A) G1/S
B) G2/M
C) spindle
D) G1/S and G2/M
E) G2/M and spindle
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The physical distribution of cytoplasmic material into the two daughter cells in plant cells is referred to as:
A) The gap phase
B) Cytokinesis
C) Binary fission
D) Interphase
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What would you expect to happen if the anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome (APC/C) failed to ubiquitinate securin?
A) The cohesin complex will be destroyed,and the cell will remain in metaphase.
B) The cohesin complex will persist,preventing the cell from entering anaphase.
C) Separase will be marked for degradation by securin,preventing the cell from entering anaphase.
D) Securin will remain intact and therefore will degrade cohesin,allowing the cell to enter anaphase.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What time point represents G2? 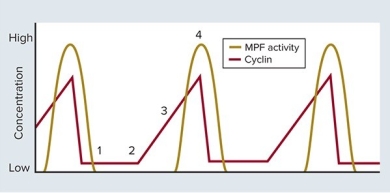
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The stage of mitosis characterized by the physical separation of sister chromatids is called:
A) Anaphase
B) Metaphase
C) Prometaphase
D) Telophase
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A scientist wants to study histones.Histones are:
A) proteins that double-stranded DNA molecules wrap around in eukaryotes.
B) proteins that double-stranded DNA molecules wrap around in prokaryotes and eukaryotes.
C) proteins that regulate checkpoints in the mitotic cell cycle.
D) proteins that serve as the spindle fiber to pull sister chromatids apart during anaphase.
E) proteins that required for the activity of Cdk enzymes.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A duplicate copy of all of the hereditary information contained in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells is made during what stage of the cell cycle?
A) G1
B) S
C) G2
D) Mitosis
E) Cytokinesis
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider the cell cycle of a human cell.During G2,what is the state of the homologous chromosomes?
A) The homologous chromosomes are lined up on the equator of the cell.
B) The homologous chromosomes have all been copied through DNA replication and are beginning to condense.
C) The homologous chromosomes have been pulled to their respective poles by the spindle apparatus.
D) The homologous chromosomes have not been replicated yet.
E) The homologous chromosomes are now in the haploid or n condition.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a cell has 32 chromosomes prior to S and undergoes mitosis followed by cytokinesis,each new daughter cell will have how many chromosomes?
A) 64
B) 32
C) 16
D) 8
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Following S phase,a human cell would have how many pairs of sister chromatids and individual DNA molecules?
A) 23 pairs of sister chromatids and 46 individual DNA molecules
B) 23 pairs of sister chromatids and 92 individual DNA molecules
C) 46 pairs of sister chromatids and 46 individual DNA molecules
D) 46 pairs of sister chromatids and 92 individual DNA molecules
E) 46 pairs of sister chromatids and 184 individual DNA molecules
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Embryonic cell cycles allow the rapid division of cells in the early embryo.These mitotic cell cycles are much shorter in length than the mitotic cell cycles of cells in a mature organism.In the embryonic cell cycles,mitosis takes approximately the same amount of time as it does in the cell cycles of mature cells.What do you think is a result of the embryonic cycle?
A) Resulting daughter cells are smaller than the mother cell in the embryonic cell cycles.
B) Resulting daughter cells do not contain the same genetic information as the mother cell in the embryonic cell cycles.
C) Resulting daughter cells cannot form a mitotic spindle in the embryonic cell cycle.
D) Mother cells in the embryonic cell cycle spend the majority of their time in G0.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
This protein or protein complex functions in the cell to stop cell division if the cell has experienced extensive DNA damage:
A) APC/C
B) p53
C) FtsZ
D) Condensin
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If there are 32 sister chromatids in a normal somatic cell,how many chromosomes are there?
A) 8
B) 16
C) 32
D) 64
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How does the organization of the bacterial genome differ from the organization of the eukaryotic genome?
A) The compaction of the eukaryotic genome involves structural maintenance of chromosome (SMC) proteins,and the compaction of the bacterial genome does not.
B) Most bacterial chromosomes are circular and the eukaryotic chromosomes contained in the nucleus are not.
C) Bacterial chromosomes are made up of RNA and eukaryotic chromosomes are made up of DNA.
D) The eukaryotic genome is found on chromosomes and there are no chromosomes in bacterial cells.
E) Eukaryotic chromosomes have to be tightly packed to fit into the nucleus,and bacterial chromosomes do not require tight packing to fit into the cell.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What stage of mitosis is essentially the reverse of prophase?
A) Anaphase
B) Prometaphase
C) Metaphase
D) Telophase
E) Cytokinesis
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The two copies of each type of chromosome found in normal somatic (body) cells in an organism,throughout the cell cycle,are called:
A) Sister chromatids
B) Homologous chromosomes
C) Daughter chromosomes
D) Kinetochores
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The point of constriction on chromosomes that contains certain repeated DNA sequences that bind specific proteins is called:
A) The kinetochore
B) The centromere
C) The cohesin complex
D) The centriole
E) The centrosome
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The accommodation of the very long DNA strands that are part of a chromosome into the limited space of the nucleus is achieved by coiling the DNA around beads of histones into repeating subunits.These DNA-wrapped histones are called:
A) Solenoids
B) Nucleosomes
C) Chromatin loops
D) Rosettes
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Animal cells typically achieve cytokinesis by:
A) binary fission.
B) forming a cell plate across the middle of the cell.
C) forming a cleavage furrow that pinches the cell into two.
D) chromosome condensation.
E) chromosome elongation.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a chromosome contains a mutation such that it cannot bind to the kinetochore complex,what would be the consequence?
A) That chromosome would not be able to be replicated.
B) That chromosome would not be able to condense.
C) That chromosome would not be able to bind to the mitotic spindle.
D) That chromosome would not be able to interact with histone proteins.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 62
Related Exams