Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the aggregate expenditures model, equilibrium GDP in a private closed economy is indicated by:
A) the equality of saving and planned investment.
B) the intersection of aggregate expenditures and the 45-degree line.
C) the absence of unplanned changes in inventories.
D) all of the above.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
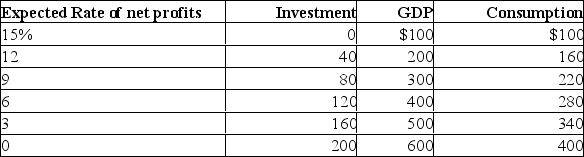 Refer to the above information.In this economy a 3 percentage point decrease in the interest rate will:
Refer to the above information.In this economy a 3 percentage point decrease in the interest rate will:
A) increase equilibrium GDP by $200.
B) increase equilibrium GDP by $100.
C) increase equilibrium GDP by $50.
D) decrease equilibrium GDP by $50.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
All else equal, a large decline in the real interest rate will shift the:
A) investment-demand curve leftward.
B) investment-demand curve rightward.
C) investment schedule upward.
D) investment schedule downward.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The open economy multiplier is:
A) larger than the simple multiplier because the latter embodies fewer leakages.
B) larger than the simple multiplier because the latter embodies more leakages.
C) smaller than the simple multiplier because the latter embodies fewer leakages.
D) smaller than the simple multiplier because the latter embodies more leakages.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A lump-sum tax causes the after-tax consumption schedule:
A) and the before-tax consumption schedule to coincide.
B) to be steeper than the before-tax consumption schedule.
C) to be flatter than the before-tax consumption schedule.
D) to be parallel to the before-tax consumption schedule.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In a private closed economy (a) the marginal propensity to save is 0.25, (b) consumption equals income when consumption is $120 billion, and (c) the level of investment is $40 billion.What is the equilibrium level of income?
A) $280 billion
B) $320 billion
C) $262 billion
D) $198 billion
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
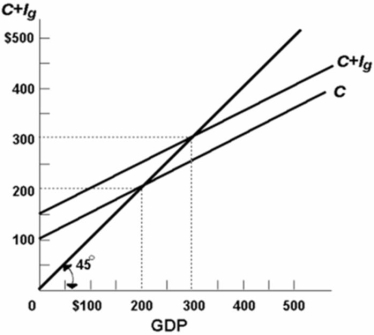 Refer to the above diagram for a private closed economy.At the $200 level of GDP:
Refer to the above diagram for a private closed economy.At the $200 level of GDP:
A) consumption is $200 and planned investment is $50 so that aggregate expenditures are $250.
B) consumption is $200 and planned investment is $100 so that aggregate expenditures are $300.
C) consumption is $250 and actual investment is $50 so that aggregate expenditures are $300.
D) aggregate expenditures is equal to the GDP.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the MPC is.50, all taxes are lump-sum taxes, and the equilibrium GDP is $40 billion below the full-employment GDP, then the size of the recessionary expenditure gap:
A) is $40 billion.
B) is $20 billion.
C) is $60 billion.
D) cannot be determined from the information given.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In a private closed economy, where aggregate expenditures exceed domestic output:
A) domestic output will decline to the break-even level.
B) business inventories will rise.
C) saving exceeds planned investment.
D) planned investment exceeds saving.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If government increases lump-sum taxes by $20 billion and the economy's MPC is .6, then the:
A) consumption schedule will shift upward by $12 billion.
B) consumption schedule will shift downward by $12 billion.
C) equilibrium GDP will increase by $40 billion.
D) equilibrium GDP will decrease by $12 billion.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The equilibrium level of GDP is associated with:
A) an excess of planned investment over saving.
B) no unintended investment in inventories.
C) an unintended decrease in business inventories.
D) an unintended increase in business inventories.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If net exports decrease from zero to some negative amount, the aggregate expenditures schedule would:
A) shift upward.
B) shift downward.
C) not move (net exports do not affect aggregate expenditures) .
D) shift upward or downward, depending on whether the negative net exports resulted from a decline in exports or an increase in imports.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The table shows a private, open economy.All figures are in billions of dollars. 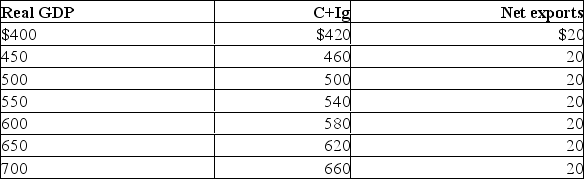 Refer to the above table.If net exports increased by $10 billion at each level of GDP, the equilibrium real GDP would be:
Refer to the above table.If net exports increased by $10 billion at each level of GDP, the equilibrium real GDP would be:
A) $550
B) $600
C) $650
D) $700
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The relationship between investment and GDP is shown by the:
A) consumption of fixed capital schedule.
B) saving schedule.
C) investment schedule.
D) consumption schedule.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is a correct statement of the impacts of a lump-sum tax?
A) Disposable income will increase by the amount of the tax and consumption at each level of GDP will decline by the amount of the tax multiplied by the MPC.
B) Disposable income will decline by the amount of the tax and consumption at each level of GDP will decline by the amount of the tax multiplied by the multiplier.
C) Disposable income will decline by the amount of the tax and consumption at each level of GDP will also decline by the amount of the tax.
D) Disposable income will decline by the amount of the tax and consumption at each level of GDP will decline by the amount of the tax multiplied by the MPC.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If APC = .6 and MPC = .7, the immediate impact of an increase in personal taxes of $20 will be to:
A) have no effect on consumption.
B) decrease consumption by $14.
C) decrease consumption by $12.
D) increase consumption by $14.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The equilibrium level of GDP always coincides with the full-employment GDP.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Equal increases in government expenditures and tax collections will leave the equilibrium GDP unchanged.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
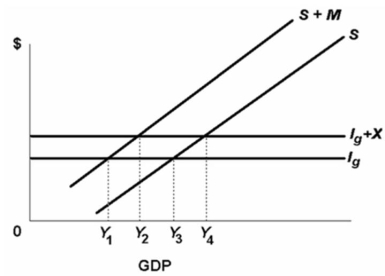 Refer to the above diagram.The equilibrium condition for a private open economy is S + M = Ig + X.
Refer to the above diagram.The equilibrium condition for a private open economy is S + M = Ig + X.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 141 - 160 of 238
Related Exams