A) an oligopoly.
B) a monopoly.
C) monopolistically competitive.
D) perfectly competitive.
E) one where each firm has limited market power.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider the following characteristics of a particular industry: - there is freedom of entry and exit - in long-run equilibrium, each firm is producing a level of output where there are increasing returns to scale This industry is likely to be
A) an oligopoly.
B) highly concentrated.
C) monopolistically competitive.
D) perfectly competitive.
E) a cartel.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An imperfectly competitive industry is often allocatively inefficient when compared to the performance of a competitive industry, because imperfect competitors
A) maximize profits.
B) make profits.
C) obtain economies of scale.
D) operate in the global economy.
E) set price above the marginal cost.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The diagram below shows selected cost and revenue curves for a firm in a monopolistically competitive industry.
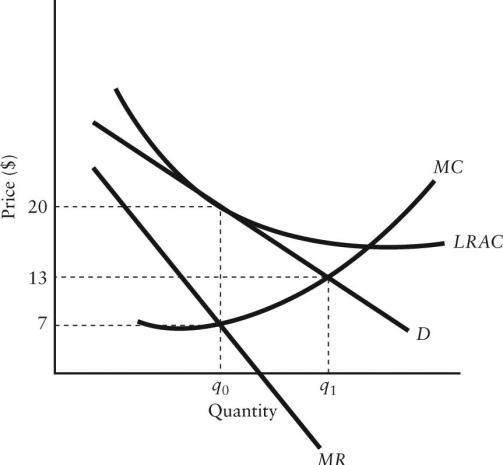 FIGURE 11-4
-Refer to Figure 11-4. How is the excess-capacity theorem demonstrated in this diagram?
FIGURE 11-4
-Refer to Figure 11-4. How is the excess-capacity theorem demonstrated in this diagram?
A) The short-run equilibrium occurs where the firm is producing output at q0, which is less than that corresponding to the lowest point on its LRAC curve.
B) The long-run equilibrium occurs where the firm is producing output at q1, which is the same as for a perfectly competitive industry.
C) In long-run equilibrium the firm is earning positive profits, but has unexploited economies of scale.
D) In long-run equilibrium, this firm has excess capacity because they are selling output at a price below their LRAC.
E) The long-run equilibrium occurs where the firm is producing output at q0, which is less than that corresponding to the lowest point on its LRAC curve.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The diagram below shows selected cost and revenue curves for a firm in a monopolistically competitive industry.
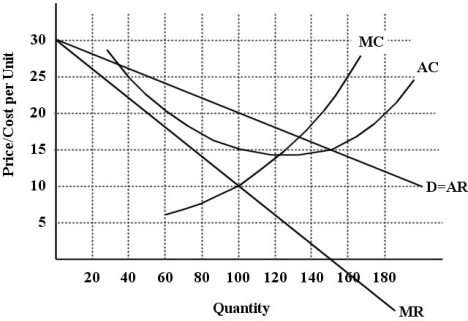 FIGURE 11-1
-Refer to Figure 11-1. Assuming this firm is producing its profit-maximizing level of output, what is the per-unit profit being earned by this firm?
FIGURE 11-1
-Refer to Figure 11-1. Assuming this firm is producing its profit-maximizing level of output, what is the per-unit profit being earned by this firm?
A) -$5
B) -$10
C) $20
D) $10
E) $5
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When a monopolistically competitive industry is in long-run equilibrium, each firm will be operating where price is
A) greater than average total cost but equal to marginal cost.
B) greater than average total cost and greater than marginal cost.
C) equal to average total cost and to marginal cost.
D) greater than marginal cost but equal to average total cost.
E) less than marginal cost and equal to average total cost.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In imperfectly competitive markets, ʺadministeredʺ prices usually change than prices in perfectly competitive markets, because .
A) more often; they are more flexible
B) more often; perfectly competitive firms are price takers
C) more often; price becomes a strategic choice
D) less often; changing prices is costly
E) less often; changing prices is costless
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When a monopolistically competitive industry is in long-run equilibrium, the excess capacity in an individual firm is indicated by the difference between
A) price and marginal cost.
B) the output at which ATC is at a minimum and the output at which price equals marginal cost.
C) zero and the output at which the demand curve is tangent to the ATC curve.
D) price and average cost.
E) the output at which ATC is at a minimum and the output at which marginal revenue is equal to marginal cost.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
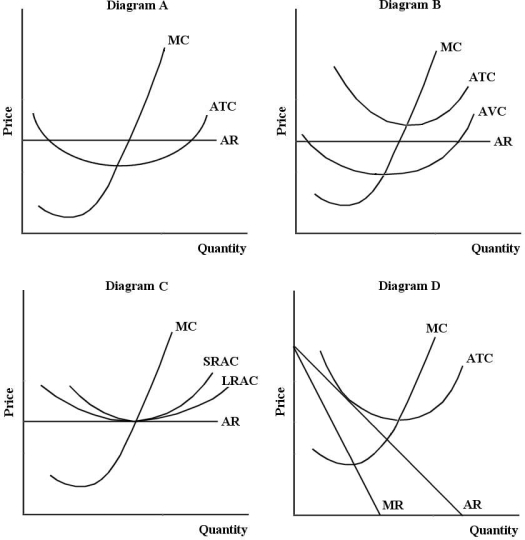 FIGURE 11-2
-Refer to Figure 11-2. A perfectly competitive firm with zero economic profits is depicted in diagram
FIGURE 11-2
-Refer to Figure 11-2. A perfectly competitive firm with zero economic profits is depicted in diagram
A) A.
B) B.
C) C.
D) D.
E) B or D
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In long-run equilibrium, a monopolistically competitive industry operates where
A) P > LRAC.
B) MR > MC.
C) LRAC is increasing.
D) LRAC > minimum average cost.
E) LRAC = MC.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If firms are able to freely enter and exit a monopolistically competitive industry, then we can predict
A) a negatively sloped demand curve for the industry.
B) strategic behaviour with regard to other firms in the industry.
C) brand proliferation.
D) zero profits in long-run equilibrium.
E) that exit will occur until no firm has excess capacity.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Monopolistic competition is similar to perfect competition in that
A) firms in both types of market structures produce a standardized product.
B) strategic behaviour is common to both market structures.
C) neither has significant barriers to entry.
D) each firm faces a horizontal demand curve.
E) firms in both types of market structure engage in non -price competition.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The diagram below shows selected cost and revenue curves for a firm in a monopolistically competitive industry.
 FIGURE 11-1
-Refer to Figure 11-1. What price will this profit-maximizing firm set?
FIGURE 11-1
-Refer to Figure 11-1. What price will this profit-maximizing firm set?
A) $5
B) $10
C) $15
D) $20
E) $25
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose the 2-firm concentration ratio measuring output) in a Canadian manufacturing industry is over 90%. Why might the market power of these 2 firms be less than the concentration ratio suggests?
A) The product is purely domestic and there is no international trade.
B) A high concentration ratio usually indicates low degrees of market power.
C) The product is traded internationally and the two Canadian firms compete with many global rivals.
D) The relevant market is regional and so the concentration ratio is not relevant.
E) A 2-firm concentration ratio does not provide enough information.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In which market structure are price fluctuations most common?
A) price fluctuations occur with the same frequency in all market structures
B) monopoly
C) oligopoly
D) monopolistic competition
E) perfect competition
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The diagram below shows demand and cost curves for a monopolistically competitive firm.
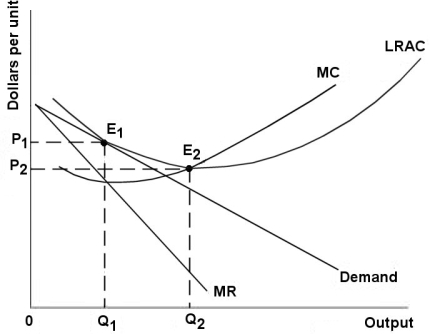 FIGURE 11-3
-Refer to Figure 11-3. If a decrease in industry demand led to an inward shift of each firmʹs demand curve, a typical firm would
FIGURE 11-3
-Refer to Figure 11-3. If a decrease in industry demand led to an inward shift of each firmʹs demand curve, a typical firm would
A) be making profits and new firms would enter the industry in the long run.
B) be making losses and some firms would exit the industry in the long run.
C) exit the industry and the industry would shut down.
D) increase costs in order to break even at PL and QL in the long run.
E) decrease costs in order to break even at PL and QL in the long run.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
 FIGURE 11-2
-Refer to Figure 11-2. The position of a typical firm when the industry is in long-run equilibrium with free entry and exit and product differentiation is exhibited in diagram
FIGURE 11-2
-Refer to Figure 11-2. The position of a typical firm when the industry is in long-run equilibrium with free entry and exit and product differentiation is exhibited in diagram
A) A.
B) B.
C) C.
D) D.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following are products that differ from each other enough that they can be sold at different prices, but are similar enough that they can be considered the same product?
A) complementary products
B) standardized products
C) necessary products
D) differentiated products
E) inferior products
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is a characteristic of oligopoly?
A) Firms compete solely on the basis of price.
B) The pricing policies of one firm have no impact on pricing policies of other firms.
C) There are large numbers of significantly sized sellers.
D) The industry usually has a low concentration ratio.
E) Prices are usually above marginal costs.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider the following characteristics of a particular industry: - the four-firm concentration ratio is 78% in the relevant market) - each firm produces output where P > MC - the products are highly differentiated This industry is likely to be
A) an oligopoly.
B) one where each firm has limited market power.
C) monopolistic.
D) perfectly competitive.
E) a cartel.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 81 - 100 of 126
Related Exams