A) higher the future payment they will expect to receive.
B) lower the future payment they will expect to receive.
C) lower the risk of not receiving that future payment.
D) more they will want to invest.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Stocks represent a debt, and buyers of stock expect to earn interest.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
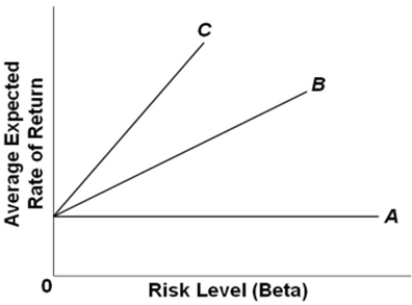 Refer to the graph.The intercept of the three Security Market Lines is determined by
Refer to the graph.The intercept of the three Security Market Lines is determined by
A) the risk-free interest rate.
B) the interest rate on financial assets with a beta of 1.
C) the rate on long-term U.S.government bonds.
D) all of these.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The primary risk that bondholders face is that
A) the bond will reduce in price.
B) the bond issuer will default.
C) inflation will decrease.
D) the rate of return will increase.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The idea that money has "time value" refers to the fact that
A) people prefer to receive a given sum of money in the future rather than in the present.
B) money can be used to purchase the services of labor, as measured in hourly units.
C) a specific amount of money is more valuable to a person the sooner it is received.
D) compound interest converts future dollars into a greater amount of current dollars.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The U.S.federal government is unlikely to default on its bond payments because
A) if necessary, it can print the money needed to make payments on time.
B) its bond payments are insured.
C) the U.S.federal budget usually runs a surplus, providing ample funds for repaying debt.
D) of all of these.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
One statistic that quantifies the risk of an investment is
A) alpha.
B) beta.
C) gamma.
D) the average expected rate of return.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Payments to shareholders from corporate profits are known as
A) dividends.
B) capital gains.
C) interest.
D) appreciation.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Lottery winners who take the lump-sum payouts instead of payments spread out over many years
A) believe the rate of return they could find in other financial assets is less than that implied in the extended payout.
B) sacrifice free money and are making an economically irrational decision.
C) prefer immediate to delayed returns.
D) are only making a rational economic decision if there is rapid inflation.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose stock X has a beta of 2.5 and stock Y has a beta of 0.5.From this we can conclude that X has
A) 5 times the nondiversifiable risk of the market portfolio.
B) 5 times the nondiversifiable risk of Y.
C) 2.5 times the nondiversifiable risk of Y.
D) 2.5 times the diversifiable risk of the market portfolio.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Investors evaluate an investment by estimating its average expected rate of return, and this estimation process assigns higher weights to
A) higher returns.
B) more likely outcomes.
C) higher risks.
D) smaller returns.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is considered to be the best measure of the risk-free interest rate?
A) the rate of return on a corporate bond index fund
B) the rate of return on a corporate stock index fund
C) the rate of return on the Standard and Poor's 500
D) the rate of return on short-term U.S.government bonds
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Diversification in one's investments reduces
A) idiosyncratic risk.
B) pooling risk.
C) systemic risk.
D) time preference risk.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which one of the following would best describe a mutual fund?
A) an investment that is available at many banks and is FDIC insured
B) a company that manages a portfolio that is purchased by pooling the money of its investors
C) a debt contract that is issued by a company and offers interest payment on the loan
D) ownership of shares in a corporation with no guarantee the company will be profitable
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
One asset has a beta of 1.5 and another asset has a beta of 0.75.The difference in beta means that the asset with a beta of 0.75 has
A) 75 percent less nondiversifiable risk than the asset with a beta of 1.5.
B) 75 percent more nondiversifiable risk than the asset with a beta of 1.5.
C) twice as much nondiversifiable risk as the asset with a beta of 1.5.
D) one-half as much nondiversifiable risk as the asset with a beta of 1.5.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Investments that are designed to match exactly the performance of a group of stocks like the Dow Jones Industrial Average or the S&P 500 are called
A) index funds.
B) dividend funds.
C) portfolio funds.
D) capital gain funds.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A horizontal Security Market Line would imply that investors
A) are unconcerned about risk and require no additional compensation for risk.
B) view all financial assets as equally risky.
C) greatly dislike risk and must be compensated for it.
D) prefer assets with greater risk.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose that Betty takes out a loan for $300 at an annually compounded interest rate of 6 percent to be repaid after five years.How much will be required to pay off the loan at the end of the five years?
A) $401.47
B) $390
C) $393.54
D) $408.75
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Security Market line (SML) shows how the average expected rates of return on assets vary with
A) stock price.
B) dividend payment.
C) risk level.
D) time preference.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The present value of a stream of lottery payments is less than the size of the stated jackpot.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 121 - 140 of 323
Related Exams