economy achieves the frontier of the production possibilities boundary.
D) producer surplus is maximized.
E) consumer surplus is maximized.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose a cell- phone service provider has monopoly rights for a geographical region and is earning monopoly profits. If the government then imposes a lump- sum tax of $X on this firm, the effect is
A) to increase the firm's average costs and reduce its profit by $X.
B) an increase in output and a decrease in price.
C) a reduction in output and an increase in price.
D) to increase the firm's marginal costs and reduce its profit by $X.
E) an increase in consumer surplus due to the tax revenue.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider a regulated natural monopoly, such as an electricity distribution company, that faces falling long- run average costs. If it is forced to price its output at average cost it will provide
A) less output than what is socially optimal.
B) so little output that there will be a shortage.
C) the socially optimal amount of output.
D) more output than what is socially optimal.
E) more output than can be absorbed by the market.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider the case of a natural monopoly with falling average total costs. If regulation sets the price equal to marginal cost, then
A) the firm would earn economic profits.
B) the outcome would be allocatively inefficient.
C) shortages would result.
D) the firm would operate at a loss and eventually go out of business.
E) the demand curve would shift to the left.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The diagram below shows supply, demand, and quantity exchanged of Monday matinee movie tickets. Assume it is a perfectly competitive market. 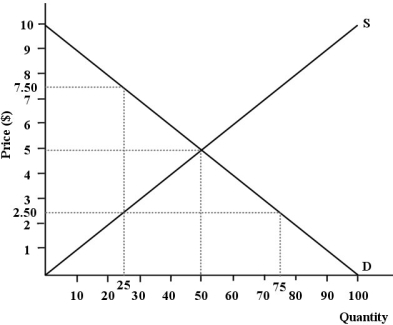 FIGURE 12- 4
-Refer to Figure 12- 4. What is the total economic surplus generated in this market at the allocatively efficient level of output?
FIGURE 12- 4
-Refer to Figure 12- 4. What is the total economic surplus generated in this market at the allocatively efficient level of output?
A) $500
B) $125
C) $250
D) $5
E) $10
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 61 - 80 of 109
Related Exams