A) $360
B) $90
C) $75
D) $60
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
All firms in an industry sell their product for the same price.This is a result of
A) collusion.
B) perfect competition.
C) a government law that specifies all firms must charge the same price.
D) a or b
E) There is not enough information to answer the question.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Exhibit 23-3
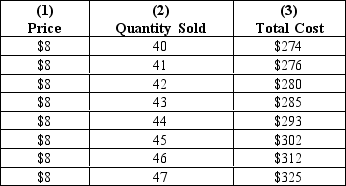 -Refer to Exhibit 23-3.Is it possible for this firm to produce "too much" in the short-run?
-Refer to Exhibit 23-3.Is it possible for this firm to produce "too much" in the short-run?
A) Any quantity above 42 units is too much.
B) Any quantity above 44 units is too much.
C) Any quantity above 40 units is too much.
D) none of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Equilibrium price is $22 in a perfectly competitive market.For a perfectly competitive firm,MR = MC at 200 units of output.At 200 units,ATC is $23,and AVC is $18.The best policy for this firm is to __________ in the short run.Also,this firm earns __________ of __________ if it produces and sells 200 units.Finally,the difference between total variable cost and total fixed cost for this firm is __________.
A) continue to produce, profits, $1800, $3,600
B) shut down, losses, $200, $3,600
C) continue to produce, losses, $200, $2,600
D) shut down, profits, $200, $1,800
E) none of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Resources are allocated efficiently when
A) the exchange value of the resources to demanders equals the opportunity cost of the resources.
B) the marginal benefit to demanders of the resources in the goods they purchase is equal to the marginal cost to suppliers of the resources they use in producing the goods.
C) firms produce the quantity of output at which price is equal to marginal cost.
D) a and b
E) a, b, and c
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is inconsistent with long-run industry equilibrium?
A) upward-sloping marginal cost curves for all of the firms in the industry
B) zero economic profits
C) P = minimum ATC
D) SRATC = LRATC
E) none of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The market demand curve in a perfectly competitive market is
A) downward sloping.
B) upward sloping.
C) perfectly horizontal.
D) perfectly vertical.
E) downward or upward sloping depending upon the type of product offered for sale.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
In order for a firm to earn economic profits,price must exceed average total cost.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
For the perfectly competitive firm,the demand curve and the marginal revenue curve are one and the same.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Assume that a decreasing-cost industry experiences an increase in demand.In the short run,this will
A) lead to a price increase.
B) lead to a price decrease.
C) have no influence on price.
D) a or b, depending on the marginal cost curve
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
In long-run competitive equilibrium,no firm has an incentive to change its plant size.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Exhibit 23-2
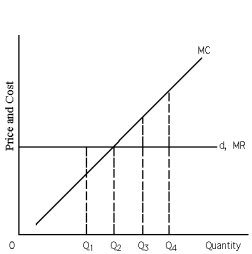 -Refer to Exhibit 23-2.What quantity does the profit-maximizing or loss-minimizing firm produce?
-Refer to Exhibit 23-2.What quantity does the profit-maximizing or loss-minimizing firm produce?
A) Q1, where "what is coming in" on the last unit is greater than "what is going out."
B) Q2, where the difference between "what is coming in" on the last unit and "what is going out" is zero.
C) Q3, where marginal cost is greater than marginal revenue.
D) Q4, which maximizes the excess of marginal cost over marginal revenue.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A price-taker firm will not sell any of its product for less than the equilibrium price because
A) it is against the law to do this.
B) it can sell all it wants at the equilibrium price.
C) this would invite competition from outside the market and end up reducing the profits of the firm.
D) this would be breaking the cartel agreement that price-taker firms often enter into.
E) none of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In a constant-cost industry,positive profits are eliminated through
A) an increase in costs only.
B) a decrease in price only.
C) both an increase in costs and a decrease in price.
D) None of the above, because positive profits are persistent in a constant-cost industry.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A constant-cost industry is characterized by
A) an upward-sloping long-run supply curve.
B) a downward-sloping long-run supply curve.
C) a perfectly elastic long-run supply curve.
D) perfectly elastic short-run and long-run supply curves.
E) a perfectly elastic short-run supply curve and an upward-sloping long-run supply curve.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Exhibit 23-7
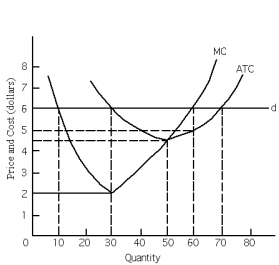 -Refer to Exhibit 23-7.At the profit-maximizing output level,average fixed cost is
-Refer to Exhibit 23-7.At the profit-maximizing output level,average fixed cost is
A) $2.00.
B) $4.00.
C) $5.00.
D) $6.00.
E) This cannot be determined based on the information provided.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Exhibit 23-9
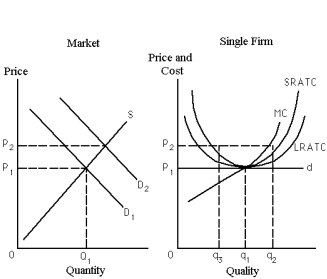 -Refer to Exhibit 23-9.Suppose that the market starts at its long-run competitive equilibrium (P1,Q1) ,and that demand increases from D1 to D2.As a consequence,the typical profit-maximizing firm will
-Refer to Exhibit 23-9.Suppose that the market starts at its long-run competitive equilibrium (P1,Q1) ,and that demand increases from D1 to D2.As a consequence,the typical profit-maximizing firm will
A) increase quantity produced by (q2 - q1) .
B) decrease quantity produced by (q2 - q1) .
C) decrease quantity produced by (q1 - q3) .
D) not change its output level because the demand curve it is facing did not change.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A firm produces the quantity of output at which P = MC and P = ATC.It follows that the firm is
A) resource allocative efficient, but not necessarily productive efficient.
B) productive efficient, but not necessarily resource allocative efficient.
C) both resource allocative and productive efficient.
D) neither resource allocative nor productive efficient.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Exhibit 23-3
 -Refer to Exhibit 23-3.What is the increase in profit that would result from producing 43 units of the product rather than producing 40 units?
-Refer to Exhibit 23-3.What is the increase in profit that would result from producing 43 units of the product rather than producing 40 units?
A) $60
B) $48
C) $28
D) $16
E) $13
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the long-run industry supply curve is downward-sloping,it follows that there are __________ costs in the industry.
A) increasing
B) constant
C) decreasing
D) a or b
E) There is not enough information to answer the question.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 61 - 80 of 191
Related Exams