A) can be made better off by buying more of a normal good and less of an inferior good.
B) is receiving the same total utility from each of the goods he or she purchases.
C) is receiving the same marginal utility from each of the goods he or she purchases.
D) has the same MU/P ratio for each of the goods he or she purchases.
E) none of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose Alice receives 250 utils from consuming one hamburger and 90 utils from consuming a second hamburger.What is the marginal utility of the second hamburger?
A) 340 utils
B) 170 utils
C) 90 utils
D) 0 utils
E) none of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is true?
A) The less you have of any one good, the less you would be willing to pay for one more unit of it.
B) The less you have of any one good, the more you would be willing to pay for one more unit of it.
C) The amount you have of any one good does not influence the price you would be willing to pay for it, but it does affect the marginal utility received from consuming a particular unit.
D) none of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Marginal utility is defined as the
A) change in marginal utility a person derives from the consumption of a good.
B) change in total utility a person derives from the consumption of a good divided by the price of that good.
C) change in total utility a person derives from the consumption of a good divided by the change in the quantity of the good consumed.
D) sum of the amounts of satisfaction a person receives from consuming a good.
E) change in total utility a person derives from the consumption of a good divided by the value in use of that good.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is true?
A) It is possible for total utility to rise as marginal utility falls.
B) Marginal utility is the same as total utility.
C) As marginal utility falls, total utility always falls.
D) a and c
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The law of diminishing marginal utility helps to explain
A) why people trade.
B) the law of demand.
C) why the production possibilities frontier is typically bowed-out.
D) a and b
E) all of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is true?
A) If a consumer is in equilibrium, it does not necessarily follow that he or she is also achieving the greatest total utility.
B) If a consumer is in equilibrium, it necessarily follows that he or she is also achieving the greatest total utility.
C) If a consumer is attaining the greatest marginal utility, then it necessarily follows that he or she is also achieving the greatest total utility.
D) If a consumer is attaining the greatest total utility, then it necessarily follows that he or she is also achieving the greatest marginal utility.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Exhibit 21-8
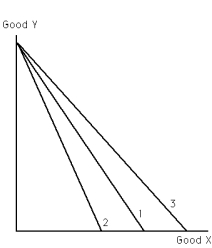 -Refer to Exhibit 21-8.If the price of good X rises,the budget constraint moves from budget constraint
-Refer to Exhibit 21-8.If the price of good X rises,the budget constraint moves from budget constraint
A) 1 to 2.
B) 2 to 3.
C) 3 to 1.
D) 1 to 3.
E) a or c
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
There are two goods,X and Y,and the absolute price of good Y falls.It follows that
A) a person can buy more of good Y.
B) a person cannot buy more of good Y.
C) the slope of the budget constraint changes.
D) the indifference curve between X and Y changes.
E) a and c
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In order for an individual to achieve consumer equilibrium through the consumption of two goods,A and B,that individual must fulfill the condition
A) TUA = TUB.
B) TUA/PA = TUB/PB.
C) MUA = MUB.
D) MUA/PA = MUB/PB.
E) MUB/PA = MUA/PB.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
This is the solution to the diamond-water paradox: Those things that have high value in use sometimes have low prices because they are consumed at low __________ utility; those things that have low value in use sometimes have high prices because they are consumed at high __________utility.
A) marginal; total
B) total; total
C) total; marginal
D) marginal; marginal
E) none of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the marginal utility of X is negative,then the last unit of X is
A) a bad
B) a normal good
C) an inferior good
D) not subject to the law of diminishing marginal utility
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Given the choice between a sure-thing option and a gamble option with the same expected payoff,a____________ person will choose gamble.
A) risk averse
B) risk loving
C) risk neutral
D) risk avoiding
E) none of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Exhibit 21-5
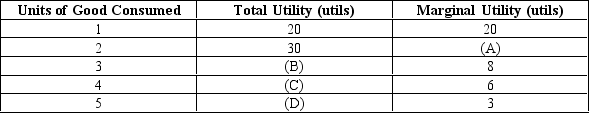 -Refer to Exhibit 21-5. What value goes in blank (D) ?
-Refer to Exhibit 21-5. What value goes in blank (D) ?
A) 47
B) 15
C) 35
D) 60
E) There is not enough information to answer this question.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose that in the year 2050,one gallon of water is more expensive than a one-carat diamond.What could explain this?
A) There is much less water in the world of 2050 than today.
B) There are many more diamonds in the world of 2050 than today.
C) The diamond-water paradox does not hold for any pair of goods.
D) The law of diminishing marginal utility no longer holds.
E) a or b
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The two white rats in the "buying" behavior study conducted at Texas A & M acted in a manner that supported the law of demand and the concept of consumer equilibrium.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Indifference curves are generally downward sloping and concave to the origin.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For economists,framing refers to the
A) manner in which a problem is presented.
B) degree of competition present in a given market.
C) total satisfaction a consumer derives from consuming a good.
D) level of total utility derived from consuming a good.
E) c and d
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a person's income and the prices of both goods all rise by the same percentage,then her budget constraint
A) moves inward toward the origin, and its slope remains the same.
B) moves outward away from the origin, and its slope changes.
C) moves outward away from the origin, and its slope remains the same.
D) does not change in any way.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
We take one dollar from a pauper and give it to a millionaire.Assuming a diminishing marginal utility of money,
A) total utility in the economy must rise.
B) total utility in the economy must fall.
C) total utility in the economy must remain the same.
D) we cannot say whether or not total utility changes.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 176
Related Exams