A) small increase; a large increase
B) small increase; a large decrease
C) large increase; a small increase
D) large increase; a small decrease
E) large increase; no change
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the basic AD/AS macro model, which of the following events could cause a negative AS shock?
A) a large decrease in wages
B) a large increase in business confidence
C) a large decrease in the net tax rate
D) a widespread outbreak of a serious infectious disease
E) a large increase in labour productivity
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An important automatic fiscal stabilizer in Canada is
A) the exchange rate.
B) the marginal propensity to consume.
C) the marginal propensity to import.
D) the income-tax system.
E) government purchases of goods and services.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following describes the distinction between the Phillips curve and the AS curve?
A) The AS curve has the price level on the vertical axis whereas the Phillips curve has the interest rate on the vertical axis.
B) The AS curve has the price level on the vertical axis whereas the Phillips curve has the rate of change in the interest rate on the vertical axis.
C) The AS curve has the price level on the vertical axis whereas the Phillips curve has the rate of wage changes on the vertical axis.
D) The AS curve has the rate of price inflation on the vertical axis whereas the Phillips curve has the rate of wage changes on the vertical axis.
E) There is no distinction: the two curves are essentially the same thing.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose the economy begins in a long-run equilibrium with Y = Y*. A permanent increase in aggregate demand will have its short-run effect on real GDP reversed in the long run with a shift of .
A) rightward; the aggregate supply curve
B) rightward; the aggregate demand curve
C) leftward; the aggregate supply curve
D) leftward; the aggregate demand curve
E) rightward; Y*
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The diagram below shows an AD/AS model for a hypothetical economy which is initially in a short -run equilibrium at point A.
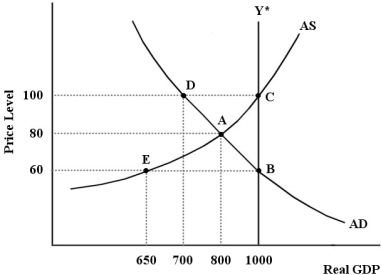 FIGURE 24-6
-Refer to Figure 24-6. The government could close the existing output gap by
FIGURE 24-6
-Refer to Figure 24-6. The government could close the existing output gap by
A) increasing the net tax rate.
B) decreasing the net tax rate.
C) decreasing government purchases.
D) decreasing government transfer payments.
E) implementing a contractionary fiscal policy.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
One advantage of using expansionary fiscal policy rather than relying on automatic adjustment to recover from a recessionary gap is that
A) the economy will overshoot potential GDP and a boom will be underway.
B) inflation will not be as stimulated.
C) price level will rise higher than otherwise.
D) the recovery may be more rapid.
E) the recovery will be slower, thereby causing less disruption.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
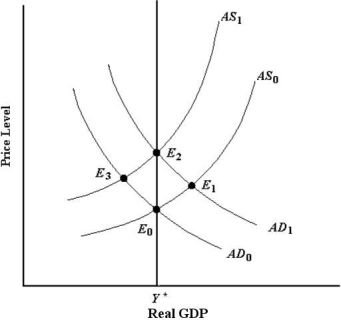 FIGURE 24-5
-Refer to Figure 24-5. The economy is not in long-run equilibrium at E1 because the
FIGURE 24-5
-Refer to Figure 24-5. The economy is not in long-run equilibrium at E1 because the
A) AD1 curve will shift back to AD0 due to an increase in the price level.
B) AD1 curve will shift back to the left due to a fall in current consumption.
C) AS will shift to the left due to an increase in wages.
D) AS will shift to the left due to an increase in the price level.
E) AS will shift to the right due to a decrease in the price level.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In our macro model, the level of aggregate output is determined in the short run by but in the long run by the level of .
A) the output gap; factor productivity
B) the AD curve; interest rates
C) the AS curve; potential output
D) the AD and AS curves; Y*
E) the AD and AS curves; factor utilization
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
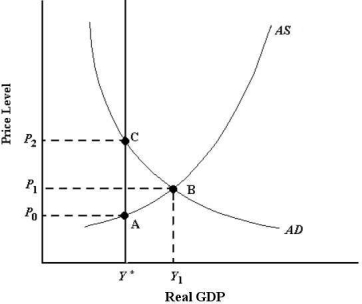 FIGURE 24-2
-Refer to Figure 24-2. If the economy is currently in a short-run equilibrium at Y1, the economy is experiencing
FIGURE 24-2
-Refer to Figure 24-2. If the economy is currently in a short-run equilibrium at Y1, the economy is experiencing
A) potential output growth.
B) a long-run equilibrium.
C) an excess supply of labour.
D) an inflationary output gap.
E) a recessionary output gap.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The table below shows data for five economies of similar size. Real GDP is measured in billions of dollars. Assume that potential output for each economy is $340 billion. 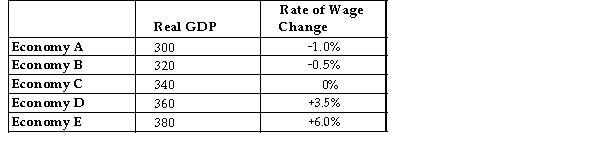 TABLE 24-1
-Suppose that the economy is initially in a long-run macroeconomic equilibrium. A shock then hits the economy and we observe that the unemployment rate increases and the price level increases. We can conclude that
Has decreased and there is now an) gap.
TABLE 24-1
-Suppose that the economy is initially in a long-run macroeconomic equilibrium. A shock then hits the economy and we observe that the unemployment rate increases and the price level increases. We can conclude that
Has decreased and there is now an) gap.
A) aggregate supply; inflationary
B) aggregate demand; recessionary
C) aggregate supply; recessionary
D) aggregate demand; inflationary
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The diagram below shows an AD/AS model for a hypothetical economy which is initially in a short -run equilibrium at point A.
 FIGURE 24-6
-Refer to Figure 24-6. If the government takes no action to change the short-run macro equilibrium in this economy, then
FIGURE 24-6
-Refer to Figure 24-6. If the government takes no action to change the short-run macro equilibrium in this economy, then
A) the AD curve will shift downward until it intersects with the AS curve at point E.
B) the AD curve will shift upward until it intersects with the AS curve at point C.
C) the AS curve will shift to the left until it intersects with the AD curve at point D.
D) the AS curve will shift to the right until it intersects with the AD curve at point B.
E) the AS curve can either shift to the right or left depending on the fiscal policy.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When we study the adjustment process in macroeconomics, what assumption are we making about potential output, Y*?
A) potential output is adjusting to changes in factor prices
B) potential output is adjusting to changes in factor supplies
C) potential output is adjusting to changes in technology
D) potential output is constant
E) potential output is not relevant to the analysis of the adjustment process
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The economyʹs output gap is defined as the
A) difference between actual GDP and potential GDP.
B) level of total output that would be produced if capacity utilization is at its normal rate.
C) difference between actual national income and desired aggregate expenditure.
D) result of economic growth.
E) difference between nominal GDP and real GDP.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The diagram below shows an AD/AS model for a hypothetical economy which is initially in a short -run equilibrium at point A.
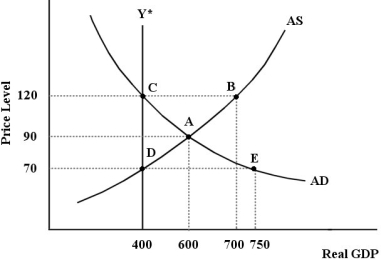 FIGURE 24-7
-Consider Figure 24-7. At the initial short-run equilibrium, there is output gap of . This gap could be closed by a .
FIGURE 24-7
-Consider Figure 24-7. At the initial short-run equilibrium, there is output gap of . This gap could be closed by a .
A) a recessionary; 100; fiscal contraction
B) a recessionary; 200; fiscal expansion
C) an inflationary; 100; fiscal contraction
D) an inflationary; 200; fiscal contraction
E) an inflationary; 350; fiscal expansion
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the basic AD/AS macro model, permanent increases in real GDP are possible only if
A) potential output is increasing.
B) the correct fiscal policy is implemented.
C) the economyʹs automatic stabilizers are allowed to operate.
D) the aggregate supply curve is vertical.
E) aggregate demand responds positively to demand shocks.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider the AD/AS model, and suppose that the economy begins at potential output. The effect of a positive AS shock on real GDP will be reversed in the long run with a shift in .
A) rightward; AS
B) rightward; AD
C) leftward; AS
D) leftward; AD
E) leftward; Y*
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Automatic fiscal stabilizers the impact of demand or supply shocks on the economy since governmentʹs net tax revenues during booms and during recessions.
A) magnify; increase; decrease
B) magnify; decrease; increase
C) dampen; increase; decrease
D) dampen; decrease; increase
E) does not affect; are constant; are constant
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider the basic AD/AS macro model, initially in a long -run equilibrium. A positive AS shock will The price level and output in the short run. In the long run, the price level will and output )
A) decrease; decrease; decrease further; will decrease further
B) decrease; increase; decrease further; will be restored to potential output
C) decrease; increase; return to its initial level; will be restored to potential output
D) increase; increase; decrease; will be restored to potential output
E) increase; increase; return to its initial level; will be restored to potential output
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is a defining assumption of the AD/AS macro model in the short run?
A) factor supplies are assumed to be flexible
B) technology used in production is endogenous and variable
C) the level of potential output fluctuates with the price level
D) factor prices are assumed to be exogenous
E) firms cannot operate near their normal capacity
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 121 - 140 of 148
Related Exams