Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The key to assessing whether fiscal policy is expansionary is to observe the change in the full-employment budget as a percentage of GDP.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Increased government spending for investments such as highways or harbours financed by increasing the public debt would most likely:
A) crowd out future public investment.
B) reduce the economy's future productive capacity.
C) increase the amount of public capital stock in the future.
D) increase the amount of private capital stock in the future.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The higher domestic interest rate resulting from an expansionary fiscal policy in Canada will tend to:
A) increase domestic investment spending.
B) increase Canadian exports.
C) increase domestic consumption spending.
D) decrease Canadian exports.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The "crowding-out effect" suggests that:
A) tax increases are paid primarily out of saving and therefore are not an effective fiscal device.
B) increases in government spending financed through borrowing will increase the interest rate and thereby reduce investment.
C) it is very difficult to have excessive aggregate spending in our economy.
D) consumer and investment spending always vary inversely.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In an economy, the government wants to increase aggregate demand by $60 billion at each price level to increase real GDP and reduce unemployment.If the MPC is .9, then it could:
A) decrease taxes by $6 billion.
B) decrease taxes by $12 billion.
C) increase government spending by $6 billion.
D) increase government spending by $12 billion.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
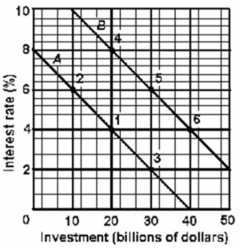 Refer to the above graph.If the economy was initially in equilibrium at point 3 and interest rates increase by 4 percentage points, then the crowding-out effect would be:
Refer to the above graph.If the economy was initially in equilibrium at point 3 and interest rates increase by 4 percentage points, then the crowding-out effect would be:
A) $10 billion in investment.
B) $20 billion in investment.
C) $30 billion in investment.
D) $35 billion in investment.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the MPS in an economy is .4, government could shift the aggregate demand curve leftward by $50 billion at each price level by:
A) reducing government expenditures by $125 billion.
B) reducing government expenditures by $20 billion.
C) increasing taxes by $50 billion.
D) increasing taxes by $250 billion.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Like households and businesses, the provincial and municipal governments increase their expenditure during good times and cut them during recession.As a result of such a practice:
A) the economic recession would be eliminated while the inflationary situation is worsened.
B) the economic recession and or inflationary situation is worsened.
C) the economic recession and or inflationary situation is more manageable.
D) the economic recession and or inflationary situation is corrected.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The net export effect works through international trade to:
A) increase the effectiveness of expansionary and contractionary fiscal policy.
B) decrease the effectiveness of expansionary and contractionary fiscal policy.
C) decrease the effectiveness of expansionary fiscal policy and increase the effectiveness of contractionary fiscal policy.
D) increase the effectiveness of expansionary fiscal policy and decrease the effectiveness of contractionary fiscal policy.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Expansionary fiscal policy is so named because it:
A) involves an expansion of the nation's money supply.
B) necessarily expands the size of government.
C) is aimed at achieving greater price stability.
D) is designed to expand real GDP.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
One of the timing problems with fiscal policy is an "operational lag" that occurs between the:
A) beginning of a recession and the time that it is recognized that the event is occurring.
B) time the need for fiscal action is recognized and the time that action is actually taken.
C) time that fiscal action is taken and the time that action has an impact on output, employment, and the price level.
D) time that fiscal action has an impact on output, employment, and the price level and the time by which it can be determined if the policy is effective.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The most likely way the public debt burdens future generations is by:
A) reducing the current level of investment.
B) causing future unemployment.
C) causing a slowly falling price level.
D) reducing real interest rates.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The following budget information is for a hypothetical economy.All data are in billions of dollars. 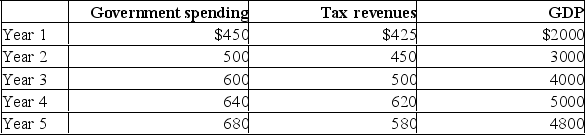 Refer to the above data.If year 1 is the first year of this nation's existence and year 5 is the present year, this nation's public debt is:
Refer to the above data.If year 1 is the first year of this nation's existence and year 5 is the present year, this nation's public debt is:
A) $295 billion.
B) $100 billion.
C) $3540 billion.
D) $230 billion.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
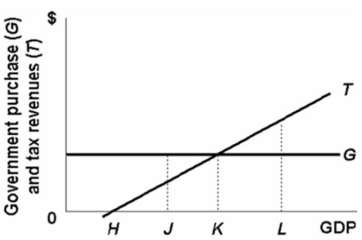 With the expenditures programs and the tax system shown in the above diagram:
With the expenditures programs and the tax system shown in the above diagram:
A) the public budget will be expansionary at all GDP levels above K, and contractionary at all GDP levels below K.
B) the public budget will be a destabilizing force at all levels of GDP.
C) deficits will be realized at income levels below K, and surpluses above K.
D) deficits will be realized at income levels below H, and surpluses above H.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A tax reduction of a specific amount will be more expansionary, the:
A) smaller is the economy's MPC.
B) larger is the economy's MPC.
C) smaller is the economy's multiplier.
D) less the economy's built-in stability.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Built-in stabilizers:
A) intensify the business cycle.
B) reduce the size of the multiplier.
C) increase the government's deficit during a recession.
D) are a part of discretionary fiscal policy.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Actual deficits are:
A) Generally smaller than actual deficits
B) Generally larger than actual deficits
C) Identical to actual deficits
D) Opposite to actual deficits
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The crowding-out effect of borrowing to finance the public debt:
A) decreases current spending for private investment.
B) increases the privately owned stock of real capital.
C) decreases the economic burden on future generations.
D) increases incentives to work and save.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is an example of an automatic stabilizer? As real GDP decreases, income tax revenues:
A) increase and transfer payments decrease.
B) decrease and transfer payments increase.
C) and transfer payments decrease.
D) and transfer payments increase.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 234
Related Exams