A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is (are) the product(s) of the following reaction? 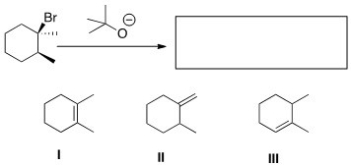
A) I and II
B) II and III
C) I and III
D) I,II,and III
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which alkyl halide(s) would give the following alkene as the only product in an elimination reaction? 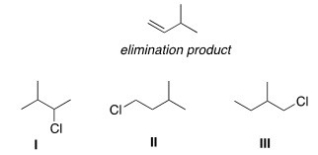
A) Only I
B) Only II
C) Only III
D) I and II
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the product of the following reaction? 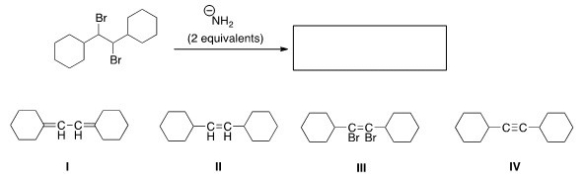
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is the least reactive substrate in an E2 reaction? 
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the labeled protons in the compound below is most readily abstracted under E2 conditions? 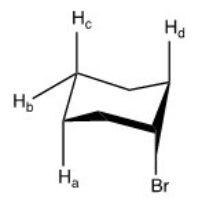
A) Ha
B) Hb
C) Hc
D) Hd
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the major elimination product obtained from the following reaction? 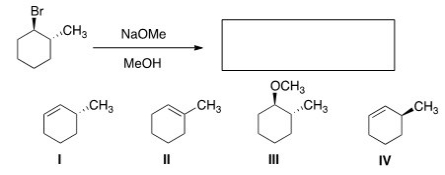
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following alkyl halides would afford the indicated product upon reaction with sodium methoxide? 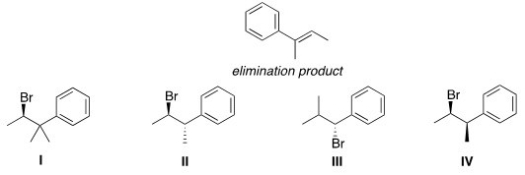
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is the major elimination product of the following reaction? 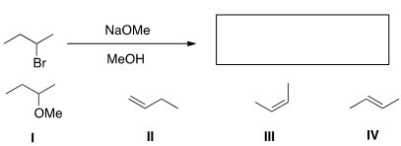
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
Correct Answer

verified
D
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the most likely mechanism for the reaction below? 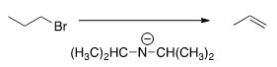
A) SN1
B) SN2
C) E1
D) E2
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the major elimination product obtained from the following reaction? 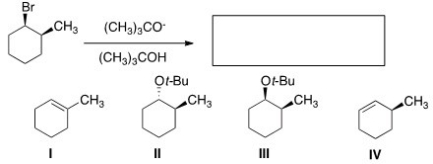
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which is the most likely mechanism for the following reaction? 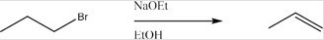
A) SN1
B) SN2
C) E1
D) E2
Correct Answer

verified
D
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements about the mechanism of an E2 reaction is true?
A) All bonds are broken and formed in multiple steps.
B) The reaction is not concerted.
C) Entropy favors the reactants of an E2 reaction.
D) Entropy favors the products of an E2 reaction.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is (are) the elimination product(s) of the following reaction? 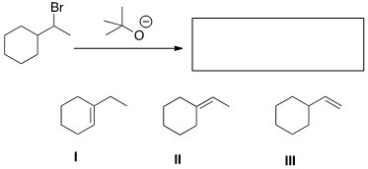
A) Only I
B) Only II
C) Only III
D) II and III
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the major elimination product in the reaction of 1-bromobutane with potassium tert-butoxide in tert-butanol?
A) cis-2-Butene
B) 1-Butene
C) trans-2-Butene
D) Butanol
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is (are) the product(s) of the following reaction? 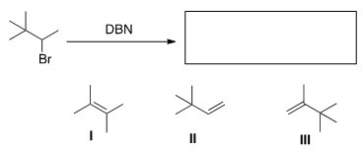
A) Only I
B) Only II
C) Only III
D) I and II
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements about an E1 mechanism is not true?
A) It is a two-step process and has the same first step as an SN1 mechanism.
B) It involves the formation of a carbocation from eliminating a good leaving group.
C) A common competing reaction is rearrangement of a less stable carbocation to a more stable carbocation.
D) The loss of a proton by the carbocation is a slow step.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is the most stable alkene? 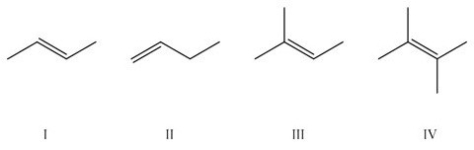
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is (are) the elimination product(s) of the following reaction? 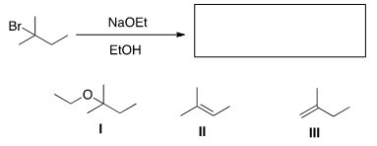
A) Only I
B) Only II
C) Only III
D) II and III
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is (are) the product(s) of the following reaction? 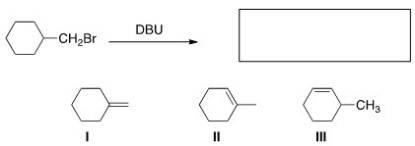
A) Only I
B) Only II
C) Only III
D) I and II
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 52
Related Exams